MMP13 Antibodies
Background
MMP13 belongs to the zinc-dependent endopeptidase family and is mainly found in connective tissue and bone development areas. This enzyme participates in physiological processes such as tissue remodeling, wound repair and bone metabolism regulation by specifically degrading extracellular matrix components like type II collagen. Under pathological conditions, the abnormal overexpression of MMP13 is closely related to diseases such as osteoarthritis and tumor metastasis. Since its clonal identification in 1994, its tertiary structure has been analyzed by X-ray crystallography, revealing the specific binding mechanism of the zinc ion cooperative catalytic domain. As the subtype with the highest collagen degradation efficiency among matrix metalloproteinases, its activity regulatory mechanism continuously provides a key theoretical basis for the development of targeted drugs and promotes a deeper understanding of the dynamic balance of extracellular matrix.
Structure of MMP13
MMP13 is a zinc-dependent protease with a molecular weight of approximately 54 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species, mainly due to the tax-specific changes in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine | Rabbit |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 54.2 | 53.8 | 53.9 | 54.5 | 54.0 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing hinge region, the catalytic domain is highly conserved | High homology with human and slightly different substrate specificity | The catalytic domain sequences are nearly consistent | There are subtle variations in the collagen-binding domain | Proenzyme forelimbs structure similar to people |
This protein is composed of 451 amino acid residues. Its spatial structure includes a catalytic domain made up of five β -sheets and three α -helices, with the central zinc ion being the key to its catalytic activity. The propeptide domain at the N-terminal of the protein plays a role in maintaining the inactivated state of the proenzyme. Its active center is composed of a highly conserved HEXGHXXGXXH zinc ion-bound motif, which undergoes catalytic reactions through glutamic acid residues. The hydrophobic pocket structure is responsible for recognizing and specifically cleave the Gly775 -ile776 peptide bond of type II collagen. The hinge region on the protein surface links the catalytic domain with the heme binding domain, regulating substrate selectivity.
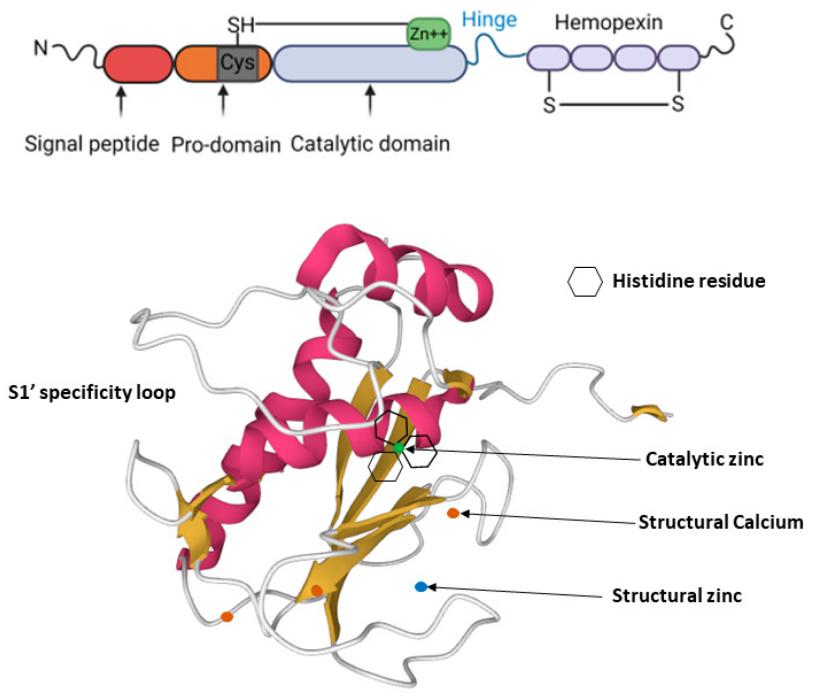 Fig. 1 MMP-13 structure: MMP-13 consists of a highly conserved signal peptide, a pro-domain, a catalytic domain, a proline-rich hinge region and a C-terminal hemopexin-like domain (top panel). 1
Fig. 1 MMP-13 structure: MMP-13 consists of a highly conserved signal peptide, a pro-domain, a catalytic domain, a proline-rich hinge region and a C-terminal hemopexin-like domain (top panel). 1
Key structural properties of MMP13:
- Zinc ion-dependent catalytic domains
- Substrate-specific fissures and hinge regions
- Calcium ions stabilize the structure
Functions of MMP13
The main function of MMP13 is to degrade type II collagen in the extracellular matrix, and it also plays multiple regulatory roles in tissue remodeling and pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Collagen degradation | Specifically cleaving the triple helix structure of type II collagen, it is the most efficient collagenase in cartilage matrix. |
| Organizational Reshaping | Mediates the physiological remodeling of connective tissue during embryonic development, bone healing and wound repair. |
| Pathology of arthritis | Overexpression in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis leads to irreversible damage to articular cartilage. |
| Tumor invasion | By destroying the basement membrane and stromal barrier, it promotes the local invasion and distant metastasis of cancer cells. |
| Inflammatory regulation | Multiple inflammatory signaling pathways are activated or inactivated by cleavage of chemokines and cytokine precursors. |
The catalytic efficiency of MMP13 is much higher than that of other matrix metalloproteinases (such as MMP1), and its Km value for type II collagen is extremely low, indicating that it has a very high affinity for the substrate and efficient hydrolytic ability, which establishes its core position in collagen metabolism.
Applications of MMP13 and MMP13 Antibody in Literature
1. Chu, Ling-Yu, et al. "Combined detection of serum EFNA1 and MMP13 as diagnostic biomarker for gastric cancer." Scientific Reports 14.1 (2024): 15957. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-65839-y
This study found through ELISA detection that the levels of MMP13 and EFNA1 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer were significantly higher than those in the normal control group (P<0.001). The combined detection of MMP13 and EFNA1 can improve the diagnostic efficacy of gastric cancer (AUC=0.794), and also has good diagnostic value for early gastric cancer, which can be used as a potential biomarker for early screening of gastric cancer.
2. Stöckl, Sabine, et al. "Semaphorin 3A-neuropilin-1 signaling modulates MMP13 expression in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes." International journal of molecular sciences 23.22 (2022): 14180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214180
Research has found that the Sema3A-Nrp-1 signaling axis in osteoarthritis (OA) chondrocytes significantly upregulates MMP13 expression by inhibiting AKT phosphorylation (approximately 75%). Targeted intervention of this pathway may inhibit MMP13-mediated cartilage degradation, providing a new strategy for the treatment of OA.
3. Wozniak, Jakub, et al. "Altered Transcript Levels of MMP13 and VIT Genes in the Muscle and Connective Tissue of Pigs with Umbilical Hernia." Genes 14.10 (2023): 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101903
Research has found that in cases of porcine umbilical hernia (UH), the expression of MMP13 shows tissue-specific changes: upregulated in muscle tissue and downregulated in connective tissue, and its DNA methylation level increases, suggesting that MMP13 may be involved in the occurrence and development of hernia.
4. Zhang, nhui, et al. "Pan-cancer analysis reveals the associations between MMP13 high expression and carcinogenesis and its value as a serum diagnostic marker." Aging (Albany NY) 15.6 (2023): 2115. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204599
Studies have shown that MMP13 is highly expressed in various cancers and indicates a poor prognosis, and its upregulation is associated with the activation of the EMT signaling pathway. Serum MMP13 levels can serve as an effective diagnostic marker for tumors such as breast cancer, head and neck cancer, and lung cancer (AUC 0.71-0.93).
5. Dumortier, Mandy, et al. "ETV4 transcription factor and MMP13 metalloprotease are interplaying actors of breast tumorigenesis." Breast Cancer Research 20.1 (2018): 73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-018-0992-0
Research has found that ETV4 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by directly regulating the expression of MMP13. Clinical data analysis shows that co-overexpression of ETV4 and MMP13 predicts a poor prognosis of breast cancer, suggesting that MMP13 is a key effector molecule of the carcinogenic effect of ETV4.
Creative Biolabs: MMP13 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality MMP13 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom MMP13 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our MMP13 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Li, Shun, David Mark Pritchard, and Lu-Gang Yu. "Regulation and function of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in cancer progression and metastasis." Cancers 14.13 (2022): 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133263
Anti-MMP13 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1200) (CBMAB-C1467-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Rat Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (16) (CBMAB-E1578-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CORO1A Recombinant Antibody (4G10) (V2LY-1206-LY806)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








