GNAO1 Antibodies
Background
The GNAO1 gene encodes an α subunit of a guanosine trinucleotide-binding protein (G protein) called Gαo, which is highly expressed in the central nervous system. It plays a core role in neuronal signal transduction, maintaining the normal electrical activity and network balance of neurons by regulating ion channel activity and neurotransmitter release. The functional loss or mutation of this gene can lead to severe neurodevelopmental disorders, such as epileptic encephalopathy and movement disorders in early infants, often accompanied by significant developmental delay. Since its functions were gradually clarified, GNAO1 has become one of the key objects in neurogenetic research. The study of its molecular mechanism not only deepens the understanding of G protein signaling pathways but also provides potential targets for the diagnosis and treatment of related neurological diseases.
Structure of GNAO1
The Gαo protein encoded by the GNAO1 gene is a G protein α subunit with a molecular weight of approximately 40 kDa. This molecular weight is relatively conserved among different mammals, with the main differences reflected in a few regulatory amino acid sites that affect GTPase activity or effector binding.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~40 | ~40 | ~40 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Regulate neuronal ion channels and synaptic transmission | Mutations at key sites lead to a motor phenotype | Often used in the study of basal neural circuits |
This protein is composed of approximately 354 amino acids, and its three-dimensional structure features a typical Gα protein folding pattern, including the GTP binding domain and the effector interaction domain. Its core function depends on the conformational changes in the "Switch" region (Switch I/II) : it is in an active state when binding to GTP and binds to downstream effectors (such as adenylate cyclase); After hydrolyzing GTP into GDP, it returns to an inactive state. This cycle precisely regulates the duration and intensity of intracellular signal transduction.
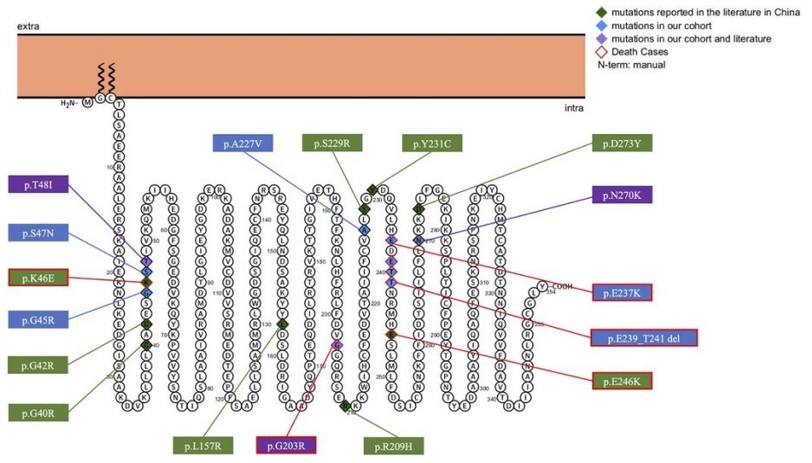 Fig. 1 Predicted Topology and Distribution of GNAO1 Variants.1
Fig. 1 Predicted Topology and Distribution of GNAO1 Variants.1
Key structural properties of GNAO1:
- Classical Gα protein folding structure
- Active pockets with GTP binding and hydrolysis
- The "switch" area controls the combination of effectors
Functions of GNAO1
The Gαo protein encoded by GNAO1 mainly functions as a key regulatory switch for neuronal signal transduction. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of neurophysiological processes, including neural excitability regulation and synaptic plasticity.
| Function | Description |
| Signal transduction | As a downstream effector of G protein-coupled receptors, it transmits receptor activation signals to intracellular targets such as ion channels and adenylate cyclase. |
| Regulation of neural excitability | Through the inhibitory G protein pathway, it negatively regulates the excitability of neurons and maintains the stability of neural networks. |
| Motion control | In the basal ganglia and brain regions high expression, is very important to coordinate voluntary movement, inhibition of abnormal action. |
| Synaptic plasticity | Regulating the release of presynaptic neurotransmitters and postsynaptic receptor responses, influencing the molecular basis of learning and memory. |
| Disease association | Loss-of-function or acquired mutations are directly associated with severe neurodevelopmental disorders such as early-onset epileptic encephalopathy and movement disorders such as choreoathetosis, respectively. |
The signal dynamics of Gαo protein exhibit the characteristics of rapid activation and relatively slow inactivation, which enables it to precisely control the duration and intensity of neuronal signal transmission. Abnormal function of this protein can directly disrupt the balance of neural networks, leading to severe clinical phenotypes.
Applications of GNAO1 and GNAO1 Antibody in Literature
1. Saez Gonzalez, Maria, et al. "Phenotypic diversity in GNAO1 patients: a comprehensive overview of variants and phenotypes." Human mutation 2023.1 (2023): 6628283. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6628283
This article reviews 398 GNAO1 gene variations, integrates data from 282 patients and 8 new cases, and summarizes 107 pathogenic related variations. It systematically analyzes the association between genotypes and phenotypes, providing a basis for establishing a variation database, assisting diagnosis and treatment, and research.
2. Yadav, Shubham, et al. "Decoding GNAO1 mutations using Caenorhabditis elegans model system: past approaches and future prospectives." Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 19 (2025): 1633744. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2025.1633744
This article reviews GNAO1 encephalopathy, points out that there is a lack of early diagnostic methods for this disease, and proposes to use the Caenorhabditis elegans model, which is highly homologous to human genes, to simulate pathogenic mutations and study its downstream pathways, in order to promote the research on pathogenic mechanisms and the development of therapeutic targets.
3. Du, Meiling, et al. "GNAO1 as a Novel Predictive Biomarker for Late Relapse in Hepatocellular Carcinoma." Journal of Healthcare Engineering 2021.1 (2021): 7631815.https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/7631815
Research has found that the expression of GNAO1 is significantly down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Its high expression indicates a lower risk of recurrence and a longer survival period for patients. The nomomap constructed based on GNAO1 and TNM staging can effectively predict the 3-year recurrence risk of liver cancer.
4. Li, Yanmei, et al. "Phenotypes in children with GNAO1 encephalopathy in China." Frontiers in Pediatrics 11 (2023): 1086970. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2023.1086970
This study analyzed 27 cases of GNAO1-related encephalopathy in China. The core clinical features are widespread and difficult-to-control movement disorders, with 67% accompanied by epilepsy. Loss-of-function variations are significantly associated with epileptic encephalopathy.
5. Shomer, Inna, et al. "Personalized allele-specific antisense oligonucleotides for GNAO1-neurodevelopmental disorder." Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids 36.1 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102432
This study developed a specific antisense oligonucleotide therapy targeting the E246K mutation of the GNAO1 gene. In vitro and mouse models have shown that targeting and reducing the expression of mutant alleles can improve functional abnormalities, providing feasible evidence for personalized RNA treatment of this disease.
Creative Biolabs: GNAO1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality GNAO1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom GNAO1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our GNAO1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Li, Yanmei, et al. "Phenotypes in children with GNAO1 encephalopathy in China." Frontiers in Pediatrics 11 (2023): 1086970. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2023.1086970
Anti-GNAO1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BZLF1 Recombinant Antibody (BZ.1) (CBMAB-AP705LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (8G8) (CBMAB-E1329-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12567) (CBMAB-1057-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








