HNF1B Antibodies
Background
The HNF1B gene encodes a transcription factor belonging to the hepatocyte nuclear factor family. This protein is mainly expressed during the development of organs such as the kidneys, pancreas, liver and reproductive tract, and participates in organ formation and cell differentiation by regulating the transcription of downstream target genes. Abnormal function can lead to adult-onset juvenile diabetes (MODY5) as well as renal cysts and diabetic syndrome (RCAD), often accompanied by structural abnormalities of the kidneys and developmental defects of the pancreas. This gene was first identified in the 1990s. The research on the association between its mutations and various congenital developmental disorders has deepened people's understanding of the role of transcriptional regulation in organ development and provided an important molecular basis for the diagnosis and mechanism exploration of related genetic diseases.
Structure of HNF1B
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the HNF1B gene is approximately 68 kDa, and this weight may fluctuate slightly among different species due to minor differences in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~68 | ~67 | ~72 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Conserved DNA binding domain | The homologous domains are highly similar | Vertebrate specific domains exist |
This protein contains approximately 557 amino acids and forms functional modules through its N-terminal dimerization domain, central DNA-binding homologous domain, and C-terminal trans-activation domain. The DNA-binding homologous domain in its three-dimensional structure adopts a typical helical - angular - helical conformation, which can specifically recognize the promoter of the target gene. A key proline-rich region is crucial for its trans-activating function, and abnormal amino acid changes within this region are associated with functional loss. The dimerization of proteins is the structural basis for their effective binding to DNA and the exercise of transcriptional regulatory functions.
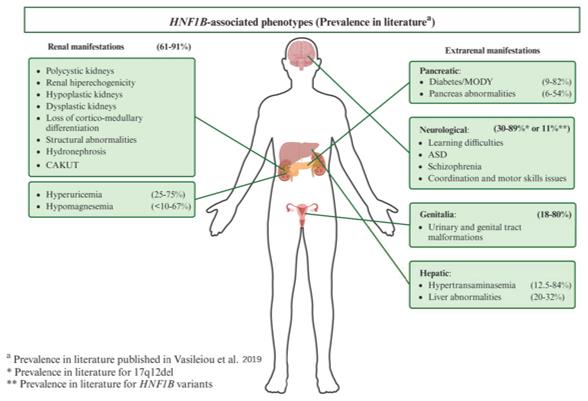 Fig. 1 Phenotypic manifestations associated with HNF1B and their prevalence in the literature.1
Fig. 1 Phenotypic manifestations associated with HNF1B and their prevalence in the literature.1
Key structural properties of HNF1B:
- Modular domain composition (including POU homologous domains)
- Function dependent on homodimerization
- Contains a conserved DNA binding motif with a trans activation domain
Functions of HNF1B
The main function of the HNF1B transcription factor is to regulate embryonic development and organ formation. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including cell differentiation, metabolic regulation and disease occurrence.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of organ development | During the embryonic development of multiple organs such as the kidneys, pancreas, liver and reproductive tract, by regulating the expression of downstream target genes, it guides their normal morphogenesis and cell differentiation. |
| Gene transcriptional regulation | As a transcription factor, it specifically binds to the promoter region of the target gene, activating or inhibiting its transcription, thereby regulating the complex gene expression network. |
| Maintenance of metabolic homeostasis | Participate in regulating pancreatic beta cells and the electrolyte balance of kidney function, its function and diabetes (e.g. MODY5) and is directly related to the occurrence of renal cyst. |
| Cell cycle and differentiation | Influence a particular cell lines, such as renal tubular epithelial cells proliferation and terminal differentiation, its exceptions can cause birth defects or cystic lesion. |
| Disease association | Heterozygous mutations of this gene are the main cause of renal cysts and diabetic syndrome (RCAD), and are closely related to other congenital abnormalities, such as reproductive tract malformations. |
HNF1B exerts its function by forming homologous or heterodimers. Its DNA binding specificity is determined by the conserved POU homologous domain, while its transcriptional activity depends on the C-terminal trans-activation domain. This structural feature makes it a key regulatory molecule for embryonic development and homeostasis maintenance in adulthood.
Applications of HNF1B and HNF1B Antibody in Literature
1. Gambella, Alessandro, et al. "The landscape of HNF1B deficiency: a syndrome not yet fully explored." Cells 12.2 (2023): 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12020307
The article indicates that HNF1B gene variations can cause multi-system lesions, mainly involving the pancreas and kidneys, leading to diabetes and renal cysts. The phenotypes of this syndrome are complex and diverse. New features such as liver involvement have attracted increasing attention, but the mechanism of its heterogeneity remains unclear.
2. Sánchez-Cazorla, Eloísa, Noa Carrera, and Miguel Ángel García-González. "HNF1B Transcription Factor: Key Regulator in Renal Physiology and Pathogenesis." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.19 (2024): 10609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910609
The article indicates that the HNF1B gene regulates the development of multiple organs, and its variations can lead to multi-system lesions such as renal cysts, diabetes, and elevated liver enzymes. Most patients carry 17q12 microdeletions. In-depth research on its mechanism will help improve diagnosis and treatment as well as genetic counseling.
3. Nittel, Clara Marie, et al. "Review of neurodevelopmental disorders in patients with HNF1B gene variations." Frontiers in Pediatrics 11 (2023): 1149875. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2023.1149875
The article indicates that HNF1B gene variations or 17q12 microdeletions increase the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, especially autism spectrum disorders and learning difficulties. The incidence rate of patients carrying microdeletions is significantly higher than that of those with intra-gene mutations, which requires clinical attention and strengthened systematic research.
4. Grand, Kelli, et al. "HNF1B alters an evolutionarily conserved nephrogenic program of target genes." Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 34.3 (2023): 412-432. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2022010076
Research has found that the HNF1B gene is a key transcription factor in kidney development. Its pathogenic mutations selectively interfere with the downstream target gene network rather than completely losing its function. This provides a new perspective for understanding the molecular mechanism of congenital kidney disease.
5. Goea, Laura, et al. "Hnf1b renal expression directed by a distal enhancer responsive to Pax8." Scientific Reports 12.1 (2022): 19921. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21171-x
In this study, using a claad model, the distal enhancer CNS1, which regulates the expression of the key gene Hnf1b in kidney development, was identified for the first time, and it was proved that its activity depends on the transcription factor Pax8. This provides new ideas for the diagnosis and disease modeling of congenital kidney diseases in humans.
Creative Biolabs: HNF1B Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality HNF1B antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom HNF1B Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our HNF1B antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Sánchez-Cazorla, Eloísa, Noa Carrera, and Miguel Ángel García-González. "HNF1B Transcription Factor: Key Regulator in Renal Physiology and Pathogenesis." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.19 (2024): 10609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910609
Anti-HNF1B antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1B1 Antibody (V2-2449) (CBMAB-1001CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CRYAB Recombinant Antibody (A4345) (CBMAB-A4345-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOE Recombinant Antibody (A1) (CBMAB-0078CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








