SCD1 Antibodies
Background
Stearoyl-coa desaturase 1 (SCD1) is A membrane-bound protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum, mainly distributed in metabolically active sites such as the liver, adipose tissue and breast. This enzyme directly regulates cell membrane fluidity, lipid metabolism balance and energy homeostasis by catalyzing the conversion of saturated fatty acids to monounsaturated fatty acids. Studies have shown that abnormal SCD1 activity is closely related to the occurrence and development of insulin resistance, obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Its role as a key node for metabolic regulation was officially clarified in 1999 and has now become an important target for the development of drugs for metabolic diseases. The catalytic center composed of the four transmembrane domains of this enzyme and histidine clusters provides a classic model for studying the working mechanism of membrane proteins and promotes a deeper understanding of the coupling mechanism between lipid metabolism networks and signal transduction.
Structure of SCD1
SCD1 is a membrane-bound protein with a molecular weight of approximately 37 kDa. Its precise molecular weight fluctuates slightly among different species due to sequence differences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 37.0 | 36.8 | 37.1 | 36.9 | 37.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains four across the membrane structure field | High homology with human | The catalytic center is highly conserved | There is a difference in the carboxyl terminal sequence | The hydrophilic area is relatively long |
This protein is composed of 359 amino acid residues, and its topological structure forms a typical quadruple transmembrane folding. The active center is composed of conserved histidine clusters, which work together to coordinate the binuclear iron center and catalyze the desaturation reaction of fatty acid substrates. The sparse helix in the transmembrane region is not only anchored to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane but also forms a rigid framework for the substrate channels. The catalytic domain located on the cytoplasmic side maintains the stability of the electron transport chain through two groups of conserved aspartic acids, and this spatial arrangement ensures the activation efficiency of oxygen molecules in a hydrophobic environment.
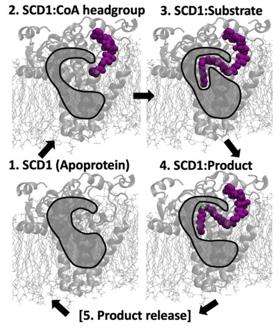 Fig. 1 SCD1 Ligand Binding Mechanism.1
Fig. 1 SCD1 Ligand Binding Mechanism.1
Key structural properties of SCD1:
- Fourfold transmembrane domains form the core topological framework
- Hydrophobic compartments encase histidine clusters with binuclear iron centers
- Conservative aspartic acid network electron transport chain
- Cytoplasmic side catalytic pockets precisely regulate fatty acid orientation
Functions of SCD1
The core function of the SCD1 gene is to catalyze the conversion of saturated fatty acids into monounsaturated fatty acids, a process that is crucial for maintaining the balance of lipid metabolism in the body. In addition, this gene is also involved in the regulation of various physiological and pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Fatty acid desaturation | Catalyze the conversion of stearoyl-Coenzyme A and palmitoyl-coenzyme A to oleoyl-Coenzyme A and palm oleoyl-coenzyme A respectively, thereby altering the membrane fluidity. |
| Energy steady-state regulation | By influencing the ratio of triglycerides to cholesterol esters, it regulates the balance between energy storage and consumption. |
| Maintenance of insulin sensitivity | Regulate the accumulation of lipid intermediate products to prevent insulin signaling pathway disorders caused by lipotoxicity. |
| Regulation of inflammatory response | The transduction efficiency of inflammatory signaling pathways is affected by altering the composition of membrane phospholipids. |
| Promotion of cell differentiation | Provides essential monounsaturated fatty acids during adipogenesis and supports lipid droplet maturation. |
The catalytic efficiency of SCD1 is strictly regulated by substrate availability and hormone signaling, and its active state directly determines the metabolic flow direction. This enzyme plays a core role in maintaining the ratio of saturated to unsaturated fatty acids, and the disruption of this balance is closely related to the occurrence and development of metabolic syndrome.
Applications of SCD1 and SCD1 Antibody in Literature
1. Xuan, Yang, et al. "SCD1/FADS2 fatty acid desaturases equipoise lipid metabolic activity and redox-driven ferroptosis in ascites-derived ovarian cancer cells." Theranostics 12.7 (2022): 3534. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.70194
The article indicates that ascites in ovarian cancer activates fatty acid desaturase SCD1/FADS2, promoting tumor progression and platinum resistance. Inhibiting both can induce ferroptosis, and when used in combination with cisplatin, it can synergistically inhibit tumor metastasis.
2. Ascenzi, Francesca, et al. "SCD1, autophagy and cancer: implications for therapy." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 40.1 (2021): 265. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-02067-6
The article indicates that SCD1 is a key protein regulating the interaction between lipid metabolism and autophagy. Its role in cancer is complex, capable of both inducing and inhibiting autophagy. Whether it ultimately promotes or inhibits tumors depends on the type and heterogeneity of the cancer.
3. Wong, Tin-Lok, et al. "ADAR1-mediated RNA editing of SCD1 drives drug resistance and self-renewal in gastric cancer." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 2861. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38581-8
Research has revealed a new mechanism of chemotherapy resistance in gastric cancer: ADAR1 enhances the stability of SCD1 mRNA and promotes lipid droplet formation to alleviate ER stress, thereby maintaining tumor self-renewal and drug resistance. Targeting SCD1 can reverse this process.
4. Katoh, Yuki, et al. "Inhibition of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1) enhances the antitumor T cell response through regulating β-catenin signaling in cancer cells and ER stress in T cells and synergizes with anti-PD-1 antibody." Journal for immunotherapy of cancer 10.7 (2022): e004616. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2022-004616
Research reveals that SCD1 inhibits tumor infiltration of dendritic cells and CD8+ T cells by enhancing Wnt signaling and ER stress, shaping a non-immune inflammatory microenvironment. Its inhibitor can reverse this inhibition and work synergistically with PD-1 antibodies.
5. Chen, Jiaping, et al. "G protein-coupled estrogen receptor activates PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling to suppress ferroptosis via SREBP1/SCD1-mediated lipogenesis." Molecular Medicine 30.1 (2024): 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-023-00763-x
Research has found that GPER1 inhibits ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and upregulating the expression of SCD1. The combination of GPER1 targeting and cisplatin can enhance the anti-tumor effect.
Creative Biolabs: SCD1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SCD1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SCD1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SCD1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Petroff, Anna B., et al. "Sequential dynamics of Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 (SCD1)/ligand binding and unbinding mechanism: A computational study." Biomolecules 11.10 (2021): 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101435
Anti-SCD1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








