His Tag Antibodies
Background
The His Tag is a short peptide sequence composed of 6 to 10 histidine residues, which is usually fused to the N-terminal or C-terminal of the target protein through genetic engineering methods. This tag can specifically bind to divalent metal ions such as nickel and cobalt, thereby achieving rapid and efficient protein purification in immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC). Since its development in the 1980s, the His tag has become one of the most commonly used tools in the purification of recombinant proteins due to its small molecular weight, no impact on protein folding and function, and wide applicability. Its simple and efficient design principle not only promotes the standardization of protein expression and purification technologies, but also provides key technical support for structural biology, drug development and molecular interaction research.
Structure of His Tag
His Tag is a kind of polypeptide tag with a relatively small molecular weight, usually composed of 6 to 10 histidine residues, and the molecular weight is approximately 0.8 to 1.2 kDa. The molecular weight of this tag varies slightly among different variants, depending on the amount of histidine and the design of the connection sequence.
| Species | 6×His | 8×His | 10×His | 6×His with connection sequences | His fusion protein with signaling peptides |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~0.84 | ~1.12 | ~1.40 | ~1.8–3.5 | Depending on the target protein |
| Primary Structural Differences | Linear polypeptide chain | The same, longer | Longer and with enhanced binding force | Includes a flexible linker | Contains secretory or localization sequences |
His Tag forms stable complexes by coordinating and binding with metal ions such as nickel and cobalt through its continuous histidine residues. After the tag is fused and expressed at the N-terminal or C-terminal of the protein, it usually does not significantly affect the folding and function of the target protein. Its binding mechanism depends on the interaction between the nitrogen atom on the histidine imidazole ring and the immobilized metal ion, and can achieve efficient purification under denatured or non-denatured conditions. This tag is colorless, has low immunogenicity, and is easily eluted through EDTA or imidazole competition. It has become one of the most commonly used tools in the purification of recombinant proteins.
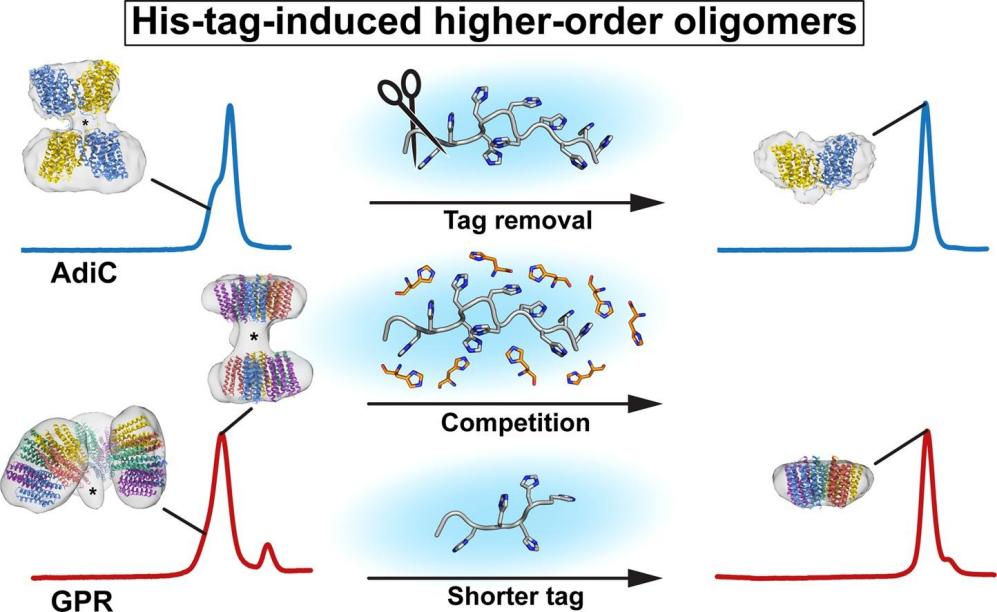 Fig. 1 His-Tag-induced higher-order oligomers.1
Fig. 1 His-Tag-induced higher-order oligomers.1
Key structural properties of His Tag:
- Short peptide composed of continuous histidine residues linear structure
- Histidine imidazole ring nitrogen atoms as metal ligand bonding sites
- Fuse to the N-terminal or C-terminal of the target protein through genetic engineering
Functions of His Tag
The main function of His Tag is to serve as an affinity tag in the expression and purification of recombinant proteins. In addition, it also plays a key role in a variety of biotechnology applications, including protein detection, immobilization and functional research.
| Function | Description |
| Protein purification | Recombinant proteins can be rapidly captured and purified in IMAC chromatography through the specific binding of histidine residues to metal ions such as nickel and cobalt. |
| Protein immobilization | By taking advantage of its metal chelating ability, the target protein can be directionally fixed on the surface of chips, magnetic beads or electrodes for interaction studies. |
| Protein detection and tracing | It can be combined with anti-His antibodies or fluorescently labeled metal chelates for detection methods such as Western Blot and immunofluorescence. |
| Functional Domain Research | By inserting His tags to mark specific domains, it assists in studying the functions, interactions and folding processes of protein domains. |
| Simplify the protein preparation process | Its small molecular weight and high stability significantly reduce the difficulty of purification and increase the throughput and efficiency of recombinant protein preparation. |
The binding of His Tag with metal ions has high affinity and reversibility. It can maintain the binding ability under different pH and denaturation conditions (such as high-concentration urea or guanidine hydrochloride), and is suitable for the renaturation purification of denatured proteins. Its binding ability increases with the increase of histidine number. The 6×His tag achieves the optimal balance between binding strength and tag size and has become one of the most commonly used affinity tags in industrial production and scientific research.
Applications of His Tag and His Tag Antibody in Literature
1. Bromberg, Raquel, et al. "The His-tag as a decoy modulating preferred orientation in cryoEM." Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 9 (2022): 912072. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.912072
This paper finds that the presence of His-tag affects the interaction between proteins and the gas-liquid interface during cryo-electron microscopy sample preparation and alters their dominant orientation distribution. Studies have shown that His tag can mask the hydrophobic/hydrophilic regions on the protein surface, and its hydrophobic linker may also enhance the interfacial interaction, suggesting that tag design can regulate protein-interface interactions.
2. Ayoub, Nooraldeen, et al. "Structural and biochemical insights into His-tag-induced higher-order oligomerization of membrane proteins by cryo-EM and size exclusion chromatography." Journal of Structural Biology 215.1 (2023): 107924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2022.107924
This study takes two His-tagged membrane proteins as examples and finds that His tags can mediate the formation of higher-order oligomers (such as tetramers, decamers, etc.). Chromatographic and cryo-electron microscopy results revealed tag-mediated specific interactions, indicating that ignoring tag removal may interfere with downstream protein structure and function studies.
3. de Almeida, Janaina Marques, et al. "Tailoring recombinant lipases: keeping the His-tag favors esterification reactions, removing it favors hydrolysis reactions." Scientific reports 8.1 (2018): 10000. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27579-8
This study explored the influence of His tags on the lipase LipC12. After removing the His tag, the enzymatic hydrolytic activity was significantly enhanced, but the activity and stability of the enzyme in organic solvents were better when the tag was present. The His tag does not affect the immobilization efficiency, but it has different effects on the catalytic activity of free and immobilized enzymes, indicating that the tag can be retained or removed according to application requirements.
4. Jureczek, Justyna, et al. "An oligo-His-tag of a targeting module does not influence its biodistribution and the retargeting capabilities of UniCAR T cells." Scientific Reports 9.1 (2019): 10547. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47044-4
This study explored the influence of oligo-His tags of targeted modules (TM) in UniCAR systems on their functions and distribution. By comparing the anti-PSCA TM with and without His tags, it was found that the His tag had no significant effect on its binding affinity, in vitro and in vivo killing effect, and biological distribution.
5. Mišković, Marija Zora, et al. "Location is everything: influence of his-tag fusion site on properties of adenylosuccinate synthetase from Helicobacter pylori." International journal of molecular sciences 25.14 (2024): 7613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147613
This study took the adenylate succinate synthase (AdSS) of Helicobacter pylori as an example and found that the N-terminal His tag would cause protein aggregation and precipitation, significantly reducing the enzyme activity, while the C-terminal tag had little effect. The results show that the position of the His tag has a crucial impact on protein solubility and function, and careful evaluation is required when making a selection.
Creative Biolabs: His Tag Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality His Tag antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom His Tag Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our His Tag antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Ayoub, Nooraldeen, et al. "Structural and biochemical insights into His-tag-induced higher-order oligomerization of membrane proteins by cryo-EM and size exclusion chromatography." Journal of Structural Biology 215.1 (2023): 107924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2022.107924
Anti-His Tag antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1200) (CBMAB-C1467-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (2Q1282) (CBMAB-C1624-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AOC3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0014) (CBMAB-0014-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






