GPX4 Antibodies
Background
GPX4 is a selenium-containing cysteine peroxidase, mainly existing in the cytoplasm and mitochondrial membranes. This enzyme plays a core role in regulating ferroptosis by catalyzing the reduction reaction of phospholipid hydroperoxides, maintaining the lipid homeostasis of cell membranes and resisting oxidative damage. The survival of mammalian cells is highly dependent on the function of GPX4, as its activity directly determines the cells' resistance to lipid peroxidation stress. This gene was first identified by the Ursini team in 1982. It is not only the first antioxidant enzyme discovered that can directly reduce lipid peroxides in biological membranes, but was also identified as a key inhibitor of ferroptosis in 2012. Its unique catalytic mechanism and biological functions continuously drive the research progress of treatment strategies for oxidative stress, cell death and related diseases.
Structure of GPX4
GPX4 is a selenoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 22-25 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly due to differences in amino acid sequences among different subtypes and species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 22.3 | 22.4 | 22.3 | 22.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains cysteine active sites | Active site highly conservative | High homology with human sequence | Individual amino acid substitutions are present |
This protein is composed of approximately 197 amino acids, and its core feature lies in the formation of a typical thioredoxin folding structure. The catalytic active center of GPX4 contains a key selenocysteine residue, which directly participates in the reduction process of peroxide substrates. The three-dimensional structure of the protein forms a hydrophobic active pocket that can specifically recognize and bind to phospholipid hydroperoxides. The adjacent glutamine and tryptophan residues jointly stabilize the transition state, ensuring the high efficiency and specificity of the catalytic reaction.
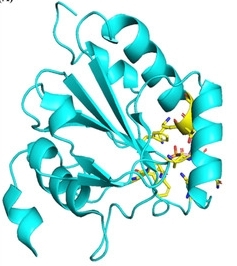 Fig. 1 Shows the full crystal structure of GPX4 (PDB entry 6ELW).1
Fig. 1 Shows the full crystal structure of GPX4 (PDB entry 6ELW).1
Key structural properties of GPX4:
- Typical thioredoxin folding conformation
- Active center to form hydrophobic pocket
- Catalytic core containing selenium generation of cysteine
Functions of GPX4
The core function of GPX4 is to catalyze the reduction of phospholipid hydroperoxides to maintain cellular oxidative homeostasis. However, this enzyme is also widely involved in various physiological and pathological processes, especially playing a core role in the regulation of ferroptosis.
| Function | Description |
| Antioxidant defense | Specifically reduce phospholipid hydroperoxides in the cell membrane, block the lipid peroxidation chain reaction, and protect the integrity of the membrane structure. |
| Ferroptosis inhibition | By eliminating lipid peroxides, it directly inhibits the occurrence of iron-dependent programmed cell death and is a key molecule for cell survival. |
| Metabolic regulation | With cell metabolism network interaction, and selenium glutathione synthesis metabolic pathway, the active by the regulation of cell types also NADPH level. |
| Inflammatory regulation | By controlling the level of lipid peroxidation, it indirectly regulates the synthesis of inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and related signaling pathways. |
| Developmental support | During embryonic development, it ensures the normal differentiation of cells and the development of tissues. Gene knockout experiments have shown that its absence can lead to the death of embryos. |
The catalytic efficiency of GPX4 depends on the selenocysteine and glutathione electron-donating system in the active center. Its specificity for phospholipid substrates is much higher than that of other glutathione peroxidases, which determines its irreplaceable guardian role in the ferroptosis pathway.
Applications of GPX4 and GPX4 Antibody in Literature
1. Yuan, Yuan, et al. "Kaempferol ameliorates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal ferroptosis by activating Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis." Biomolecules 11.7 (2021): 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11070923
This study explored the protective effect of kaempferol on neuronal oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) injury. The results indicated that kaempferol alleviated OGD/ R-induced ferroptosis in neurons by activating the Nrf2/SLC7A11 pathway, upregulating the expression of GPX4 protein, enhancing antioxidant capacity and inhibiting lipid peroxidation.
2. Mayr, Lisa, et al. "Dietary lipids fuel GPX4-restricted enteritis resembling Crohn's disease." Nature Communications 11.1 (2020): 1775. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15646-6
Studies have shown that the activity of GPX4 in intestinal epithelial cells of patients with Crohn's disease is impaired. A Western diet rich in omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids can induce lipid peroxidation. GPX4 limits the occurrence of intestinal inflammation by inhibiting such peroxidation reactions. This study reveals the mechanism by which diet triggers GPX4-related mucosal inflammation.
3. Wang, Xiaohong, et al. "STING aggravates ferroptosis-dependent myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting GPX4 for autophagic degradation." Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 10.1 (2025): 136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-025-02216-9
This study reveals a new mechanism of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: the cGAS-STING signaling pathway directly leads to the degradation of GPX4 protein by promoting autophagy, thereby inducing ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Inhibiting this pathway can stabilize GPX4, effectively alleviate myocardial injury, and provide a new target for treatment.
4. Zheng, Qiang, et al. "PRDM16 suppresses ferroptosis to protect against sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by targeting the NRF2/GPX4 axis." Redox biology 78 (2024): 103417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2024.103417
This study reveals that PRDM16 exerts a protective effect in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by directly or via the NRF2 pathway up-regulating the expression of GPX4 and inhibiting ferroptosis in the kidneys. Targeting this mechanism provides a new strategy for treatment.
5. Yu, Dianping, et al. "Acevaltrate as a novel ferroptosis inducer with dual targets of PCBP1/2 and GPX4 in colorectal cancer." Signal transduction and targeted therapy 10.1 (2025): 211. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-025-02296-7
Research has found that the natural product ACE can effectively induce ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Its mechanism of action lies in directly targeting GPX4, inhibiting the enzyme's activity and promoting its degradation, thereby disrupting the cell's antioxidant defense system. This effect enables ACE to exhibit a significant anti-tumor effect.
Creative Biolabs: GPX4 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality GPX4 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom GPX4 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our GPX4 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Weaver, Kamari, and Rachid Skouta. "The selenoprotein glutathione peroxidase 4: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities." Biomedicines 10.4 (2022): 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040891
Anti-GPX4 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






