FUT5 Antibodies
Background
The FUT5 gene encodes a type II membrane protein belonging to the α-1, 3-fucosyltransferase family, which is mainly expressed on the surface of various epithelial tissues and immune cells in the human body. This enzyme plays a key role in the biosynthesis of Lewis blood group antigens (such as sLe^x and sLe^A) on the cell surface by catalyzing the specific binding of GDP-fucose to N-acetylglucosamine at the terminal of glycoprotein or glycolipid receptors. The sugar chain structure it generates is directly involved in pathophysiological processes such as white blood cell adhesion, inflammatory response and tumor metastasis. Research has found that FUT5 presents a dynamic expression pattern during embryonic development, and its abnormal regulation is closely related to the malignant progression of colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer. Due to the significant role of this gene in intercellular recognition and signal transduction, it has currently become one of the research objects in the field of glycobiology for exploring the molecular mechanisms of diseases and targeted therapeutic strategies.
Structure of FUT5
FUT5 gene encoding the alpha 1, 3 - fucose base transferase transmembrane protein is a kind of Ⅱ type, its molecular weight is about 45 to 50 kDa. This protein is composed of approximately 360 amino acids and features typical glycosyltransferase structural characteristics: a short cytoplasmic tail, transmembrane domain, stem region, and catalytic domain located within the Golgi cavity. Its catalytic domain presents a classic GT10 family folding pattern, with the central β sheet and the surrounding α helix jointly forming the active pocket. The key amino acid residues include the Arg/Lys cluster responsible for GDP-fucose recognition, as well as the Glu/Asp site involved in substrate-specific recognition. The DXMotif at the C-terminal of the protein is directly involved in the binding of sugar nucleotides, while the "flexible loop" region is responsible for regulating the selectivity of receptor substrates. This structural feature enables FUT5 to specifically catalyze the formation of α1, 3-glycosidic bonds, thereby participating in the synthesis of various sugar antigens on the cell surface.
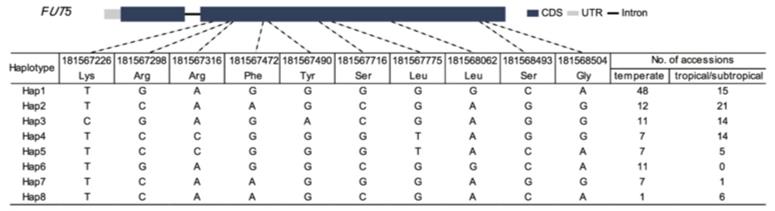 Fig. 1 Haplotypes of FUT5 amongst maize natural variations.1
Fig. 1 Haplotypes of FUT5 amongst maize natural variations.1
Key structural properties of FUT5:
- Typical type II transmembrane protein topology
- The catalytic center adopts the unique α/β/α sandwich folding conformation of the GT10 family
- Conserved GDP-fucose-binding motif (DXD motif) and receptor substrate recognition cavity
Functions of FUT5
The core function of the FUT5 gene is to catalyze fucosylation modification and participate in the synthesis of glycocomplexes on the cell membrane surface. Its specific functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Synthesis of blood group antigens | Catalytic generated Lewis X and Lewis, A blood type antigenic determinant, affect the cell surface immune recognition characteristics. |
| Regulation of cell adhesion | By modifying selectin ligands, it regulates the adhesion process between white blood cells and endothelial cells and participates in inflammatory responses. |
| Embryonic development participation | In early embryonic tissue specific expression, mediating cell recognition and signal transduction. |
| Promotion of tumor metastasis | In a variety of cancers increased, enhance the select element combining ability of tumor cells, promote blood line. |
| Pathogen identification | Some intestinal pathogenic bacteria utilize the sugar chains synthesized by FUT5 as receptors to achieve host cell invasion. |
The reaction catalyzed by this enzyme has strict substrate specificity and preferentially recognizes the Type II sugar chain structure (Galβ1-4GlcNAc-), and its activity is precisely regulated by the pH value of the Golgi complex and the concentration of manganese ions.
Applications of FUT5 and FUT5 Antibody in Literature
1. Liang, Leilei, et al. "miR-125a-3p/FUT5-FUT6 axis mediates colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion and pathological angiogenesis via PI3K-Akt pathway." Cell death & disease 8.8 (2017): e2968-e2968. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.352
The article indicates that in colorectal cancer, miR-125a-3p can act as an upstream regulatory factor of FUT5 and FUT6, exerting tumor suppressor effects by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway, and is expected to become a new biomarker and therapeutic target.
2. Mehta, Kruti, et al. "Altered mRNA expression of fucosyltransferases and fucosidase predicts prognosis in human oral carcinoma." International journal of molecular and cellular medicine 10.2 (2021): 123. https://doi.org/10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.10.2.123
Studies have shown that in oral cancer, elevated mRNA expression of FUT4, FUT5 and FUT8 is associated with tumor progression and lymph node metastasis, and may serve as a predictor of poor prognosis.
3. Yun, Jae Won, et al. "Dysregulation of cancer genes by recurrent intergenic fusions." Genome biology 21.1 (2020): 166. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-020-02076-2
Research has revealed the carcinogenic mechanism of intergenic region fusion: the generation of chimeric transcripts (such as ETV4) through splicing or the repositioning of distal enhancers leads to gene overexpression, which recurs in various cancers.
4. Guo, Weijun, et al. "Phenotyping, genome‐wide dissection, and prediction of maize root architecture for temperate adaptability." iMeta 4.2 (2025): e70015. https://doi.org/10.1002/imt2.70015
The study analyzed the root configuration of maize through microscopic phenotypes and GWAS, and found that different haplotypes of the fucosyltransferase gene FUT5 can regulate the development of primary roots and heat tolerance, providing new resources for molecular design breeding.
5. Carrascal, Mylène A., et al. "Inhibition of fucosylation in human invasive ductal carcinoma reduces E‐selectin ligand expression, cell proliferation, and ERK 1/2 and p38 MAPK activation." Molecular oncology 12.5 (2018): 579-593. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12163
Studies have confirmed that fucosylation modifications (such as sLeX/A) are mediated by the FUTs family and drive malignant tumor progression by enhancing the adhesion, migration, proliferation and growth factor expression of e-selectin in breast cancer cells.
Creative Biolabs: FUT5 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality FUT5 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom FUT5 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our FUT5 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Guo, Weijun, et al. "Phenotyping, genome‐wide dissection, and prediction of maize root architecture for temperate adaptability." iMeta 4.2 (2025): e70015. https://doi.org/10.1002/imt2.70015
Anti-FUT5 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CHRNA9 Recombinant Antibody (8E4) (CBMAB-C9161-LY)

-
Rat Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (16) (CBMAB-E1578-FY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








