CD163 Antibodies
Background
CD163 is a transmembrane scavenger receptor protein mainly expressed in the mononuclear-macrophage system. It plays a key role in iron metabolism and anti-inflammatory responses in the body by specifically binding to the hemoglobin-globin complex. This protein helps maintain iron homeostasis in the body and reduce oxidative damage by mediating the clearance of hemoglobin, and is particularly significant during hemolytic diseases and infections. CD163, due to its specific expression in the immune regulation of macrophages, is often used as a marker of this cell lineage and its molecular characteristics were analyzed by a Danish research team in 2000. Its soluble form (sCD163) has become an important biomarker for clinical monitoring of inflammatory diseases, providing an important molecular basis for the study of pathological mechanisms such as sepsis and atherosclerosis.
Structure of CD163
CD163 is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 130 kDa. Its exact weight varies slightly due to species and glycosylation modifications.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Pig |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 130 | 125-130 | 132 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains nine SRCR domain structure | Highly conserved SRCR structure domain | High homology with human |
The extracellular region of this protein is composed of nine scavenger receptor cysteine-enriched (SRCR) domains in tandem, among which the seventh SRCR domain is a key region for binding to the hemoglob-haptoglobin complex. Its tertiary structure forms a rigid conformation through abundant disulfide bonds, providing a structural basis for ligand recognition. The transmembrane region and intracellular segment mediate signal transduction through the PDZ domain to complete the ligand localization process.
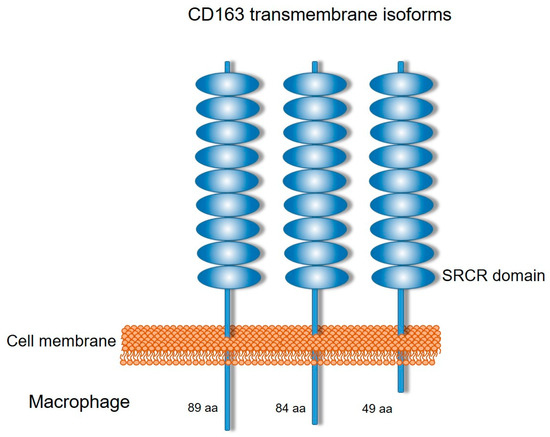 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the three CD163 transmembrane isoforms.1
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the three CD163 transmembrane isoforms.1
Key structural properties of CD163:
- Encode the extracellular region containing multiple SRCR domains
- Rich in cysteine to form stable disulfide bonds
- Specifically recognize the hemoglobin - haptoglobin complex
Functions of CD163
The main function of CD163 is to mediate the clearance of hemoglobin and participate in immune regulation. However, it also involves a wide variety of physiological and pathological processes such as anti-inflammatory responses, tissue repair and iron metabolism.
| Function | Description |
| Hemoglobin clearance | Specifically recognize and bind to the hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex, internalize and degrade it, and remove free hemoglobin in the circulation. |
| Recycling of iron | Within macrophages decomposition hemoglobin, release and recovery of iron, maintain the body's iron steady state. |
| Anti-inflammatory effect | By generating metabolites with anti-inflammatory activity (such as biliverdin and carbon dioxide), it inhibits excessive inflammatory responses. |
| Tissue repair | Promote tissue repair and regeneration of the late inflammation to repair its expression is raised macrophage phenotypes (M2) an important symbol of polarization. |
| Pathogen sensing | As a co-receptor of Toll-like receptors (TLRS), it participates in recognizing bacterial components and regulating innate immune responses. |
CD163 has an extremely high affinity for the hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex, and its binding curve shows typical saturation kinetic characteristics, which is consistent with its efficient clearance function as a specific scavenger receptor. Its intracellular domain coordinates the completion of ligand localization, catabolism and subsequent cellular responses through specific signal transduction pathways.
Applications of CD163 and CD163 Antibody in Literature
1. Nielsen, Marlene Christina, et al. "Macrophage activation markers, CD163 and CD206, in acute-on-chronic liver failure." Cells 9.5 (2020): 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051175
The article indicates that the macrophage scavenger receptors CD163 and CD206 have significant biomarker value in acute and chronic liver diseases. The release of its soluble forms sCD163 and sCD206 is enhanced with inflammatory activation, especially in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). The levels of both are significantly correlated with disease severity and mortality, but due to the differences in their release mechanisms, their prognostic assessment values vary.
2. Ratajczak, Wiktoria, Sarah D. Atkinson, and Catriona Kelly. "The TWEAK/Fn14/CD163 axis—implications for metabolic disease." Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders 23.3 (2022): 449-462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-021-09688-4
The article indicates that TWEAK is a pleiotropic cytokine that functions through two receptors, Fn14 and CD163. CD163 acts as a scavenger receptor and is responsible for eliminating soluble tweGs. Under chronic inflammatory conditions, the TWEAK/Fn14/CD163 axis signals are dysregulated, shifting from protective to harmful, and become a key immunomodulatory pathway for the development of chronic diseases such as metabolic disorders.
3. Sakamoto, Atsushi, et al. "CD163+ macrophages restrain vascular calcification, promoting the development of high-risk plaque." JCI insight 8.5 (2023): e154922. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.154922
Studies have shown that CD163+ macrophages within atherosclerotic plaques have a new function of inhibiting vascular calcification. It activates the NF-κB pathway through the hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex, thereby inducing smooth muscle cells to produce hyaluronic acid and thus hindering the calcification process. This explains why high-risk plaques that are prone to rupture actually have a lower degree of calcification.
4. Plevriti, Andriana, et al. "The role of soluble CD163 (sCD163) in human physiology and pathophysiology." Cells 13.20 (2024): 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201679
Studies have shown that soluble CD163 (sCD163) is an important marker of macrophage activation. It is formed by the shedding of CD163 receptors on the cell membrane, and its plasma concentration reflects the activation level of macrophages in the body. sCD163 has multiple functions such as hemoglobin clearance and immune regulation. Its level is closely related to the severity and prognosis of various acute and chronic inflammatory diseases, metabolic diseases and tumors.
5. Skytthe, Maria K., Jonas Heilskov Graversen, and Søren K. Moestrup. "Targeting of CD163+ macrophages in inflammatory and malignant diseases." International journal of molecular sciences 21.15 (2020): 5497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155497
Studies have shown that CD163 is a surface marker of a specific macrophage subpopulation and is highly enriched in inflammatory and tumor microenvironments. Based on its internalization characteristics, drug conjugates targeting CD163 (such as those linked to antibiotics or glucocorticoids) can precisely deliver drugs in animal models, significantly enhancing efficacy and reducing toxicity, demonstrating broad prospects for targeted therapy.
Creative Biolabs: CD163 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CD163 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CD163 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CD163 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Plevriti, Andriana, et al. "The role of soluble CD163 (sCD163) in human physiology and pathophysiology." Cells 13.20 (2024): 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201679
Anti-CD163 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (8G8) (CBMAB-E1329-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (7G4.2E8) (CBMAB-C8725-LY)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






