CBFB Antibodies
Background
The CBFB (core binding factor β subunit) gene encodes an important transcriptional regulatory protein, which mainly functions by forming a heterodimer complex with RUNX family transcription factors. This combination can stabilize the structure of the RUNX protein and enhance its binding ability to DNA, thereby synergistically regulating key biological processes such as hematopoiesis and bone development. This gene was first identified in the research of acute myeloid leukemia in the early 1990s. The CBFB-MYH11 fusion gene caused by its abnormal translocation is a molecular marker of M4EO-type acute myeloid leukemia. The CBFB protein functions through its conserved dimerization and interaction domains. Its regulatory mechanisms and expression patterns have become important research models in the fields of blood differentiation, immune cell development, and disease occurrence, deepening people's understanding of the functions of transcriptional complexes and the molecular mechanisms of hematological malignancies.
Structure of CBFB
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the CBFB gene is approximately 22 kDa, and this molecular weight varies slightly among different species due to minor differences in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Fruit fly |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 22.0 | 21.8 | 22.5 | About 19.0 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains RUNX binding domain and nuclear localization signal | Highly conservative, with functions similar to those of humans | Vertebrate homologous structures exist | Simplify the structure, functional domains are different |
The CBFB protein is composed of 187 amino acids and presents a typical spherical structure. Its core function relies on a conserved dimerization domain, which tightly binds to RUNX transcription factors (such as RUNX1) to form a heterodimer to stabilize the DNA binding ability of RUNX. The secondary structure of this protein is mainly composed of α -helices and β -folds, which together form a hydrophobic core and precisely mediate protein-protein interactions, thereby playing a crucial transcriptional regulatory role in processes such as hematopoietic differentiation and bone development.
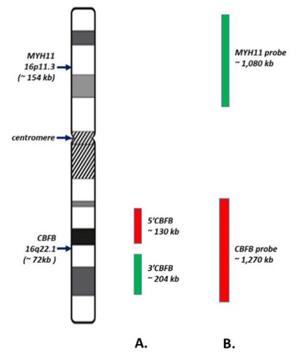 Fig. 1 Schematic of CBFB FISH Probe Sets (BAP/DF).1
Fig. 1 Schematic of CBFB FISH Probe Sets (BAP/DF).1
Key structural properties of CBFB:
- Contains conserved dimerization domains for binding to RUNX proteins
- With a signal of check and ratify, lead the protein into the nucleus
- A spherical folded structure consisting of a β-sheet and α-helix
- Stabilize the complex formed with RUNX through hydrophobic interaction
- There are multiple regulation of phosphorylation sites, affect its transcriptional activity
Functions of CBFB
The core function of the CBFB gene is to form a heterodimer with the RUNX transcription factor and jointly regulate gene expression. Its specific functions in physiological processes are shown in the following table:
| Function | Description |
| Hematopoietic regulation | By binding to RUNX1, it stabilizes its binding ability with DNA and precisely regulates the differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells and the generation of various blood cells. |
| Transcriptional synergy | As a transcriptional cofactor, it does not directly bind to DNA itself, but can enhance the transcriptional activation or inhibition activity of RUNX family proteins. |
| Leukemia inhibition | Its normal function is crucial for maintaining bone marrow homeostasis. The fusion gene CBFB-MYH11 with RUNX1 is a key factor inducing acute myeloid leukemia. |
| Bone development | In osteoblast differentiation, CBFB and RUNX2 work in synergy to regulate the expression of genes related to bone formation. |
| Differentiation of immune cells | Participate in regulating the growth of T cells, B cells and other immune cells and function. |
The interaction mode between CBFB protein and RUNX factor is highly specific and non-DNA-binding dependent, which contrasts with the characteristic of hemoglobin tetramer coexisting to bind oxygen, highlighting its core role as a specific framework and stabilizer in the transcriptional complex.
Applications of CBFB and CBFB Antibody in Literature
1. Malik, Navdeep, et al. "CBFB cooperates with p53 to maintain TAp73 expression and suppress breast cancer." PLoS Genetics 17.5 (2021): e1009553. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1009553
Research shows that CBFB and p53 synergistically inhibit breast cancer by jointly activating TAp73. The absence of either one leads to the down-regulation of TAp73 expression and promotes tumorigenesis. Studies have shown that TAp73 is frequently inactivated in breast cancer, revealing an important tumor suppressor mechanism of the CBFB-p53-TAp73 pathway.
2. Yang, Richard K., et al. "CBFB break-apart FISH testing: an analysis of 1629 AML cases with a focus on atypical findings and their implications in clinical diagnosis and management." Cancers 13.21 (2021): 5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215354
Studies have found that in more than 5% of inv(16) acute myeloid leukemia cases, the CBFB-FISH results are atypical or inconsistent with RT-PCR, often accompanied by other chromosome 16 abnormalities. These findings have significant clinical guiding significance for diagnosis, prognosis judgment, and validation of next-generation sequencing methods.
3. Talami, Annalisa, et al. "How to improve prognostication in acute myeloid leukemia with CBFB-MYH11 fusion transcript: focus on the role of molecular measurable residual disease (MRD) monitoring." Biomedicines 9.8 (2021): 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080953
Studies have found that AML with the CBFB-MYH11 fusion gene has a good prognosis, but about 30% will relapse. Monitoring the level of minimal residual disease (MRD) by qRT-PCR can effectively predict recurrence and is superior to other indicators. Clinically, it is necessary to clearly define the monitoring frequency, key thresholds (such as 0.1%), and sample sources. A persistently low level of MRD does not imply recurrence, but an increase indicates the need for vigilance.
4. Wang, Zhecheng, et al. "circ-CBFB upregulates p66Shc to perturb mitochondrial dynamics in APAP-induced liver injury." Cell death & disease 11.11 (2020): 953. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03160-y
Studies have revealed that the circular RNA circ-CBFB, as a competitive endogenous RNA, regulates the expression of p66Shc by adsorbed miR-185-5p, thereby mediating mitochondrial dynamic disorders and playing a key role in APAP-induced liver injury.
5. Qin, Wei, et al. "Comprehensive mutation profile in acute myeloid leukemia patients with RUNX1-RUNX1T1 or CBFB-MYH11 fusions." Turkish Journal of Hematology 39.2 (2022): 84. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjh.galenos.2022.2021.0641
This study, by analyzing the gene mutation profiles of 134 CBF-AML patients, revealed the significant differences between the two subtypes t(8;21) and inv(16). inv(16) patients are more prone to NRAS/KRAS mutations and abnormal signaling pathways, while t(8;21) patients are more likely to have adhesin complex mutations, providing a new basis for precise classification.
Creative Biolabs: CBFB Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CBFB antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CBFB Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CBFB antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- YaYang, Richard K., et al. "CBFB break-apart FISH testing: an analysis of 1629 AML cases with a focus on atypical findings and their implications in clinical diagnosis and management." Cancers 13.21 (2021): 5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215354
Anti-CBFB antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BPGM Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1806) (CBMAB-2155-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FOSB Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3593) (CBMAB-F2522-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADV Recombinant Antibody (V2-503423) (CBMAB-V208-1364-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






