CDKN1A Antibodies
Background
CDKN1A encodes a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor called p21, which regulates G1/S phase transition of the cell cycle by inhibiting the activity of the CDK complex. As a key downstream effector molecule of the p53 signaling pathway, it is involved in important biological processes such as DNA damage response, cellular senescence and tumor suppression. Since its discovery in 1994, this gene has been widely studied for its core regulatory role in cell cycle checkpoints, and its abnormal expression is closely related to the occurrence and development of various cancers. In-depth research on CDKN1A has greatly promoted people's understanding of tumorigenesis mechanisms, cell cycle regulatory networks, and DNA damage repair mechanisms.
Structure of CDKN1A
The molecular weight of CDKN1A (p21) protein is approximately 21.1 kDa. This value varies among different species, mainly due to its amino acid composition and post-translational modifications.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Macaque |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 21.1 | 20.9 | 21.0 | 21.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 148 amino acids, N end as the CDK combining domain | Highly conserved, with homology exceeding 80% | Highly similar to the human p21 functional domain | Primato-specific amino acid substitution |
This protein is composed of 164 amino acids, and its N-terminal domain can bind to multiple cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) complexes, thereby inhibiting their activity. Its C-end is involved in regulating the processes of cell proliferation and apoptosis. The secondary structure is mainly α -helical, and the key functional region is located at amino acid residues 17 to 24. This region is crucial for its binding and inhibition of the CDK2-cyclin E complex.
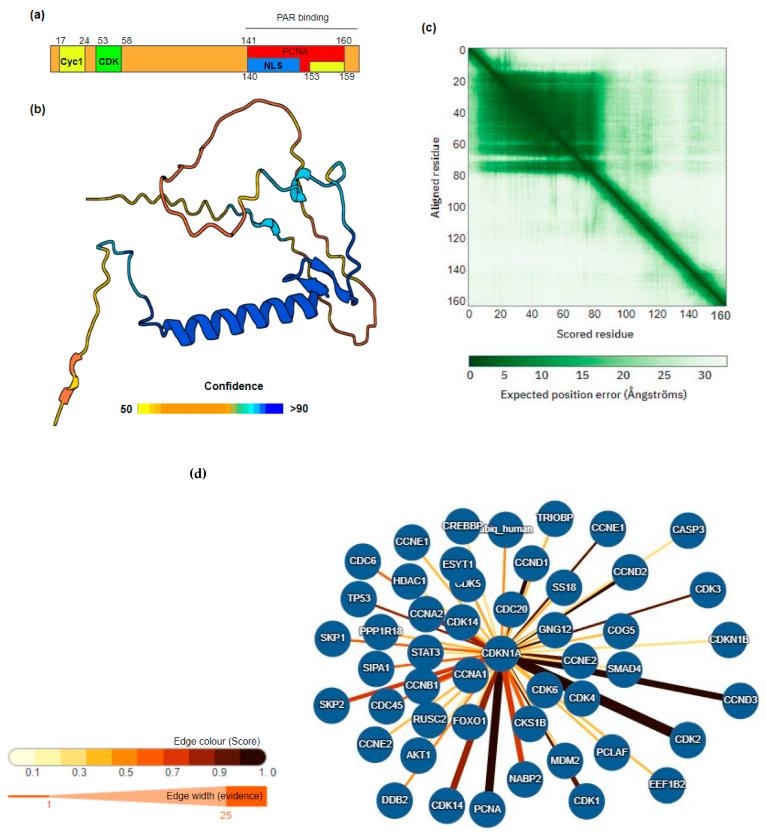 Fig. 1 Structure and interactors of CDKN1A/p21.1
Fig. 1 Structure and interactors of CDKN1A/p21.1
Key structural properties of CDKN1A:
- Contains a conserved N-terminal kinase inhibitory domain
- Extensive binding to a variety of cyclin-cyclin-CDK complexes through this domain
- The C terminal areas involved in regulating the cell positioning and protein stability
Functions of CDKN1A
The core function of the CDKN1A (p21) protein is to act as a key negative regulatory factor in the cell cycle process. However, it is also widely involved in various cellular life activities, including DNA damage responses, cell differentiation and senescence, etc.
| Function | Description |
| Cell cycle arrest | By inhibiting the activity of CDK (cyclin-dependent kinase), cells are prevented from entering the S phase from the G1 phase, thereby suspending cell division. |
| DNA damage response | As a key downstream effector molecule of the p53 tumor suppressor protein, it mediates the suspension of the cell cycle after DNA damage, buying time for repair. |
| Regulation of cellular senescence | Through continuous high expression, it induces and maintains an irreversible growth arrest state of cells, that is, cellular senescence. |
| Transcriptional regulation | Can interact with a variety of transcription factors and regulatory proteins, affect the gene expression patterns, involved in cell differentiation process. |
| Apoptosis regulation | Under specific conditions, changes in its expression level can affect the decision of cells to move towards programmed death (apoptosis). |
The inhibitory effect of CDKN1A on CDK is extensive and non-specific (it can inhibit multiple complexes such as CDK1, CDK2, and CDK4/6), which is different from many more specific CDkis (such as p16), highlighting its fundamental guarding role in maintaining genomic stability.
Applications of CDKN1A and CDKN1A Antibody in Literature
1. Manousakis, Evangelos, et al. "CDKN1A/p21 in Breast Cancer: Part of the Problem, or Part of the Solution?." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.24 (2023): 17488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417488
The article indicates that CDKN1A/p21 is a cell cycle regulatory protein with dual functions, which can both inhibit tumors and potentially promote cancer development. It is involved in processes such as cell proliferation, DNA damage response, tumor stem cell renewal and chemotherapy resistance. Its expression varies among different tumors. Targeted regulation of p21 provides a potential strategy for cancer treatment.
2. Ben-Oz, Bella M., et al. "A dual role of RBM42 in modulating splicing and translation of CDKN1A/p21 during DNA damage response." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 7628. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43495-6
Research has found that the RBM42 protein maintains genomic stability in DNA damage responses by regulating the expression of CDKN1A/p21. On the one hand, RBM42 promotes the splicing of CDKN1A precursor mRNA and antagonizes the splicing inhibitory function of RBM4. On the other hand, it also participates in regulating the translation process of multiple target genes including CDKN1A, thereby precisely controlling the p21 protein level at the post-transcriptional level.
3. Murphy, Michael R., et al. "Long non-coding RNA generated from CDKN1A gene by alternative polyadenylation regulates p21 expression during DNA damage response." Nucleic Acids Research 51.21 (2023): 11911-11926. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad899
Research has found that in the DNA damage response, the first intron of the CDKN1A gene undergoes selective polyadenylation (APA), generating an lncRNA named SPUD. SPUD promotes the expression of p21 protein at the translation level by binding to the p21 translation regulatory factors Calreticulin and CUGBP1, thereby influencing the cell cycle process and DNA damage response.
4. Cheng, Wen-Yu, et al. "Polymorphism at codon 31 of CDKN1A (p21) as a predictive factor for bevacizumab therapy in glioblastoma multiforme." BMC cancer 23.1 (2023): 886. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-023-11400-5
Research has found that the CDKN1A gene c.93C>A (Ser31Arg) polymorphism is associated with the response to bevacizumab treatment in patients with glioblastoma (GBM). Studies have found that patients carrying the Arg/Arg and Arg/Ser genotypes have more significant survival benefits after receiving bevacizumab combined with chemoradiotherapy. This polymorphism can serve as an early predictor of the efficacy of bevacizumab.
5. Muto, Jun, et al. "Highly concentrated trehalose induces prohealing senescence-like state in fibroblasts via CDKN1A/p21." Communications biology 6.1 (2023): 13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-04408-3
Research has found that high-concentration trehalose enhances epidermal expansion and angiogenesis in skin-equivalent models by inducing fibroblast-like senescence, activating the CDKN1A/p21 pathway, and promoting the expression of factors such as DPT and VEGFA, thereby accelerating wound healing in mice. Knockout of CDKN1A can reverse this effect.
Creative Biolabs: CDKN1A Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CDKN1A antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CDKN1A Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CDKN1A antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Manousakis, Evangelos, et al. "CDKN1A/p21 in Breast Cancer: Part of the Problem, or Part of the Solution?." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.24 (2023): 17488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417488
Anti-CDKN1A antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CORO1A Recombinant Antibody (4G10) (V2LY-1206-LY806)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








