HCK Antibodies
Background
HCK is an important member of the Src family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases and is mainly expressed in myeloid cells. As a key signal transduction molecule, HCK participates in regulating the activation, proliferation and migration processes of immune cells through its unique SH3, SH2 and kinase domains. Research has found that HCK plays a core regulatory role in immune responses such as macrophage polarization, neutrophil degranulation, and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Its abnormal activation is closely related to various inflammatory diseases and fibrotic lesions, which makes HCK an important target for the treatment of chronic kidney disease, atherosclerosis and other diseases. In recent years, the development of specific HCK inhibitors has provided new strategies for the treatment of related diseases.
Structure of HCK
HCK is a tyrosine kinase in the Src family that is mainly expressed in myeloid cells and has a typical modular structure: the N-terminal myristic acylation site mediates membrane localization, the SH3 and SH2 domains recognize proline-rich sequences and phosphorylated tyrosine, respectively, and the C-terminal kinase domain contains an ATP-binding pocket and a catalytic center. Its uniqueness lies in maintaining a self-inhibitory state through intramolecular interactions - SH3 binds to the junction region and SH2 binds to the C-terminal pTyr522. This ingenious conformational regulation enables it to respond rapidly to external stimuli. When activated, the SH3/SH2 domain instead binds to effector proteins, while Tyr411 autophosphylation enhances activity, thereby precisely regulating the activation, migration and phagocytosis functions of myeloid cells. This special structural feature of HCK makes it an important target for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
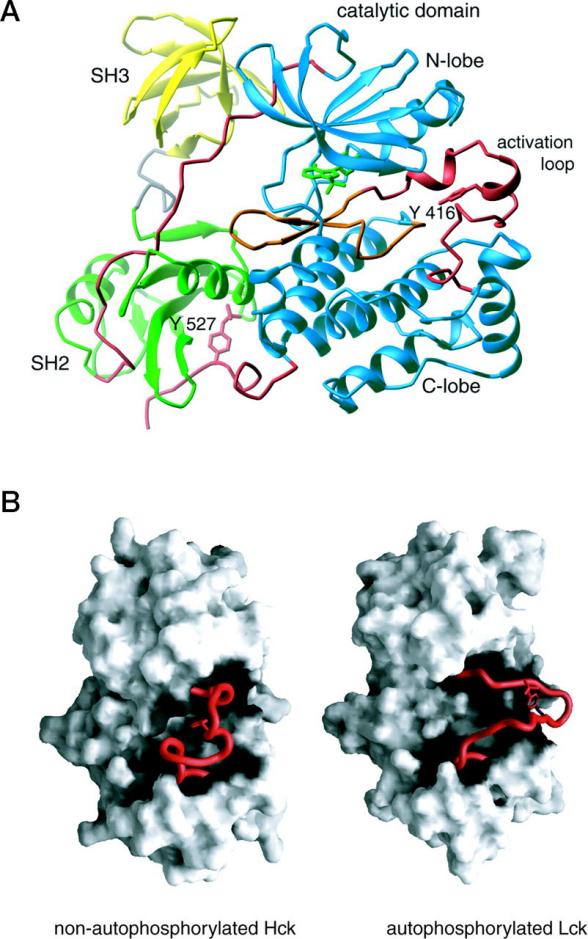 Fig. 1 Structure of Hck.1
Fig. 1 Structure of Hck.1
Functions of HCK
HCK is a core regulatory factor for signal transduction in myeloid cells and plays multiple functions in immune responses and inflammatory reactions.
| Function | Description |
| Activation of immune cells | Regulate the activation thresholds of macrophages and neutrophils by phosphorylating downstream signaling molecules. |
| Regulation of inflammatory response | Mediate the assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome and promote the release of pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-1β. |
| Cell migration control | Integrate chemokine signals to regulate the directional movement and infiltration of immune cells. |
| Regulation of phagocytic function | It participates in the Fcγ receptor signaling pathway and affects the phagocytic efficiency of macrophages. |
| Shaping of the tumor microenvironment | Abnormally activated in tumor-associated macrophages, promoting the formation of an immunosuppressive microenvironment. |
The activity of HCK exhibits typical biphase regulatory characteristics: it maintains self-inhibition through phosphorylation of C-terminal Tyr522 in the basal state, but can be rapidly activated and form a positive feedback amplification signal after stimulation. This precise spatiotemporal regulation makes it a key molecular node connecting innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Unlike the broad-spectrum action of most kinases, HCK exhibits obvious myeloid cell specificity, which provides it with a unique advantage as a therapeutic target.
Applications of HCK and HCK Antibody in Literature
1. Chen, Man, et al. "HCK induces macrophage activation to promote renal inflammation and fibrosis via suppression of autophagy." Nature communications 14.1 (2023): 4297. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40086-3
Research has found that hematopoietic cell kinase (HCK) exacerbates renal inflammation and fibrosis in chronic kidney disease (CKD) by promoting M1-type polarization, proliferation and migration of macrophages. HCK antibodies or inhibitors alleviate fibrosis by inhibiting autophagic flow in macrophages. Targeting HCK may become a new strategy for anti-renal fibrosis.
2. Scholz, Glen, Kellie Cartledge, and Ashley R. Dunn. "Hck enhances the adherence of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages via Cbl and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase." Journal of Biological Chemistry 275.19 (2000): 14615-14623. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.19.14615
Research has found that HCK antibodies can inhibit the adhesion of LPS-activated macrophages. HCK directly phosphorylates Cbl through the SH3 domain, promoting its binding to the PI3K p85 subunit, thereby enhancing the cytoskeletal recombination and adhesion ability of macrophages. This process depends on the activity of Src family kinases.
3. Kong, Xiangxi, et al. "Hematopoietic cell kinase (HCK) is essential for NLRP3 inflammasome activation and lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in vivo." Frontiers in pharmacology 11 (2020): 581011. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.581011
Research has found that HCK antibodies reduce the release of IL-1β and caspase-1(P20) by inhibiting the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. HCK directly binds to the NBD and LRR domains of NLRP3. Its inhibitors can block ASC oligomerization and alleviate LPS-induced liver inflammation, suggesting that targeting HCK may be effective in treating acute inflammatory diseases.
4. Welch, Heidi, and Isabelle Maridonneau-Parini. "Hck is activated by opsonized zymosan and A23187 in distinct subcellular fractions of human granulocytes." Journal of Biological Chemistry 272.1 (1997): 102-109. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.1.102
Studies have shown that HCK antibodies can regulate the activation of neutrophils. HCK is selectively activated by different stimuli (conditioning yeoglycan /A23187) in the particle-rich region and membrane region, participating in the regulation of degranulation reactions, suggesting that it has specific functions in different subcellular compartments.
5. Yokoyama, Noriko, and W. Todd Miller. "Biochemical properties of the Cdc42-associated tyrosine kinase ACK1: Substrate specificity, autophosphorylation, and interaction with Hck." Journal of Biological Chemistry 278.48 (2003): 47713-47723. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M306716200
Research has found that HCK binds to the C-terminal proline-rich region of ACK1 through the SH3 domain and phosphorylates ACK1 (Tyr284 site), thereby enhancing its kinase activity. This interaction reveals the key role of HCK in regulating the ACK1 signaling pathway.
Creative Biolabs: HCK Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality HCK antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom HCK Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our HCK antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at please contact us.
Reference
- Porter, Margaret, et al. "Reciprocal regulation of Hck activity by phosphorylation of Tyr527 and Tyr416: effect of introducing a high affinity intramolecular SH2 ligand." Journal of Biological Chemistry 275.4 (2000): 2721-2726. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.4.2721
Anti-HCK antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CHRNA9 Recombinant Antibody (8E4) (CBMAB-C9161-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (8G8) (CBMAB-E1329-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Rat Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (16) (CBMAB-E1578-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








