PDGFC Antibodies
Background
PDGFC is a type of protein that comes in pairs and contains sugar molecules; it is mainly present, in tissues in the body. Plays a crucial part in cell growth and movement as well as tissue healing processes. It attaches to receptors known as PDGFRA and PDGF RB which then trigger communication pathways that support cell development and specialization. The presence of PDGF C is vital for the repair of wounds and the formation of blood vessels; when its function goes awry it has been linked to conditions like fibrosis and the advancement of cancer. First discovered back in the 1970s; PDGF C has been extensively researched due to its significance in both growth processes well, as diseases. The way its built and how it works has given us an understanding of how growth factors signal and how cells react to damage or injury situations; exploring PDGF C has expanded our comprehension of healing processes and created opportunities, for treatments aimed at managing fibrosis and cancer growth.
Structure of PDGFC
PDGF C is a type of protein that comes in pairs and has a weight of 30 kilodaltons (kDa). Its actual weight may differ slightly because of the way sugars attach to it and the unique variations, in amino acid sequences, among species.
| Species | Human | Bovine | Porcine | Mice |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 34 | 32 | 25.6 | 56 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains an N-terminal CUB structural domain and a C-terminal PDGF homologous structural domain | The structure is similar to that of human PDGFC, but the molecular weight is slightly smaller, probably related to minor differences in amino acid sequence. | The small molecular weight may be related to differences in amino acid sequences and post-translational modifications. | The large molecular weight may be related to specific structural or post-translational modifications of mouse PDGFC. |
PDGF C is a protein made up of two parts and sugars that consists of 126 building blocks called acids and has a structure, with a CUB part at the beginning and a PDGF homology part at the end. The CUB section keeps it stable in a form while the PDGF part connects with receptors like PDGFRA and PDGNRB to trigger pathways for communication within cells. In terms of its structure PDGF C has shapes and flat shapes that come together at the center. Joining together into pairs is crucial for its functions, in promoting cell growth, movement and repairing tissues.
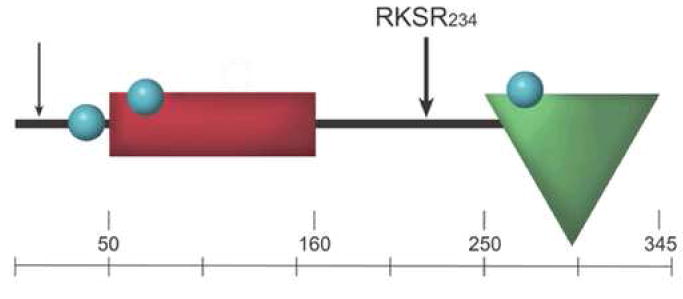 Fig. 1 The domains of PDGFC.1
Fig. 1 The domains of PDGFC.1
Key structural properties of PDGFC:
- CUB domain (residues 50-160), encoded by exons 2-3.
- Growth factor domain (residues 231-345), forms cysteine knot.
- Signal peptide encoded by exon 1, cleaved at residues 22-23.
- Three N-linked glycosylation sites at positions 25, 55, 254.
- Hinge region (residues 161-230) connects domains.
- Latent form, activated by proteases like plasmin or tPA.
Functions of PDGFC
PDGFC primarily drives cell proliferation and survival, while also promoting angiogenesis, embryonic development, wound healing, fibrosis, and stem/progenitor cell regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Cell Proliferation | PDGFC stimulates cell division and growth, particularly in tissues undergoing repair or development. |
| Angiogenesis | It promotes the formation of new blood vessels, crucial for tissue regeneration and wound healing. |
| Embryonic Development | PDGFC plays a key role in organogenesis and tissue formation during embryonic development. |
| Wound Healing | It accelerates the healing process by stimulating cell migration and proliferation at the wound site. |
| Fibrosis | PDGFC can contribute to fibrotic processes by promoting the accumulation of extracellular matrix components. |
| Stem/Progenitor Cell Regulation | It influences the differentiation and function of stem and progenitor cells in various tissues. |
The activity of PDGFC is regulated by proteolytic activation, in contrast to other growth factors that may rely on receptor binding alone, indicating its latent form and requirement for processing to function.
Applications of PDGFC and PDGFC Antibody in Literature
1. Shi, Yin-Hao, et al. "Imatinib facilitates gemcitabine sensitivity by targeting epigenetically activated PDGFC signaling in pancreatic cancer." Molecular Therapy 31.2 (2023): 503-516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.11.004
The article shows that imatinib makes pancreatic cancer cells more responsive to gemcitabine through its action on the epigenetically activated PDGFC signaling pathway. The article explains how PDGFC signaling functions in pancreatic cancer while showing how imatinib treatment affects this pathway to enhance gemcitabine effectiveness.
2. Li, Xuri, et al. "Revascularization of ischemic tissues by PDGF-CC via effects on endothelial cells and their progenitors." The Journal of clinical investigation 115.1 (2005): 118-127. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI19189
The article shows that PDGF-CC drives tissue revascularization through its ability to activate endothelial cells and their stem cells which makes it a promising therapeutic option for treating ischemic diseases.
3. Zwerner, Jeffrey P., and William A. May. "Dominant negative PDGF-C inhibits growth of Ewing family tumor cell lines." Oncogene 21.24 (2002): 3847-3854. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205486
This article demonstrates that dominant negative PDGF-C inhibits the growth of Ewing family tumor cell lines, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic strategy for these cancers.
4. Crawford, Yongping, et al. "PDGF-C mediates the angiogenic and tumorigenic properties of fibroblasts associated with tumors refractory to anti-VEGF treatment." Cancer cell 15.1 (2009): 21-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2008.12.004
This article explains how PDGF-C plays a role in promoting the growth of blood vessels and tumors in cases where anti cancer treatment targeting VEGF's ineffective It highlights PDGF-C as a target, for potential therapeutic interventions, in such situations.
5. Yoon, Hyunho, et al. "Cancer-associated fibroblast secretion of PDGFC promotes gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and metastasis." Oncogene 40.11 (2021): 1957-1973. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01685-w
The article shows that cancer-associated fibroblasts produce PDGFC which drives the growth and spread of gastrointestinal stromal tumors thus establishing PDGFC as a vital factor in tumor progression.
Creative Biolabs: PDGFC Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs is known for creating PDGF antibodies intended for research and medical use applications of the quality standards available, in the market right now. Our product range consists of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies customized for ELISA tests as Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry procedures along, with other diagnostic techniques.
- Custom PDGFC Antibody Development: Bespoke solutions to fulfill precise research needs.
- Large-Scale Manufacturing: High-volume antibody production for industrial partners.
- Expert Consultation: Professional support for optimizing protocols and solving issues.
- Custom Aliquoting: Practical aliquot sizes for extended storage and reliable results.
For further information on our PDGFC antibodies, custom services, or technical assistance, please reach out to us via info@creative-biolabs.com.
Reference
- Lei, Hetian, and Andrius Kazlauskas. "Focus on molecules: platelet-derived growth factor C, PDGF-C." Experimental eye research 86.5 (2007): 711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2007.08.007
Anti-PDGFC antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Rat Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (7G4.2E8) (CBMAB-C8725-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








