CD59 Antibodies
Background
CD59 is a glycosylated phosphatidylinositol anchoring protein that is widely expressed on the surface of various human cells. The protein encoded by this gene can protect host cells from complement system-mediated lysis by inhibiting the formation of membrane attack complexes, thereby maintaining the immune homeostasis of the body. Its main mechanism of action is to prevent the assembly of the membrane attack complex by binding to the complement C8/C9 component. This gene was first identified in 1989 and is the smallest member of the complement regulatory protein family. Due to its unique "ping-pong" inhibition mechanism, it has become an important model for studying complement cascade reactions. In-depth research on the structure and function of CD59 not only reveals the key mechanism by which cells defend against complement injury, but also provides an important target for treating diseases related to complement overactivation.
Structure of CD59
CD59 is a glycosylated protein with a molecular weight of approximately 14-20 kDa, and its specific value varies slightly due to species differences. The molecular weight difference of this protein mainly stems from the degree of glycosylation modification and minor changes in the amino acid sequence.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Pig |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 18-20 | 14-16 | 15-17 | 17-19 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Mature peptide containing 77 amino acids, GPI anchor anchor point | The degree of glycosylation is relatively low | Sequence highly homologous with humans | Glycosylation pattern similar to humans |
The CD59 protein is a mature peptide composed of 77 amino acids and is anchored to the cell membrane via GPI. Its spatial structure contains a core domain stabilized by disulfide bonds, forming a typical folded Ly-6 antigen superfamily. This structure interacts with the complement C8/C9 component through five specific binding sites, among which the circular region composed of amino acids at positions 40-46 is a key active center that inhibits the formation of membrane attack complexes.
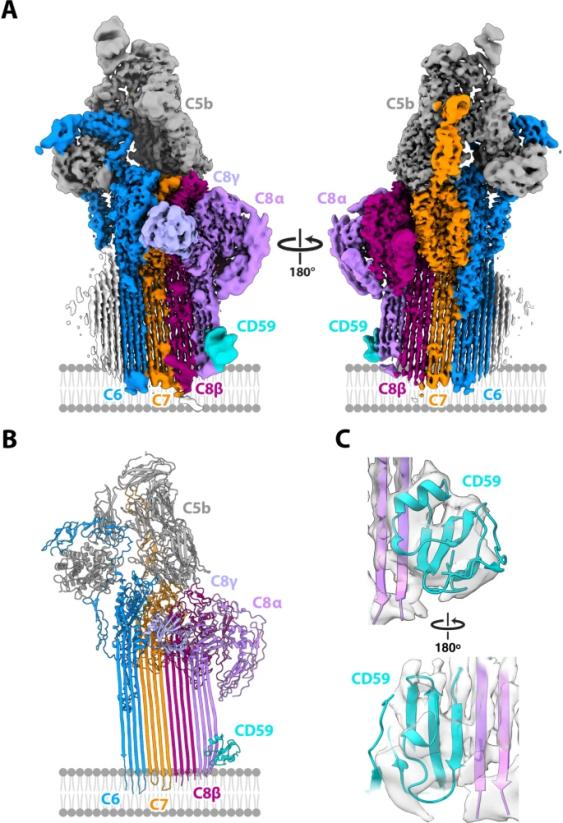 Fig. 1 Structure of the C5b8-CD59 complex.1
Fig. 1 Structure of the C5b8-CD59 complex.1
Key structural properties of CD59:
- Conserved Ly-6/uPAR/α -neurotoxin domain
- By intramolecular disulfide bond finger core stability
- Specifically binds the active site loop of complement C8/C9
Functions of CD59
The core function of CD59 is to inhibit the formation of the complement system membrane attack complex and protect autologous cells from immune misinjury. In addition, it is also involved in various cellular activities, including signal transduction and immune regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Complement regulation | By binding to C8/C9, it prevents membrane attack complex assembly and stops cell lysis. |
| Cell protection | Widely expressed in nucleated cells and red blood cell surface, constitutes a first barrier defence complement body injury. |
| Signal transduction is involved | Through the interaction with cell surface signal molecule, involved in T cell activation and the immune synapse formation process. |
| Disease association | Lack of its function and the paroxysmal diseases such as sleep sex is disease of haemoglobin are closely related. |
| Maintenance of immune homeostasis | By precisely regulating the degree of complement activation, balance immune defense and autologous tissue protection. |
The inhibition of the membrane attack complex by CD59 exhibits rapid and dose-dependent characteristics, and its efficiency of action depends on the expression density on the cell surface. This feature makes it a key membrane binding regulator in the complement cascade reaction.
Applications of CD59 and CD59 Antibody in Literature
1. Couves, Emma C., et al. "Structural basis for membrane attack complex inhibition by CD59." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 890. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36441-z
The article indicates that CD59 protects human cells from damage to the complement system by binding to the complement protein C8, inhibiting its β -hairpin structure from penetrating the cell membrane, and thereby blocking the aggregation of the C9 membrane attack complex.
2. Asadi, Zahra, et al. "Plasma Glycated CD59 and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review." Endocrinology, diabetes & metabolism 7.6 (2024): e70013. https://doi.org/10.1002/edm2.70013
The article indicates that plasma glycated CD59 is a potential novel biomarker for gestational diabetes. Studies have shown that the level of pGCD59 in the second trimester of pregnancy can not only predict the outcome of the oral glucose tolerance test, but also be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes such as neonatal hypoglycemia and large-for-gestational age infants.
3. Voisin, Tomas B., et al. "Dynamics and molecular interactions of GPI-anchored CD59." Toxins 15.7 (2023): 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070430
The article indicates that CD59 is a key receptor that inhibits pore formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC). Research has found that its GPI-anchored structure endows it with conformational flexibility, enabling it to both bind to complement proteins (such as C6 and C8β) to block human MAC and be hijacked by bacterial proteins to attack cells.
4. Sandomenico, Annamaria, et al. "Unveiling CD59-Antibody Interactions to Design Paratope-Mimicking Peptides for Complement Modulation." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.10 (2023): 8561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108561
The article indicates that CD59 is a key protein that inhibits the membrane attack complex of the complement system. Viruses (such as HIV-1) and cancer cells evade immune attacks by highly expressing CD59. Based on its interaction interface with antibodies, this study designed and prepared a circular simulated peptide targeting CD59, laying the foundation for the development of complementary targeted therapies.
5. Wang, Wanying, et al. "Glycated CD59 is a potential biomarker for gestational diabetes mellitus." Frontiers in Endocrinology 15 (2024): 1374253. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1374253
The article indicates that glycated CD59 is an independent risk factor for gestational diabetes. Studies show that the level of gCD59 in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is significantly higher. The area under the curve for diagnosing GDM was 0.681, and the sensitivity was 71.7%. When gCD59 is combined with fasting blood glucose for detection, the diagnostic efficiency is significantly enhanced.
Creative Biolabs: CD59 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CD59 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CD59 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CD59 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Couves, Emma C., et al. "Structural basis for membrane attack complex inhibition by CD59." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 890. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36441-z
Anti-CD59 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








