RALA Antibodies
Background
RALA is a small GTP-binding protein that mainly exists in the cytoplasm and cell membrane of eukaryotic cells. This protein plays a key role in the material transport and signal transduction of the intracellular membrane system by regulating vesicle transport and membrane fusion processes. Studies have shown that RALA is involved in a variety of physiological processes, including cell proliferation, migration and tumorigenesis, etc. In 1996, scientists first discovered the RALA protein in mammals. Its unique molecular switch properties have made it an important model for cell biology research. The research on RALA and its signaling pathways provides important clues for understanding intracellular transport mechanisms and developing cancer therapeutic targets, and has extensive research value in the field of molecular and cellular biology.
Structure of RALA
RALA is a small GTP-binding protein with a molecular weight of approximately 23 kDa, and its molecular weight varies slightly among different species.
| Species | Human | Mice | Rats | Fruit flies | Yeast |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 23.1 | 23.0 | 23.2 | 22.8 | 22.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Highly conservative GTP binding domains | Highly homologous to humans | Similar to mice, but slightly different for the C-end | Simplify the structure while retaining the core functions | More streamlined and suitable for lower eukaryotic cells |
RALA is composed of approximately 200 amino acids and features typical Ras superfamily structural characteristics, including a highly conserved GTP/GDP binding domain (G1-G5 motif). Its three-dimensional structure presents a typical GTPase folding pattern, including 6 β-folded sheets and 5 α -helixes.
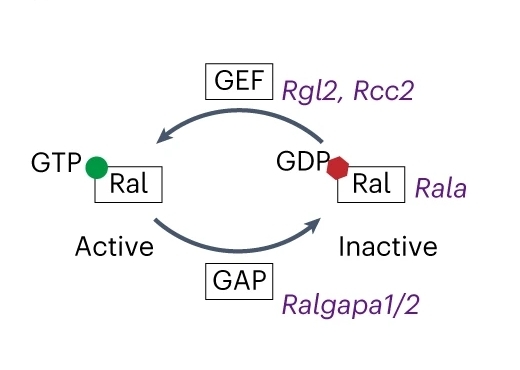 Fig. 1 Scheme illustrating RalA activation network involving genes encoding RalA, GEF and GAP.1
Fig. 1 Scheme illustrating RalA activation network involving genes encoding RalA, GEF and GAP.1
Key structural properties of RALA:
- Switch I & II regions
- C-terminal lipidation modification site
- Effector protein binding interface
Functions of RALA
RALA (Ras-like protein A) is a small GTP enzyme. Its main function is to regulate intracellular vesicle transport and membrane fusion processes, and it is also involved in various cellular physiological activities.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of vesicle transport | As a molecular switch, it regulates secretory vesicles and endosome transport through changes in the GTP/GDP cycle state, influencing protein sorting and membrane transport. |
| Cell signaling | Through the activation of downstream effector proteins (such as EXOC2, RLIP76, etc.), it participates in the signaling of growth factors and hormones. |
| Regulation of cell migration | Regulate the cytoskeletal recombination of actin and affect the invasion and metastasis ability of tumor cells. |
| Autophagy is involved | By autophagy related protein (such as ATG5) interaction, control the formation of autophagosome and degradation. |
| Tumorigenesis association | In a variety of cancer (e.g., pancreatic cancer, breast cancer) express, promoting tumor proliferation and drug resistance. |
The GTPase activity of RALA exhibits a typical bistable regulatory mode (activation of GTP binding state and inactivation of GDP binding state), which is different from the classical Ras protein. It has a higher selectivity for effector proteins, enabling it to play a more precise regulatory role in specific membrane transport pathways.
Applications of RALA and RALA Antibody in Literature
1. Xia, Wenmin, et al. "Obesity causes mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction in white adipocytes due to RalA activation." Nature metabolism 6.2 (2024): 273-289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-024-00978-0
The article indicates that a high-fat diet aggravates obesity and insulin resistance by activating the RalA protein in white adipocytes, promoting the dephosphorylation of the mitochondrial fission protein Drp1, leading to excessive mitochondrial division and impaired oxidation function, and inhibiting fatty acid oxidation. Inhibiting RalA can reverse this process.
2. Long, Yufei, et al. "FOXD1-dependent RalA-ANXA2-Src complex promotes CTC formation in breast cancer." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 41.1 (2022): 301.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-022-02504-0
Studies have shown that in breast cancer, FOXD1 directly activates the expression of RalA, promotes the formation of the RALa-ANXA2-SRC complex, enhances the tyrosine phosphorylation of ANXA2, and thereby activates the ERK1/2 signaling pathway, driving the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tumor cells and the generation of circulating tumor cells (CTCS), accelerating metastasis. Targeted inhibition of RalA or ERK1/2 can block this process.
3. Fan, Gentao, et al. "Identification of RALA as a therapeutic target and prognostic predictor of osteosarcoma." BioMed Research International 2023.1 (2023): 1150768. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/1150768
The article shows that RALA is highly expressed in osteosarcoma and works in synergy with ABCE1 to promote tumor proliferation, migration and invasion, while also influencing immune infiltration and DNA methylation in the tumor microenvironment. Targeting RALA may become a new strategy for the treatment of osteosarcoma.
4. Richardson, Dillon S., et al. "The RAL enigma: distinct roles of RALA and RALB in cancer." Cells 11.10 (2022): 1645.https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101645
The article shows that RALA and RALB are RAS superfamily homologous small G proteins, which regulate processes such as vesicle transport and mitochondrial division through GTP/GDP conversion. Although sharing GEFs/GAPs and effectors, both have redundant, unique and even antagonistic functions in cancer, but the specific mechanisms remain unclear.
5. Thies, Katie A., et al. "The small G-protein RalA promotes progression and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer." Breast Cancer Research 23.1 (2021): 65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-021-01438-3
Research has found that in TNBC (triple-negative breast cancer), RALA and RALB have antagonistic effects: RALA promotes tumor growth and metastasis, while RALB inhibits these processes. High RALA expression is associated with poor prognosis in TNBC patients. Targeted inhibition of RALA can reduce tumor progression and metastasis, suggesting its potential as a new therapeutic target for TNBC.
Creative Biolabs: RALA Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality RALA antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom RALA Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our RALA antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Xia, Wenmin, et al. "Obesity causes mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction in white adipocytes due to RalA activation." Nature metabolism 6.2 (2024): 273-289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-024-00978-0
Anti-RALA antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








