SETX Antibodies
Background
The SETX gene encodes senataxin protein, an RNA/DNA helicase widely expressed in eukaryotic cells, which is mainly involved in transcription regulation and DNA damage repair processes. This protein maintains genomic stability by addressing the R-loop-mediated transcriptional termination issue, which is particularly crucial for the maintenance of neuronal function. Its mutations are associated with two neurological disorders: autosomal dominant amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS4) and autosomal recessive ataxia (AOA2). This gene was first identified through localization cloning technology in 2004. Its unique HELICc domain and nuclease active site reveal an important molecular connection between RNA processing and DNA integrity, providing a key molecular perspective for studying the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases.
Structure of SETX
The senataxin protein encoded by the SETX gene is a large multifunctional protein with a molecular weight of approximately 303 kDa. This protein belongs to the Upf1-like helicase superfamily, and its precise molecular weight may vary depending on the transcript subtype or species. The following table lists the molecular weight and main functional domain characteristics of SETX proteins in different species:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Fruit fly |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~303 | ~302 | ~250 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains a highly conserved SF1 superfamily helicase domain, responsible for ATP-dependent nucleic acid unwinding activity, and a C-terminal nuclease domain essential for R-loop resolution | SETX is highly homologous to human SETX, and the functional domain structure is conserved. It is a commonly used animal model for the study of nervous system diseases | Homologous genes are called "cbc" and have similar helicase functions, participating in transcription termination and DNA damage repair |
The core structure of the Senataxin protein is a multi-domain complex. Its N-terminal contains a helicase domain composed of seven conserved motifs, which is responsible for binding ATP and catalyzing the dissociation of RNA/DNA double strands. The C-terminal region is crucial for its interaction with various proteins, such as RNA polymerase II, and for recruiting DNA repair factors. This protein plays a core role in gene transcription termination, R-loop resolution and maintaining genomic stability through its unique biochemical activity.
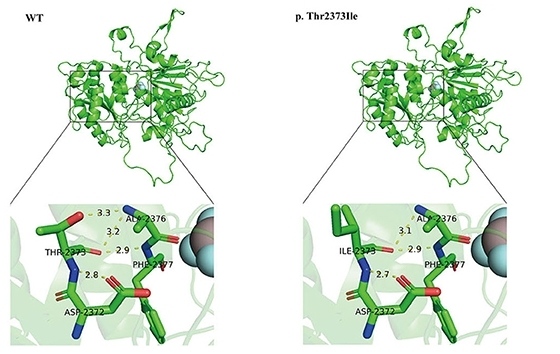 Fig. 1 SETX (p.Thr2373Ile) mutation is predicted to alter senataxin's 3D structure.1
Fig. 1 SETX (p.Thr2373Ile) mutation is predicted to alter senataxin's 3D structure.1
Key structural properties of SETX:
- Contains the conserved SF1 superfamily helicase domain
- Characteristic nucleic acid binding channels
- C terminal contains important protein interaction area
Functions of SETX
The core function of the senataxin protein encoded by the SETX gene is to maintain genomic stability, especially playing a key role in transcription and DNA damage repair processes. However, it is also widely involved in various biological processes such as the development and functional maintenance of the nervous system.
| Function | Description |
| R-loop parsing | Uncoiled RNA/DNA hybrids, which prevent transcription-replication conflicts and DNA double-strand breaks, are the core mechanisms for maintaining genomic stability. |
| Regulation of transcriptional termination | Promote transcriptional termination at the 3' end of the gene to ensure the correct processing and release of mRNA. |
| DNA damage repair | Participate in double-stranded DNA fracture repair, such as by homologous recombination and oxidative damage response, which is the key factor of the cell response to genetic toxic stress. |
| Maintenance of neural function | Its mutations lead to ataxia (AOA2) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS4), highlighting its indispensability in neuronal survival and function. |
| Transcriptional stress response | Solve the accumulation of R-Loops in the transcriptional active regions, prevent transcriptional arrest, and ensure the smooth progress of gene expression. |
Unlike many structurally specialized DNA repair enzymes, senataxin, as a multifunctional nuclease, achieves real-time monitoring and repair of genomic risks during transcription through its physical and functional coupling with transcription machines, which explains why its functional mutations specifically cause neurodegenerative diseases.
Applications of SETX and SETX Antibody in Literature
1. Ramachandran, Shaliny, et al. "Hypoxia-induced SETX links replication stress with the unfolded protein response." Nature communications 12.1 (2021): 3686. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24066-z
The article indicates that tumor hypoxia can induce the expression of SETX, an RNA/DNA helicase that can clear R-loop, reduce DNA damage and maintain replication rate. Its regulation depends on the PERK/ATF4 unfolded protein response pathway, thereby connecting the stress response with the DNA damage repair mechanism.
2. Said, Maha, et al. "FANCD2 promotes mitotic rescue from transcription-mediated replication stress in SETX-deficient cancer cells." Communications Biology 5.1 (2022): 1395. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-04360-2
The article indicates that the deletion of SETX leads to transcription-replication conflicts and the accumulation of R-loops, triggering replication stress and chromosomal instability. Fanconi anemia pathway protein FANCD2 repairs this damage by promoting XPF/ MUS81-dependent DNA synthesis. Co-deletion of SETX and FA genes can specifically inhibit cancer cell proliferation and has the potential for synthetic lethal treatment.
3. Rao, Satyajeet, et al. "Senataxin RNA/DNA helicase promotes replication restart at co-transcriptional R-loops to prevent MUS81-dependent fork degradation." Nucleic Acids Research 52.17 (2024): 10355-10369. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae673
The article indicates that SETX promotes replication fork reactivation by unwinding the R-loop, and it works in synergy with the MUS81-LIG4-ELL pathway to alleviate transcription-replication conflicts. The absence of SETX leads to DNA2-mediated replication fork degradation and, together with DDX17, inhibits R-loop-mediated replication stress.
4. Nanetti, Lorenzo, et al. "SETX mutations are a frequent genetic cause of juvenile and adult onset cerebellar ataxia with neuropathy and elevated serum alpha-fetoprotein." Orphanet journal of rare diseases 8.1 (2013): 123. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-8-123
This study conducted genetic analysis on 22 Italian patients with ataxia accompanied by eye movement disorders and found that 57% carried SETX mutations (AOA2 type), and 14 novel mutations and 3 known mutations were identified. The patients mainly presented with gait ataxia, facial movement disorders and elevated AFP, but none of them had significant apraxia of eye movement, suggesting that SETX is the main pathogenic gene for this phenotype.
5. Szaluś-Jordanow, Olga, et al. "A primary multiple pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma of the heart in an adult dog." BMC Veterinary Research 19.1 (2023): 137. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-021-01277-5
The article indicates that the p.ter8met de novo mutation in the SETX gene leads to early-onset severe peripheral neuropathy. Transcriptional network analysis shows that it is highly associated with ALS4 (functional acquisition) rather than AOA2 (functional loss) characteristics, confirming that this mutation is pathogenic and expanding the phenotypic spectrum of SETX-related diseases.
Creative Biolabs: SETX Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SETX antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom Myoglobin Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SETX antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Chen, Shuaishuai, et al. "Ataxia with oculomotor apraxia type 2 caused by a novel homozygous mutation in SETX gene, and literature review." Frontiers in molecular neuroscience 15 (2022): 1019974. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2022.1019974
Anti-SETX antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






