GHR Antibodies
Background
The GHR gene encodes growth hormone receptors, which are type I cytokine receptors distributed on the surface of cell membranes and mainly exist in various tissues such as the liver and cartilage. This receptor activates the JAK-STAT signaling pathway by specifically binding to growth hormone, regulating physiological processes such as growth and development, metabolic balance, and cell proliferation of the body. Research on GHR gene mutations has revealed the molecular mechanisms of growth disorders such as Laren's dwarfism. Since its cloning in the 1980s, its crystal structure was resolved in 2008, promoting the development of targeted drugs for the growth hormone pathway. This gene, as a key node in the endocrine regulatory network, provides an important model for studying signal transduction mechanisms and hereditary metabolic diseases.
Structure of GHR
GHR is a transmembrane receptor protein, and its molecular weight varies within the range of 70 to 130 kDa depending on the degree of glycosylation. This difference mainly stems from the variation in the number of N-junction glycosylation sites in the extracellular domain of receptors among species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Rabbit | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 130 | 120 | 118 | 125 | 128 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Extracellular domain containing 9 conservative cysteine | About 70% homology with human | Gly-Arg Insertion Box 1 motif | Differences in glycosylation patterns | The extracellular segment is longer |
This protein is composed of 620 amino acids and includes an extracellular ligand binding domain, a single transmembrane helix and an intracellular signaling domain. Its extracellular segment adopts β -cloverleaf folding and stabilizes the structure through disulfide bonds. The transmembrane region is composed of 24 hydrophobic amino acids. The intracellular segment contains conserved Box1/Box2 motifs for coupling with JAK2 kinases. The dimerization of the receptor is the key to activation, triggering the cascade reaction of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway.
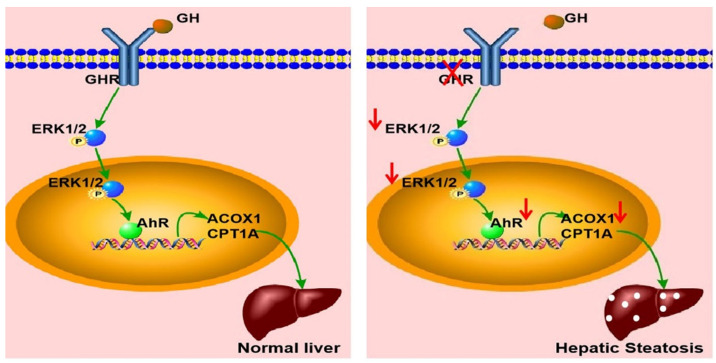 Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of the proposed role of GHR in hepatic steatosis.1
Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of the proposed role of GHR in hepatic steatosis.1
Key structural properties of GHR:
- The extracellular region adopts a β -cloverleaf folding configuration
- The single transmembrane α-helix structure realizes signal transduction across the membrane
- Intracellular area contains a conservative Box1 / Box2 motif
- Receptor dimerization interface realizes growth hormone signal transduction regulation
Functions of GHR
The main function of the growth hormone receptor (GHR) is to mediate growth hormone signal transduction and participate in the regulation of various physiological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of growth and development | Activate the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, promote the synthesis of insulin-like growth factors, and drive bone growth and organ development. |
| Maintenance of metabolic homeostasis | Regulate glucose metabolism and lipid breakdown, and influence energy balance and body composition. |
| Cell proliferation and differentiation | The proliferation and differentiation processes of various tissue cells are controlled through the MAPK pathway. |
| Immune regulatory function | Expressed in immune cells, and participate in inflammation and the regulation of immune cell function. |
| Tissue repair support | Promote the process of tissue regeneration and repair after injury, especially in skeletal and cardiac muscles. |
The signal transduction of GHR exhibits typical dimerization activation characteristics. After binding with growth hormone, conformational changes are triggered. This mechanism differs from the pre-dimerization features of other cytokine receptors, demonstrating its specificity in precisely regulating the growth and development process.
Applications of GHR and GHR Antibody in Literature
1. Juliana Bezerra Medeiros, et al. "ARCGHR neurons regulate muscle glucose uptake." Cells 10.5 (2021): 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051093
In this study, GHRcre transgenic mice were used and it was found that GHR neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus coexist with AgRP and other neurons. After activation, they can increase respiratory quotient and promote eating. Under starvation conditions, the activation of GHR neurons preferentially promotes glucose utilization rather than fat, significantly improving glucose tolerance and muscle insulin sensitivity, indicating that it is a key regulatory factor for glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in the body.
2. Yan, Hong‐Zhu, et al. "GHR is involved in gastric cell growth and apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signalling." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 25.5 (2021): 2450-2458. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16160
The article indicates that the growth hormone receptor (GHR) plays a crucial role in gastric cancer. Research has found that inhibiting GHR can significantly inhibit the growth of tumor cells and tumor formation in vivo by blocking the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, inducing G1 phase arrest of gastric cancer cells and promoting their apoptosis.
3. George, Ashwin Mathew, et al. "Role of the growth hormone receptor (GHR) gene in skeletal Class II malocclusion and its significant influence on the skeletal facial profile in both the sagittal and vertical dimensions: a systematic review." Cureus 16.2 (2024). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.53596
The article indicates that the polymorphism of the growth hormone receptor (GHR) gene is associated with skeletal malocclusion. Studies have shown that GHR gene variations mainly affect the vertical growth of the ascending branch of the mandible and the length of the mandibular body, with limited effect on the maxilla. It is an important genetic indicator for predicting the morphological and developmental differences of the mandible.
4. Schilloks, Marie-Christin, et al. "Effects of GHR deficiency and juvenile hypoglycemia on immune cells of a porcine model for laron syndrome." Biomolecules 13.4 (2023): 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040597
The article indicates that pigs with growth hormone receptor (GHR) gene knockout are models for studying Laren syndrome. This study shows that the absence of GHR signaling alters the proportion of lymphocyte subsets and serum interferon levels, and significantly affects the metabolism-related proteome within CD4+ and CD4- lymphocytes, revealing the regulatory role of GHR on immune cell function.
5. Han, Qi, et al. "Systemic deficiency of GHR in pigs leads to hepatic steatosis via negative regulation of AHR signaling." International Journal of Biological Sciences 17.15 (2021): 4108. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.64894
The article indicates that mutations in the growth hormone receptor (GHR) gene lead to abnormal lipid metabolism by disrupting the ERK-AHR signaling pathway. Research has found that the absence of GHR down-regulates the transcription factor AHR, inhibits the key fatty acid oxidation genes ACOX1 and CPT1A regulated by it, thereby triggering liver steatosis and providing a therapeutic target for related metabolic disorders.
Creative Biolabs: GHR Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality GHR antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom GHR Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our GHR antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Han, Qi, et al. "Systemic deficiency of GHR in pigs leads to hepatic steatosis via negative regulation of AHR signaling." International Journal of Biological Sciences 17.15 (2021): 4108. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.64894
Anti-GHR antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC25 Recombinant Antibody (CBLC132-LY) (CBMAB-C9786-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALK (Phosphorylated Y1278) Recombinant Antibody (D59G10) (PTM-CBMAB-0035YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CORO1A Recombinant Antibody (4G10) (V2LY-1206-LY806)

-
Rat Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (7G4.2E8) (CBMAB-C8725-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






