IFI16 Antibodies
Background
IFI16 is a large interferon-induced protein existing in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm, mainly functioning as a receptor for viral DNA. This protein can recognize and bind to exogenous or abnormal self-double-stranded DNA, thereby activating the expression of interferons and other inflammatory factors, and thus initiating an antiviral innate immune response. IFI16 has drawn attention due to its crucial role in sensing infections caused by pathogens such as herpesviruses and HIV. It was systematically identified and established as an important component of innate immunity in the early 21st century. Its unique PYHIN domain and multi-functional modular structure have become one of the core models for studying host defense mechanisms, autoimmune diseases and cellular stress responses, greatly deepening people's understanding of immune recognition and signal transduction networks.
Structure of IFI16
IFI16 is a relatively large human protein, and its molecular weight varies slightly in different studies, usually reported to be approximately 80-86 kDa. This difference mainly stems from the presence of multiple alternative splicing subtypes, such as the longer subtype IFI16-HINb (approximately 86 kDa) and the shorter subtype (approximately 80 kDa).
| Species | Human | Mouse | Non-human primates |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 80-86 | About 78 | About 82-85 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains two HIN domains and one Pyrin domain | There is only one HIN domain, and its function is conservative | IFI16 highly homologous with humans, the structure is similar |
This protein is composed of 729 amino acids (based on the main subtypes), and its tertiary structure is mainly made up of three core functional domains: an N-terminal Pyrin domain (PYD) and two C-terminal HIN domains (Hin-A, Hin-B). These domains work together to enable IFI16 to specifically bind to double-stranded DNA through its HIN domain and recruit downstream signaling molecules (such as ASC) through its PYD domain, thereby initiating antiviral and inflammatory signaling pathways in the nucleus and cytoplasm and playing a key role in innate immunity.
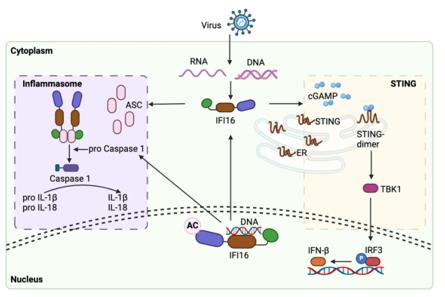 Fig. 1 Structure and mechanism of IFI16.1
Fig. 1 Structure and mechanism of IFI16.1
Key structural properties of IFI16:
- Modular multi-functional domain structure (Pyrin + double HIN domain)
- Nuclear location signal and nuclear mass shuttle capability
- Oligomerization interfaces promote the assembly of signal complexes
- DNA binding pocket in HIN domain structure
Functions of IFI16
The main function of IFI16 is to act as a viral DNA receptor in the innate immune system. In addition, it is also involved in regulating various cellular processes such as the cell cycle, cellular senescence and inflammatory responses.
| Function | Description |
| Viral DNA perception | In the nucleus and cytoplasm of identification and combining the exogenous virus double-stranded DNA, start the antiviral immune response. |
| Interferon signal activation | By oligomerization and recruitment of adaptor proteins such as STING, the transcriptional expression of type I interferons and inflammatory factors is activated. |
| Cell cycle regulation | Within the cell nucleus and p53 protein interactions, participate in DNA damage response, regulating cell proliferation and apoptosis. |
| Inflammasome formation | Under specific conditions, it can assemble with proteins such as ASC to form inflammasomors, promoting the maturation and release of pro-inflammatory factors such as interleukin-1 β. |
| Autoimmune regulation | Abnormal expression or dysfunction is closely related to the development of autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus. |
Unlike most immune receptors, the functional activity of IFI16 is highly dependent on its subcellular localization (in the nucleus and cytoplasm) and post-translational modifications (such as phosphorylation). This dual localization enables it to adopt differentiated immune surveillance strategies against DNA threats from different sources.
Applications of IFI16 and IFI16 Antibody in Literature
1. Dunphy, Gillian, et al. "Non-canonical activation of the DNA sensing adaptor STING by ATM and IFI16 mediates NF-κB signaling after nuclear DNA damage." Molecular cell 71.5 (2018): 745-760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.07.034
Research has found that after DNA damage, cells can non-classically activate the STING pathway through IFI16 in combination with ATM and PARP-1, and activate NF-κB through TRAF6 ubiquitination, inducing a unique transcriptional program and revealing the mechanism of STING as a signaling hub.
2. Chang, Xindi, et al. "The role of IFI16 in regulating PANoptosis and implication in heart diseases." Cell Death Discovery 10.1 (2024): 204. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-024-01978-5
Research has found that IFI16 is a DNA sensor that regulates various forms of cell death such as pyroptosis, apoptosis and necrosis by identifying abnormal DNA, and is closely related to the PANoptosis process. This article reviews the mechanism by which IFI16 regulates PANoptosis in heart diseases such as atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction, with the aim of providing new strategies for the treatment of heart diseases.
3. Yan, Qin, et al. "NAT10-dependent N 4‐acetylcytidine modification mediates PAN RNA stability, KSHV reactivation, and IFI16-related inflammasome activation." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 6327. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-42135-3
Research has found that acetyltransferase NAT10 catalyzes the ac4C modification of KSHV virus PAN RNA, thereby activating viral lysis and replication. This modification also stabilizes IFI16 mRNA to activate inflammasomes, revealing a new mechanism by which ac4C modification regulates viral replication and host immunity.
4. Griffante, Gloria, et al. "IFI16 impacts metabolic reprogramming during human cytomegalovirus infection." Mbio 13.3 (2022): e00435-22. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00435-22
Research has found that IFI16 can inhibit the expression of the glucose transporter GLUT4 by interacting with ChREBP, reducing the reprogramming of glycolipid metabolism and lipid synthesis induced by HCMV infection, thereby restricting the encapsulation and maturation of viral particles. This mechanism reveals the novel metabolic regulatory function of IFI16 in antiviral effects.
5. Liu, Dawei, et al. "IFI16 phase separation via multi-phosphorylation drives innate immune signaling." Nucleic acids research 51.13 (2023): 6819-6840. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad449
Research has found that IFI16 can drive antiviral immune responses by binding to viral DNA to undergo liquid-liquid phase separation. The phosphorylation of its disordered domain is regulated by CDK2/GSK3β, which can switch the IFI16 active state and respectively control the expression of cytokines and the inhibitory function of viral transcription.
Creative Biolabs: IFI16 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality IFI16 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom IFI16 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our IFI16 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Chang, Xindi, et al. "The role of IFI16 in regulating PANoptosis and implication in heart diseases." Cell Death Discovery 10.1 (2024): 204. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-024-01978-5
Anti-IFI16 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1200) (CBMAB-C1467-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261270) (CBMAB-C0813-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (2Q1282) (CBMAB-C1624-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Rat Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (16) (CBMAB-E1578-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






