IDO1 Antibodies
Background
IDO1 is a heme oligomerase mainly distributed in the immune organs of mammals (such as the spleen and lymph nodes) and the placenta. This enzyme participates in the regulatory mechanism of immune tolerance by catalyzing the catabolism of tryptophan along the kynuurine pathway and plays a key role in maintaining the immune homeostasis of the body. In the tumor microenvironment, the overexpression of IDO1 inhibits T cell activity by depleting local tryptophan, thereby promoting the phenomenon of immune escape. This enzyme was first characterized by the team of Japanese scholar Hidetaka Mashima in the study of rabbit intestines in the 1960s. Its crystal structure was analyzed in 2006, revealing the unique binding mode of heme cofactors and substrates at the active site. As a core regulatory protein in the field of immune metabolism, IDO1 has become an important target for tumor immunotherapy, and the development of its inhibitors has promoted a deeper understanding of the mechanism of immune checkpoints.
Structure of IDO1
IDO1 is an intracellular enzyme with a molecular weight of approximately 45 kDa. Its weight varies by about 2-3 kDa among different mammals, mainly due to the interspecies differences in the C-terminal domain of the enzyme protein.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Rabbit | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 45.2 | 44.8 | 44.9 | 47.1 | 45.3 |
| Primary Structural Differences | 423 amino acids containing signal peptides | Lack of phosphorylation sites | Substrate-binding cavity variation | C-end extended segment | Highly homologous to humans |
This protein is composed of two domains: a large domain is responsible for forming the active center, and a small domain is involved in stabilizing the protein conformation. Its active center is embedded with a heme cofactor, which achieves catalytic function by coordinating with conserved histidine residues. The secondary structure of IDO1 is characterized by the alternating arrangement of α -helices and β -folds, jointly forming a hydrophobic channel. This channel not only ensures the effective entry of thiosine but also provides precise binding sites for oxygen molecules. Iron atoms located in the active center mediate oxidation reactions through valence state changes, while histidine at the distal end regulates substrate specificity through steric hindrance effects to prevent peroxidation damage.
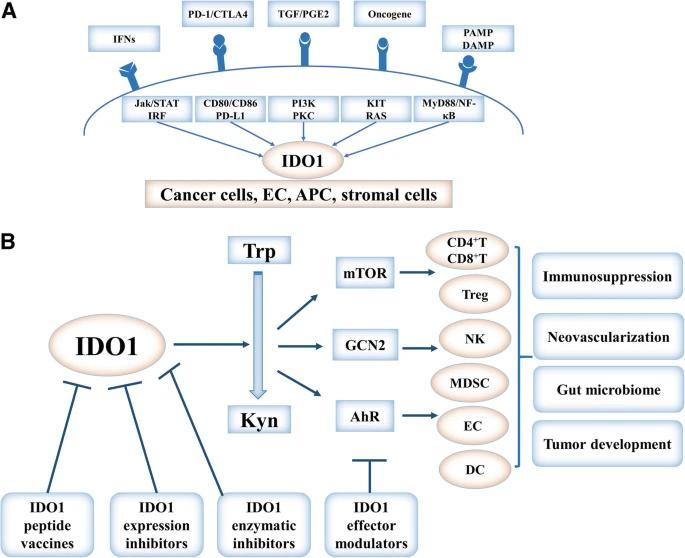 Fig. 1 Regulation, function, and targeting of IDO1 in cancer.1
Fig. 1 Regulation, function, and targeting of IDO1 in cancer.1
Key structural properties of IDO1:
- An α/β type folded architecture composed of two domains
- Hydrophobic channels permeate the protein and embed heme cogroups
- Heme containing divalent iron ions serves as the catalytic center
- Conserved histidine stabilizes iron ions through coordination bonds
Functions of IDO1
The core function of IDO1 is to mediate tryptophan metabolism and participate in immune regulation. In addition, this enzyme is also involved in a variety of pathophysiological processes, including tumor immune escape, pregnancy maintenance and neuroinflammatory regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Tryptophan depletion | Catalyze the decomposition of tryptophan along the kynurenine pathway, reduce the concentration of tryptophan in the microenvironment, and inhibit the activation and proliferation of T cells. |
| Induction of immune tolerance | By activating aromatic hydrocarbon receptors through the metabolite kynurenine, it promotes the differentiation of regulatory T cells and establishes an immunosuppressive microenvironment. |
| Tumor immune escape | Highly expressed in tumor tissues, it helps tumor cells resist immune system attacks and is an important immune checkpoint molecule. |
| Maintenance of pregnancy | Expression in placenta chorionic trophoblast cells, through the establishment of maternal-fetal immune tolerance to prevent embryo is maternal immune system. |
| Neuroprotection and injury | In the brain involved in nerve inflammation control, it may lead to excessive activation neurotoxicity metabolite accumulation, associated with neurodegenerative diseases. |
The enzyme kinetics curve of IDO1 exhibits typical Mie equation characteristics, which is different from the S-shaped curve of hemoglobin. This reflects its single substrate binding site structure and functional characteristics of maintaining catalytic activity at low tryptophan concentrations, making it suitable for precisely regulating immune responses in local microenvironments.
Applications of IDO1 and IDO1 Antibody in Literature
1. Zeitler, Leonie, and Peter J. Murray. "IL4i1 and IDO1: oxidases that control a tryptophan metabolic nexus in cancer." Journal of Biological Chemistry 299.6 (2023): 104827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104827
Research has found that in the tumor microenvironment, IDO1 and IL4i1 synergistically promote immune tolerance through mechanisms such as consuming tryptophan, activating AhR, and inhibiting ferroptosis. Studies have shown that IDO1 inhibitors need to be combined with IL4i1 inhibitors to achieve better therapeutic effects in cancer treatment.
2. Muller, Alexander J., et al. "IDO1 and inflammatory neovascularization: bringing new blood to tumor-promoting inflammation." Frontiers in oncology 13 (2023): 1165298. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1165298
Research has found that IDO1 is a core factor in the pro-inflammatory environment of tumors. It not only helps tumors escape by inducing immune tolerance, but new research has also found that it promotes pathological angiogenesis through unique myeloid cells (IDVCs). This function involves offsetting IFNγ and stimulating IL6 to provide blood supply for tumors, similar to physiological processes such as wound healing.
3. Merlo, Lauren MF, Weidan Peng, and Laura Mandik-Nayak. "Impact of IDO1 and IDO2 on the B Cell Immune Response." Frontiers in immunology 13 (2022): 886225. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.886225
Research has found that IDO1 and IDO2 are tryptophan metabolic enzymes and their roles in immune regulation are contrary. IDO1 mainly inhibits immune responses, promotes tumor immune escape and maternal and fetal tolerance. IDO2, on the other hand, drives inflammation, especially in autoimmunity. The latest research reveals that the two have crucial and opposite regulatory effects on B-cell function, which provides new potential targets for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and the like.
4. Tang, Kai, et al. "Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitors in clinical trials for cancer immunotherapy." Journal of Hematology & Oncology 14.1 (2021): 68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01080-8
Research has found that IDO1 is a key enzyme in tryptophan metabolism, and its overexpression promotes tumor immune escape and is associated with a poor prognosis. Currently, multiple therapies targeting IDO1, including small molecule inhibitors, peptide vaccines, and PROTAC degraders, are under development, providing new potential strategies for cancer treatment.
5. Liu, Ming, et al. "Targeting the IDO1 pathway in cancer: from bench to bedside." Journal of hematology & oncology 11.1 (2018): 100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-018-0644-y
Research has found that IDO1 is a key rate-limiting enzyme in the tryptophan-macrourine pathway. By consuming tryptophan and accumulating macrourine, it inhibits the functions of effector T cells and NK cells, and activates Treg cells and MDSC, thereby driving tumor immune escape, angiogenesis, and resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors. At present, its inhibitors have become an important research direction in cancer immunotherapy.
Creative Biolabs: IDO1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality IDO1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom IDO1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our IDO1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Liu, Ming, et al. "Targeting the IDO1 pathway in cancer: from bench to bedside." Journal of hematology & oncology 11.1 (2018): 100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-018-0644-y
Anti-IDO1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Rat Anti-CD300A Recombinant Antibody (172224) (CBMAB-C0423-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (61-3E7) (CBMAB-1183-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






