IGF1R Antibodies
Background
The IGF1R gene encodes a tyrosine kinase receptor protein located on the cell membrane, which is mainly distributed on the cell surface of various tissues. This protein plays a crucial role in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation and metabolic balance by binding to insulin-like growth factors and activating downstream signaling pathways. Since its complete identification in 1986, IGF1R has become the first growth factor receptor confirmed to have tyrosine kinase activity, and the analysis of its structure has provided an important model for the study of receptor signal transduction. The abnormal expression of this gene is closely related to tumorigenesis and metabolic diseases. The research on the molecular mechanism mediated by it continuously promotes the development of targeted drugs and has a profound impact on the cognition of cell signaling networks.
Structure of IGF1R
IGF1R is a transmembrane glycoprotein receptor with a molecular weight of approximately 180 kDa. Its precise molecular weight may fluctuate slightly due to differences in glycosylation modifications among different species.
| Species | Human | Bovine | Porcine | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~180 | ~175 | ~178 | ~182 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Typical tyrosine kinase domains | The intracellular segment is highly conserved | The similarity of ligand binding regions is high | There are subtle differences in the extracellular domain glycosylation sites |
This protein is composed of 1,367 amino acid residues, and its primary structure folds into an extracellular ligand-binding region rich in β sheets, a single transmembrane region, and an intracellular tyrosine kinase region. In its three-dimensional structure, the L-shaped extracellular domain composed of two cysteine-rich regions is responsible for specifically recognizing ligands, while the kinase domain in the intracellular segment regulates phosphorylation activity through a conserved activation loop. The JM domain near the transmembrane region self-inhibits kinase activity in an inactive state, while the specific tyrosine residue at the C-terminal tail provides anchoring sites for downstream signaling proteins.
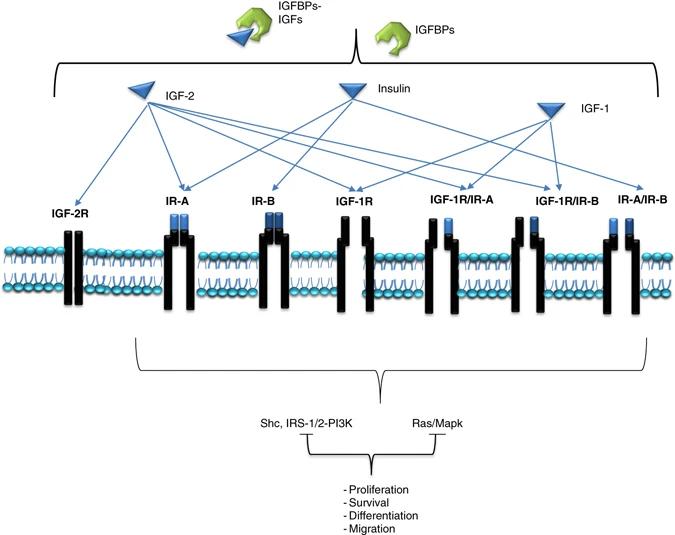 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the type I IGF-1R and IR signaling network.1
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the type I IGF-1R and IR signaling network.1
Key structural properties of IGF1R:
- Extracellular ligand binding domains rich in cysteine
- A single transmembrane α -helix is anchored to the cell membrane
- Intracellular tyrosine kinase activity core
Functions of IGF1R
The core function of IGF1R is to mediate cell growth, proliferation and metabolic regulation. Furthermore, it is also widely involved in a variety of key pathophysiological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Promote cell proliferation | Activating signaling pathways such as MAPK directly drives cell cycle progression and division and proliferation, which is crucial for embryonic development. |
| Anti-apoptosis | The PI3K-Akt pathway transmits survival signals, inhibits the activity of apoptosis-related proteins, and enhances cell survival. |
| Metabolic regulation | Regulate glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis, coordinate the utilization of nutrients and energy metabolism, and support cell growth. |
| Differentiation support | In specific lineages such as osteoblasts and myocytes, it provides necessary signal support for the differentiation and maturation of cells. |
| Tumorigenesis promotion | The excessive activation of its signaling pathway is a hallmark of various cancers, continuously driving tumor growth and invasion through autocrine circuits. |
Unlike insulin receptors that mainly regulate metabolic functions, the signaling network mediated by IGF1R is more complex and has a longer-lasting effect, which is consistent with its core position in promoting long-term growth events such as development and tumor formation.
Applications of IGF1R and IGF1R Antibody in Literature
1. Tang, Yi-fang, et al. "circ_PPAPDC1A promotes Osimertinib resistance by sponging the miR-30a-3p/IGF1R pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)." Molecular cancer 23.1 (2024): 91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-024-01998-w
This study discovered for the first time that the circular RNA circ_PPAPDC1A competitively binds to miR-30a-3p through "sponge" adsorption in osimertinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer, thereby relieving its inhibition of the downstream target gene IGF1R. The activated IGF1R then drives the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, ultimately leading to tumor drug resistance. This study revealed a new mechanism by which circ_PPAPDC1A serves as a oncogenic factor and a potential therapeutic target.
2. Krieger, Christine C., Susanne Neumann, and Marvin C. Gershengorn. "Is there evidence for IGF1R-stimulating abs in Graves' orbitopathy pathogenesis?." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21.18 (2020): 6561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186561
This review refutes the view that IGF1R is a direct autoantibody target for Graves' ophthalmopathy. Existing evidence supports that its pathogenesis stems from signal crosstalk between TSHR and IGF1R, rather than antibodies that directly stimulate IGF1R. Therefore, TSHR is the core autoantibody target, and therapies targeting TSHR/IGF1R crosstalk should be the main direction of future drug development.
3. Bulatowicz, Joseph J., and Teresa L. Wood. "Activation versus inhibition of IGF1R: a dual role in breast tumorigenesis." Frontiers in Endocrinology 13 (2022): 911079. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.911079
This article reviews the dual role of IGF1R in breast cancer. The traditional view holds that it promotes tumor occurrence, but new evidence reveals its potential function in inhibiting tumor and metastasis. The article focuses on combining mouse models to explore how these two seemingly contradictory functions are unified in the context of cell growth and differentiation, providing a new perspective for understanding the complex functions of IGF1R.
4. Erlandsson, Malin C., et al. "IGF1R signalling is a guardian of self-tolerance restricting autoantibody production." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 958206. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.958206
This study confirmed through experimental models and clinical samples that IGF1R maintains immune tolerance in antigen-presenting cells by regulating FoxO1 phosphorylation, ICOSL/CXCR5 expression and cellular metabolism. Inhibiting the IGF1R signal can lead to the activation of B cells in the marginal zone and the production of autoantibodies, thereby inducing autoimmunity. Research suggests that when treating with IGF1R, one should be vigilant about the risk of its disruption of immune tolerance.
5. Zheng, Ke, et al. "IGF1R-phosphorylated PYCR1 facilitates ELK4 transcriptional activity and sustains tumor growth under hypoxia." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 6117. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41658-z
The article indicates that under hypoxic conditions, IGF1R in the nucleus phosphorylates the Tyr-135 site of PYCR1, promoting its binding to ELK4 and recruitment to the promoter region of the target gene. PYCR1 enhances SIRT7-mediated H3K18ac deacetylation by catalyzing NAD+ production, inhibits gene transcription and promotes colorectal cancer growth. This mechanism reveals the key role of PYCR1 in tumor hypoxia adaptation.
Creative Biolabs: IGF1R Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality IGF1R antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom IGF1R Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our IGF1R antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Ekyalongo, Roudy Chiminch, and Douglas Yee. "Revisiting the IGF-1R as a breast cancer target." NPJ precision oncology 1.1 (2017): 14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-017-0017-y
Anti-IGF1R antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BBS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0253) (CBMAB-0254-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (P67.6) (CBMAB-C10189-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0733) (CBMAB-F0435-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








