COL2A1 Antibodies
Background
COL2A1 gene coding is the alpha 1 chain of type II collagen, the protein mainly exist in the transparent cartilage tissue of vertebrates, vitreous body and intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus. It constitutes the basic framework of the extracellular matrix by forming a three-helical structure, not only providing tensile strength and mechanical support for cartilage, but also participating in cell adhesion, migration and tissue development regulation. Mutations in this gene can disrupt the normal assembly of collagen fibers, leading to type II collagenopathy, typically characterized by abnormal bone development and joint dysfunction, such as type II achondroplasia and Stickler syndrome. Since its discovery in the 1970s, COL2A1 has become an important model for studying connective tissue biosynthesis and hereditary bone diseases. The research on its molecular mechanism has greatly advanced our understanding of extracellular matrix assembly, bone development and related genetic pathologies.
Structure of COL2A1
The molecular weight of the type II collagen α1 chain encoded by the COL2A1 gene is approximately 140 kDa, and its precise value varies by species, mainly due to the length polymorphism of the propeptide segment. This protein is composed of approximately 1,400 amino acid residues, and its primary structure presents a typical Gly-X-Y triple repeat sequence. This characteristic motif forms a stable supersecondary structure through triple helical folding. The stability of the tertiary structure of proteins depends on interchain hydrogen bonds and hydroxylation modifications, among which proline hydroxylation at the Y site plays a key role in maintaining the helical conformation. The core functional region of the molecule is composed of three α chains wound together, and the N-terminal propeptide forms a spherical domain through intramchain disulfide bonds, which jointly maintain the network assembly of collagen fibers and the biomechanical functions of the extracellular matrix.
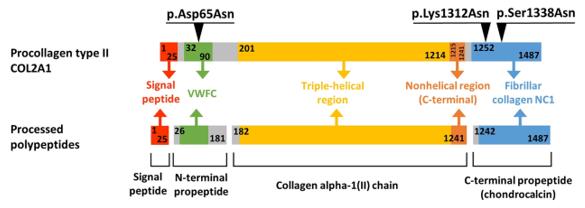 Fig. 1 Domain Organization and Maturation Pathways of the COL2A1 Protein.1
Fig. 1 Domain Organization and Maturation Pathways of the COL2A1 Protein.1
Key structural properties of COL2A1:
- Triple helix structure formed by three α chains winding
- Glycine, proline - hydroxyproline repetitive sequence consisting of rigid frame
- Inter-chain hydrogen bonds and hydroxylation modifications maintain helical stability
Functions of COL2A1
The type II collagen encoded by the COL2A1 gene mainly functions to form the extracellular matrix framework and maintain the integrity of cartilage tissue, while also participating in various biological processes, including the regulation of bone development and cell signal transduction.
| Function | Description |
| Mechanical support | In cartilage tissues formed three spiral fiber network, provide the joints and bones compressive strength and elastic support. |
| Regulation of cell adhesion | Mediate the interaction between chondrocytes and the matrix through integrin binding sites, influencing the processes of cell migration and differentiation. |
| Guidance on bone development | Targeted expression in embryonic cartilage primordia provides a template for endogenesis and coordinates the orderly differentiation of growth plates. |
| Maintenance of tissue homeostasis | Cooperate with proteoglycan, hyaluronic acid and other matrix components to maintain the metabolic balance and repair ability of cartilage tissue. |
| Signal transduction is involved | By interacting with growth factors through extracellular domains, it regulates the activity of chondrogenic signaling pathways such as BMP/TGF-β. |
The three-dimensional grid structure of type II collagen forms a mechanical buffering system through periodic band-like arrangement. This unique quasicrystal arrangement enables it to undergo reversible deformation under pressure, effectively distributing the load on the joints.
Applications of COL2A1 and COL2A1 Antibody in Literature
1. Akahira-Azuma, Moe, et al. "Novel COL2A1 variants in Japanese patients with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita." Human Genome Variation 9.1 (2022): 16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41439-022-00193-x
Five Japanese patients with congenital SEDC were found to have novel glycine mutations in COL2A1 gene. Clarifying the genotype-phenotype association is crucial for the early prevention and treatment of extra-skeletal complications such as ocular complications.
2. Higuchi, Yousuke, et al. "A novel mutation in the COL2A1 gene in a patient with Stickler syndrome type 1: a case report and review of the literature." Journal of medical case reports 11.1 (2017): 237. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-017-1396-y
A study found that a Japanese boy was short since childhood and had features such as cleft palate and cataracts. A novel missense mutation (p.gl381ASP) in COL2A1 was detected through genetic testing, and it was diagnosed as Stickler syndrome. The case shows that the facial and maxillofacial features improve with age, highlighting the importance of genetic diagnosis for this disease.
3. Demal, Till Joscha, et al. "Expanding the clinical spectrum of COL2A1 related disorders by a mass like phenotype." Scientific Reports 12.1 (2022): 4489. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08476-7
Research has found that de novo missense mutations in the COL2A1 gene can lead to phenotypes similar to MASS syndrome. This discovery expands the disease spectrum of type II collagen diseases and has guiding significance for the differential diagnosis of FBN1-negative patients.
4. Markova, Tatyana, et al. "Clinical and genetic characteristics of COL2A1-associated skeletal dysplasias in 60 Russian patients: Part I." Genes 13.1 (2022): 137.https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13010137
This study analyzed the clinical and genetic characteristics of 60 Russian children. The results showed that glycine replacement in the triple helix region of the COL2A1 gene mostly led to congenital epiphyseal dysplasia of the spine, while variations in the C-terminal propeptide region were associated with atypical phenotypes.
5. Liu, Xiuzhen, et al. "A Novel missense mutation of COL2A1 gene in a large family with stickler syndrome type I." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 26.5 (2022): 1530-1539. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17187
A study has identified a non-syndromic ocular Stickler syndrome family associated with a novel COL2A1 variant (P. Cys34ARG). This variant may affect protein structure, and the phenotypes of patients are diverse with a certain male tendency.
Creative Biolabs: COL2A1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality COL2A1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom COL2A1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our COL2A1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Demal, Till Joscha, et al. "Expanding the clinical spectrum of COL2A1 related disorders by a mass like phenotype." Scientific Reports 12.1 (2022): 4489. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08476-7
Anti-COL2A1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (A2) (CBMAB-A2316-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








