NLRP3 Antibodies
Background
NLRP3 is an important inflammasome sensor protein, mainly existing in the cytoplasm of immune cells. As a key component of the innate immune system, it can recognize various pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), and after activation, form inflammasome complexes, promoting the maturation and release of pro-inflammatory factors such as interleukin-1 β. In 2001, three independent research teams simultaneously identified that the abnormal activation of NLRP3 is closely related to a variety of autoinflammatory diseases and metabolic disorders. Its unique structure and regulatory mechanism have become a research hotspot in the field of innate immunity, providing an important theoretical basis for understanding the occurrence mechanism of inflammatory responses and developing treatment strategies for related diseases.
Structure of NLRP3
NLRP3 is an inflammasome sensor protein with a molecular weight of approximately 118 kDa, and its molecular weight varies to some extent among different species. The following is a comparison of NLRP3 characteristics of major species:
| Species | Human | Mice | Rats |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 118 | 117 | 119 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing LRR domains | Highly conserved NACHT structure domain | PYD structure domain interspecific variations |
This protein achieves oligomerization through the ATPase activity of its NACHT domain, forming an inflammasome core. The PYD domain is responsible for interacting with the adaptor protein ASC, while the LRR domain is involved in ligand recognition. The activation of NLRP3 requires two signals: the initiation signal (such as TLR ligands) and the activation signal (such as ATP or crystals). This dual regulatory mechanism ensures the precise control of inflammatory responses.
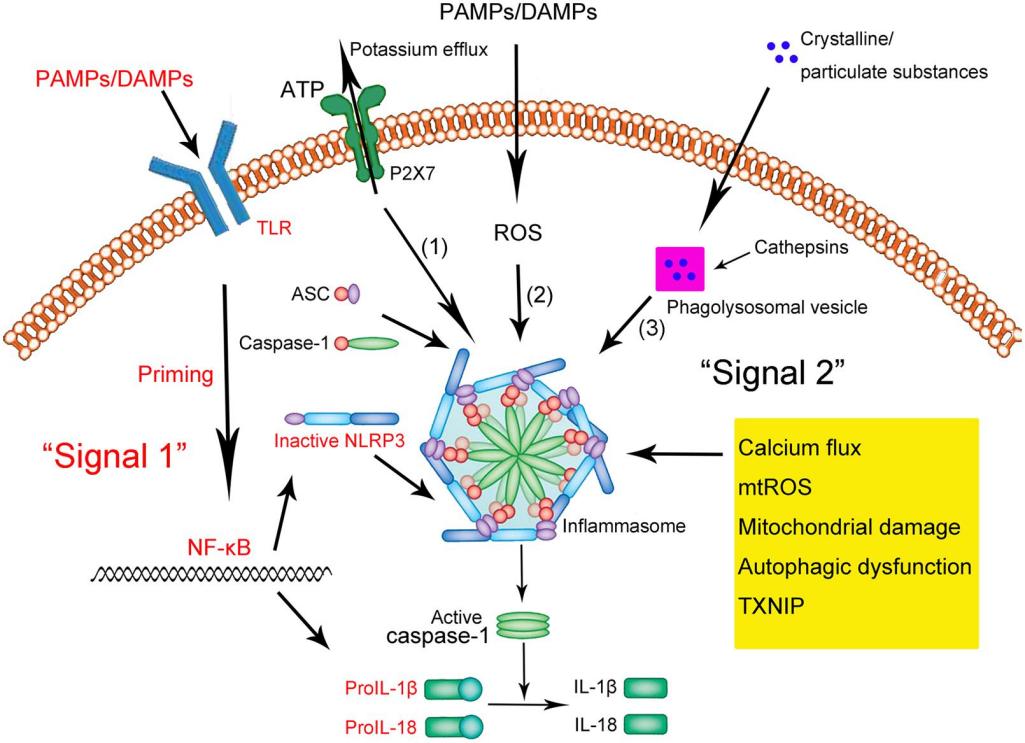 Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of the NLRP3 inflammasome activation.1
Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of the NLRP3 inflammasome activation.1
Key structural properties of NLRP3:
- Multi-domain composition (PYD-NACHT-LRR)
- Atpase activity NACHT structure domain
- LRR structure domain is responsible for the pathogen recognition
- PYD domains mediate protein interactions
Functions of NLRP3
The core function of NLRP3 is to serve as a danger signal sensor for the innate immune system and simultaneously participate in multiple pathophysiological processes:
| Function | Description |
| Inflammasome activation | After identifying PAMPs/DAMPs, oligomerization occurs, forming inflammasome complexes. |
| Pyroptosis induction | Programmed cell death is triggered by activating caspase-1 to cut GSDMD. |
| Cytokine maturation | Promote the cleavage and release of IL-1β and IL-18 precursors. |
| Immune defense | The first line of defense against intracellular pathogen infection. |
| Disease association | Abnormal activation is closely related to gout, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, etc. |
Applications of NLRP3 and NLRP3 Antibody in Literature
1. Shao, Bo-Zong, et al. "NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: a review." Frontiers in pharmacology 6 (2015): 262. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00262
The article indicates that NLRP3 antibodies target key proteins of inflammasomes, regulate innate immunity, and are closely related to metabolic disorders, autoimmune diseases, etc. Current research focuses on its structure, activation mechanism and inhibitor development, providing new strategies for the treatment of related diseases.
2. Moossavi, Maryam, et al. "Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer." Molecular cancer 17.1 (2018): 158. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0900-3
The article indicates that the NLRP3 antibody targets inflammasomes, regulates the activation of caspase-1 and the release of IL-1β/IL-18, and affects tumorigenesis and development. Its role in cancer remains controversial, but it is a potential therapeutic target.
3. Yang, Yang, et al. "Recent advances in the mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its inhibitors." Cell death & disease 10.2 (2019): 128.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1413-8
The article indicates that the NLRP3 antibody regulates the release of IL-1β/IL-18 by targeting the inflammasome complex and participates in the disease processes such as Alzheimer's disease and diabetes. Studying its activation mechanism and specific inhibitors is of great significance for the treatment of related diseases.
4. Zhen, Yu, and Hu Zhang. "NLRP3 inflammasome and inflammatory bowel disease." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 276. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00276
The article indicates that NLRP3 antibody regulates caspase-1 activation by targeting the PYD domain of the inflammasome and affects the secretion of IL-1β/IL-18, exerting a dual role (pro-inflammatory/protective) in intestinal mucosal immunity in IBD. The study of its mechanism provides a new target for the treatment of IBD.
5. Bai, Baochen, et al. "NLRP3 inflammasome in endothelial dysfunction." Cell death & disease 11.9 (2020): 776. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02985-x
The article indicates that the NLRP3 antibody targets inflammasomes, inhibits Caspase-1-mediated IL-1β/IL-18 release and pyroptosis, improves oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction, and provides a new strategy for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Creative Biolabs: NLRP3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality NLRP3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom NLRP3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our NLRP3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Shao, Bo-Zong, et al. "NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: a review." Frontiers in pharmacology 6 (2015): 262. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00262
Anti-NLRP3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






