PARP1 Antibodies
Background
PARP1 is a key DNA repair protein widely present in eukaryotic cell nuclei. Its structure mainly consists of the zinc finger domain, the automodification domain and the catalytic domain. This protein participates in the repair process of DNA single-strand breaks and maintains genomic stability by recognizing DNA damage sites and catalyzing the polymerization of ADP-ribose units. Cancer cells often utilize the repair mechanism of PARP1 to achieve survival, so PARP inhibitors have become an important direction for targeted therapy. Since its first discovery by the Chambon team in 1963, PARP1 has not only been the first ADP-ribonylase to be clarified, but also has become a core target in cancer treatment research due to its functional characteristics. Its in-depth research on the response mechanism of DNA damage continuously drives breakthroughs in the fields of tumor treatment, aging research and epigenetics.
Structure of PARP1
Myoglobin is a relatively small protein with a molecular weight of approximately 16.7 kDa. This weight may slightly vary between species due to minor differences in amino acid sequence.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine | African clawed toad |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 113 | 112.8 | 112.9 | 112.7 | 112.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains six zinc finger domain structure | 93% homologous to humans | 92% homologous to humans | 95% homologous to humans | 85% homologous to humans |
The PARP1 protein is organized in a modular structure, consisting of an N-terminal DNA-binding domain (with two zinc finger molds), a central automodification domain, and a C-terminal catalytic domain. Its tertiary structure forms a functional synergy unit. When the zinc finger domain specifically recognizes the DNA break site, it will induce conformational changes and activate the catalytic domain. This catalytic domain utilizes NAD+ as the substrate to catalyze the synthesis of polyADP-ribose chains (PAR chains), a process that is crucial for recruiting DNA repair proteins. The enzymatic active center of this protein retains a highly conserved histidine-tyrosine catalytic motif, which is the structural basis of its catalytic function.
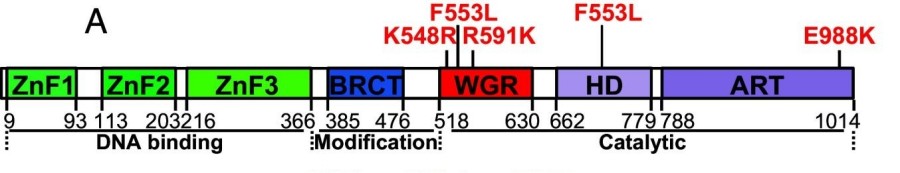 Fig. 1 Schematic of human PARP1 domains and subdomains.1
Fig. 1 Schematic of human PARP1 domains and subdomains.1
Key structural properties of PARP1:
- Modular multi-domain structure (including zinc finger domain, BRCT domain and catalytic domain)
- Hydrophobic cores maintain structural stability and promote DNA binding
- Conserved catalytic residues (His-Tyr double motif) are responsible for the ribosylation activity of ADP
Functions of PARP1
The main function of the PARP1 protein is to participate in DNA damage repair and cellular stress response. In addition, it is also widely involved in a variety of cellular processes, including chromatin remodeling, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis and inflammatory responses.
| Function | Description |
| DNA damage repair | Recognize DNA single-strand breaks and catalyze ADP-ribonylation, recruiting repair proteins to complete damage repair. |
| Transcriptional regulation | Regulate gene expression levels by modifying transcription factors and chromatin structure. |
| Regulation of apoptosis | Overactivation in severe DNA damage leads to energy depletion and guides cells towards programmed death. |
| Chromatin remodeling | By PAR-modifying histones, chromatin relaxation and gene accessibility are affected. |
| Regulation of inflammatory response | It is involved in the regulation of NF-κB and other signaling pathways, and affects the production of inflammatory factors and immune response. |
The enzymatic activity of PARP1 is highly dependent on NAD+ concentration. Its kinetic curve shows a typical substrate dependence and is significantly activated after DNA binding, indicating that it plays a rapid molecular sensor role in genomic maintenance.
Applications of PARP1 and PARP1 Antibody in Literature
1. Alemasova, Elizaveta E., and Olga I. Lavrik. "Poly (ADP-ribosyl) ation by PARP1: reaction mechanism and regulatory proteins." Nucleic acids research 47.8 (2019): 3811-3827. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz120
The article indicates that PARP1 is a key enzyme responsible for protein PARylation modification in DNA damage repair. Its simultaneous role as both a catalytic substrate and a acceptor has led to numerous controversies. This article reviews the PARylation mechanism and the influence of regulatory factors on PAR synthesis, providing a reference for the design of PARP inhibitors.
2. Gong, Yamin, et al. "PARP1 UFMylation ensures the stability of stalled replication forks." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 121.18 (2024): e2322520121. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2322520121
This study reveals that PARP1 is modified by UFM1 at the K548 site during replication stress, thereby enhancing its catalytic activity, promoting the activation of CHK1 and the stability of the arrest replication fork. The absence of UFMylation will weaken the DNA repair ability, affect genomic stability, and increase the sensitivity to anti-cancer treatment.
3. Spiegel, Jacob O., Bennett Van Houten, and Jacob D. Durrant. "PARP1: Structural insights and pharmacological targets for inhibition." DNA repair 103 (2021): 103125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103125
The article indicates that PARP1 is a multifunctional ADP-ribose transferase in the human body and is involved in multiple DNA repair pathways. It responds to DNA damage by catalyzing protein ADP-ribonylation and can serve as a target for anti-cancer drugs. This review provides an overview of the function of PARP1, with a focus on its novel allosteric inhibition strategies and clinical resistance challenges.
4. Ding,a, et al. "PARP1-SNAI2 transcription axis drives resistance to PARP inhibitor, Talazoparib." Scientific Reports 12.1 (2022): 12501. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16623-3
This study reveals that during the caspase-mediated apoptosis process, PARP1 is cleaved to produce 89-kDa and 24-kDa fragments. Among them, the 89-kDa fragment carrying the PAR chain translocates to the cytoplasm, promoting the release of AIF from mitochondria and into the nucleus, thereby connecting the two programmed cell death pathways of apoptosis and parthanatos, providing a new target for related treatments.
5. Reber, Julia M., et al. "PARP1 and XRCC1 exhibit a reciprocal relationship in genotoxic stress response." Cell Biology and Toxicology 39.1 (2023): 345-364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-022-09739-9
This study reveals that PARP1 and XRCC1 have a bidirectional interaction relationship in the response to genotoxic stress. XRCC1 deletion leads to hypersensitivity of cells to chemotherapy drugs. This phenotype can be saved by PARP1 gene knockout or drug inhibition, indicating that PARP1 aggravates DNA damage toxicity in the context of XRCC1 deletion. The regulation of its interaction plays a key role in repair efficiency and cell survival.
Creative Biolabs: PARP1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PARP1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PARP1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PARP1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Gong, Yamin, et al. "PARP1 UFMylation ensures the stability of stalled replication forks." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 121.18 (2024): e2322520121. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2322520121
Anti-PARP1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-FLI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0733) (CBMAB-F0435-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BBS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0253) (CBMAB-0254-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1B1 Antibody (V2-2449) (CBMAB-1001CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (P67.6) (CBMAB-C10189-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








