ALCAM Antibodies
Background
ALCAM is a transmembrane glycoprotein, mainly expressed on the surface of immune cells, neurons and endothelial cells. The protein encoded by this gene participates in key biological processes such as immune response regulation, neural axon orientation, and tumor metastasis by mediating intercellular homotypic or heterotypic adhesion interactions. Since its first identification in 1992, ALCAM has become a research hotspot due to its significant role in T-cell activation, maintenance of the blood-brain barrier and cancer progression. Its extracellular domain contains five characteristic modalities of immunoglobulin-like domains, providing a classic model for the study of the interaction mechanism of cell surface receptors and making continuous contributions to developmental biology and the development of disease therapeutic targets.
Structure of ALCAM
ALCAM is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 90-110 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly due to differences in glycosylation levels and species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Chicken | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 100-110 | 95-105 | 97-107 | 92-100 | 102-110 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing five domain Ig sample structure | ALCAM 76% homology with people | 85% homology with the rat | With avian specific sequence variation | Highly conserved to human proteins |
This protein is composed of 526 amino acids, and its extracellular region contains five immunoglobulin-like domains (V-V-C2-C2-C2 type), forming an extended molecular structure. The third C2-type domain of ALCAM contains a conserved ligand binding site that mediates specific binding to receptors such as CD6. The transmembrane region of the protein is composed of 23 amino acids, and the intracellular segment contains 32 amino acid residues, which participate in intracellular signal transduction through the phosphorylation site at its C-terminal. The V-shaped domain of ALCAM forms a dimerization interface, and this oligomerization state is crucial for its cell adhesion function.
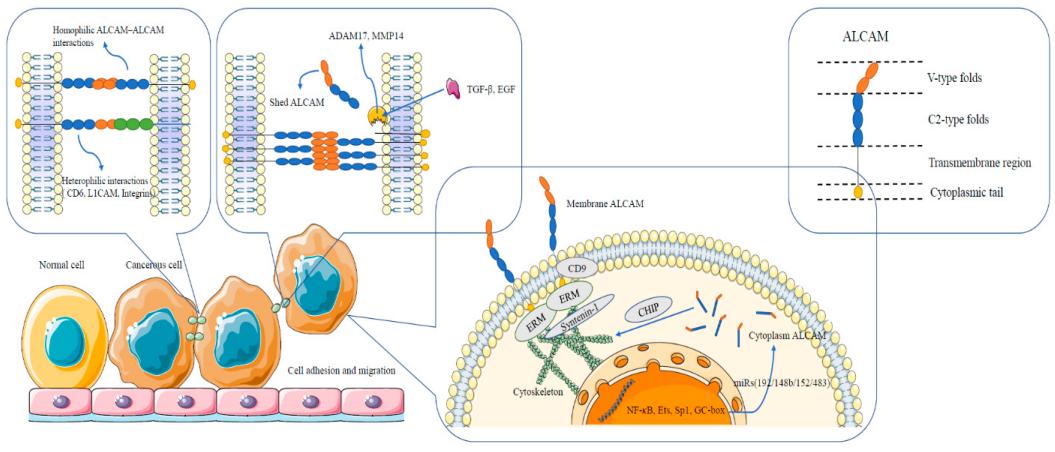 Fig. 1 Diagrammatic representation of ALCAM structure and interactions between and within cells.1
Fig. 1 Diagrammatic representation of ALCAM structure and interactions between and within cells.1
Key structural properties of ALCAM:
- Extracellular region contains five immunoglobulin domain sample structure
- Conserved ligand binding sites are located in the third C2-type domain
- Across the membrane area anchor cell membrane, intracellular through carboxyl terminal involved in signal transduction
Functions of ALCAM
The main function of ALCAM is to mediate intercellular adhesion and signal transduction. However, it is also involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including immune regulation, neurodevelopment and tumor metastasis.
| Function | Description |
| Homomorphic and heteromorphic adhesion | ALCAM mediates intercellular homotypic (ALCAM-ALCAM) and heterotypic (such as ALCAM-CD6) interactions through its immunoglobulin domain, promoting the formation of immune synapses and cell aggregation. |
| Activation of immune cells | By binding to CD6 on the surface of T cells, it participates in the activation and proliferation process of T cells and regulates adaptive immune responses. |
| Neuronal migration and orientation | In the lead in the development of the nervous system growth and neuronal migration, axon neural circuits involved in formation. |
| Tumor cell spread | Multiple cancer cells highly express ALCAM, enhancing their invasion and migration capabilities, and promoting tumor metastasis and angiogenesis. |
| Maintenance of the endothelial barrier | ALCAM expressed in endothelial cells helps maintain the integrity of the blood-brain barrier and regulate white blood cell extravasation. |
The binding of ALCAM to ligands is calcium-independent, and its affinity is regulated by the glycosylation state of the protein and membrane localization. This characteristic distinguishes it from calcium-dependent adhesion molecules, demonstrating its adaptive adhesion regulation function in dynamic microenvironments.
Applications of ALCAM and ALCAM Antibody in Literature
1. Wang, Fangfang, et al. "ALCAM regulates multiple myeloma chemoresistant side population." Cell Death & Disease 13.2 (2022): 136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04556-8
Research reveals that ALCAM negatively regulates drug resistance in multiple myeloma (MM) by inhibiting the EGF/EGFR signaling pathway. Targeting EGFR can effectively inhibit the proliferation of tumor stem cells, enhance the effect of chemotherapy and improve prognosis.
2. Chen, Jian, et al. "Increase of ALCAM and VCAM-1 in the plasma predicts the Alzheimer's disease." Frontiers in immunology 13 (2023): 1097409. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1097409
Research has found that the levels of ALCAM and VCAM-1 in plasma are significantly associated with cognitive decline and medial temporal lobe atrophy in Alzheimer's disease, and are also associated with multiple inflammatory factors. The combination of the two with indicators such as APOE4 can effectively predict AD.
3. Bauer, Aline, et al. "Optimization and Characterization of Novel ALCAM-Targeting Antibody Fragments for Transepithelial Delivery." Pharmaceutics 15.7 (2023): 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071841
This study developed a novel anti-AlCAM antibody fragment, which features multi-species reactivity and high stability. It can effectively block the interaction between ALCAM and CD6/ALCAM and penetrate the corneal epithelium. Nasal administration can reduce white blood cell infiltration in asthma models, proving that ALCAM can be used as a local therapeutic target in the lungs.
4. Willrodt, Ann-Helen, et al. "ALCAM mediates DC migration through afferent lymphatics and promotes allospecific immune reactions." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 759. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00759
This study developed a monoclonal antibody that specifically blocks ALCAM in mice, which can inhibit T cell activation, dendritic cell migration and lymphangiogenesis, and effectively prevent corneal transplant rejection in mouse models, indicating that ALCAM is a potential therapeutic target for human corneal transplant rejection.
5. Yang, Yiming, et al. "The clinical and theranostic values of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM)/CD166 in human solid cancers." Cancers 13.20 (2021): 5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205187
This study demonstrates that ALCAM (CD166) is a cell adhesion molecule that plays a significant regulatory role in solid tumors. Its expression level is closely related to cancer metastasis and prognosis. The soluble form in circulation (sALCAM) can serve as a prognostic indicator and a potential therapeutic target.
Creative Biolabs: ALCAM Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ALCAM antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ALCAM Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ALCAM antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Yang, Yiming, et al. "The clinical and theranostic values of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM)/CD166 in human solid cancers." Cancers 13.20 (2021): 5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205187
Anti-ALCAM antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (2Q1282) (CBMAB-C1624-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






