LRP1 Antibodies
Background
The LRP1 gene encodes a large transmembrane protein called low-density lipoprotein receptor-associated protein 1, which is widely distributed in various cell types and is highly expressed in liver, brain and vascular tissues. As a multifunctional receptor, it not only participates in lipoprotein metabolism but also mediates cell signal transduction, endocytosis and extracellular matrix remodeling, which is crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis and embryonic development. This gene was first identified in 1988, and its functional defect has been confirmed to be closely related to diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis and tumor metastasis. LRP1, due to its core role in connecting lipid metabolism and cellular signaling networks, has become an important molecular target for studying the mechanisms of metabolic diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.
Structure of LRP1
LRP1 is a large type I transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 515 kDa. This protein is composed of an extracellular α chain of approximately 500 kDa and a transmembrane β chain of 85 kDa linked by non-covalent bonds. Its molecular weight fluctuates slightly among different species due to differences in glycosylation modifications.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 515 | 512 | 514 | 516 |
| Primary Structural Differences | There were 4 ligand-binding clusters and 31 EGF-like repeats | Structure and human highly conservative, in combination with field similarity of 95% | Extracellular domain structure and anthropogenic highly homologous | Ligand binding domain structure in line with mammals conservative |
The extracellular segment of LRP1 is composed of four ligand binding clusters (I-IV), including 31 EGF-like repeat sequences and 22 typical LDLR domains, forming multiple ligand binding sites. Its transmembrane region is a single-pass transmembrane structure, and the intracellular segment contains two NPxY internalizing moieties, which are responsible for mediating mesin-dependent endocytosis processes and cellular signal transduction. This protein specifically binds to over 40 ligands, including apolipoprotein E and α 2-macroglobulin, through its modular extracellular domain, playing a core role in lipid metabolism and cellular signal regulation.
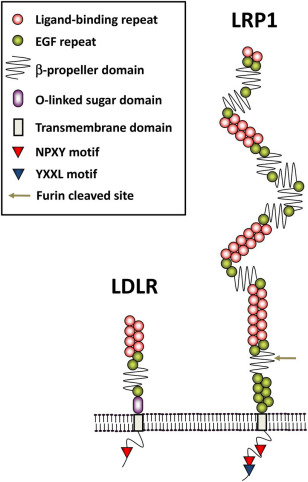 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of domain structure for LRP1 and LDLR.1
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of domain structure for LRP1 and LDLR.1
Key structural properties of LRP1:
- Giant modular extracellular domain (containing 4 ligand binding clusters)
- Highly conservative transmembrane helical anchoring structure
- Intracellular segment double NPxY internalized motifs mediate signal transduction
- Multiple EGF-like repeat sequences regulate PH-dependent ligand release
Functions of LRP1
The main function of the LRP1 gene is to act as a multifunctional receptor on the cell surface, mediating ligand-localization and cell signal transduction. However, it is also widely involved in various physiological and pathological processes, including lipid metabolism, cell migration and tissue remodeling.
| Function | Description |
| Lipoprotein metabolism | Remove chylomicron residues and various apolipoproteins in tissues such as the liver to maintain plasma lipid homeostasis. |
| Cell signal regulation | By interacting with over 40 ligands, it regulates multiple signaling pathways including PDGF and TGF-β, influencing cell proliferation and differentiation. |
| Tissue damage repair | Participation from the blood protease inhibitor compounds, regulate inflammation, promote tissue repair and remodeling. |
| Maintenance of brain homeostasis | Regulation of amyloid clearance in the brain affects the integrity of the blood-brain barrier and is associated with neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Cell migration support | By integrating extracellular matrix signals, it influences the adhesion and migration processes of cells and plays a role in embryonic development and cancer metastasis. |
The binding affinity of LRP1 to ligands is synergistic regulated by its multiple helper receptors, which contrasts sharply with the single oxygen-binding mode of myoglobin and highlights its core position as a complex signal integration center.
Applications of LRP1 and LRP1 Antibody in Literature
1. Shinohara, Mitsuru, et al. "Role of LRP1 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: evidence from clinical and preclinical studies: Thematic Review Series: ApoE and Lipid Homeostasis in Alzheimer's Disease." Journal of lipid research 58.7 (2017): 1267-1281. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R075796
In the research of Alzheimer's disease (AD), LRP1, as A member of the low-density lipoprotein receptor family, participates in the disease process in both Aβ -dependent and non-dependent pathways by regulating Aβ metabolism, maintaining brain homeostasis and influencing apoE action. Both clinical and preclinical studies support its potential pathogenic mechanism, but its specific role still needs in-depth exploration, and its value as a therapeutic target has also attracted much attention.
2. Chen, Kai, et al. "LRP1 is a neuronal receptor for α-synuclein uptake and spread." Molecular neurodegeneration 17.1 (2022): 57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-022-00560-w
This study confirmed that LRP1 is a key receptor regulating the uptake of α -Syn by neurons and the transmission of α -SYN in the brain. Gene knockout experiments have shown that the deletion of LRP1 significantly reduces the uptake of α -Syn monomers, oligomers and pathological fibers by neurons, and effectively inhibits the spread of α -Syn in mouse models. This discovery reveals the core role of LRP1 in synucleinopathies such as Parkinson's disease, providing a new target for treatment.
3. Yan, Wenjin, et al. "Heterozygous LRP1 deficiency causes developmental dysplasia of the hip by impairing triradiate chondrocytes differentiation due to inhibition of autophagy." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 119.37 (2022): e2203557119. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2203557119
This study has for the first time discovered that pathogenic variations in the LRP1 gene are closely related to congenital hip dysplasia (DDH). Animal models have confirmed that the absence of LRP1 accelerates the premature development of tridirectional cartilage, leading to acetabular and femoral head deformities, and significantly weakens the ability of cartilage formation. This study reveals the key role of LRP1 in the etiology of DDH, providing a new direction for treatment.
4. He, Lingnan, et al. "FUT2 inhibits the EMT and metastasis of colorectal cancer by increasing LRP1 fucosylation." Cell Communication and Signaling 21.1 (2023): 63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-023-01060-0
This study reveals that the FUT2 enzyme inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis process of colorectal cancer by mediating α-1,2 fucosylation modification of the LRP1 protein. Experiments have shown that the absence of FUT2 weakens the tumor suppressor function of LRP1, promoting tumor invasion and spread. This discovery clarifies the key role of LRP1 in the FUT2 tumor suppressor pathway and provides a new target for treatment.
5. Liu, Lu, et al. "LRP1 Repression by SNAIL Results in ECM Remodeling in Genetic Risk for Vascular Diseases." Circulation Research 135.11 (2024): 1084-1097. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.325269
This study reveals that the pathogenic variant rs11172113 located in the LRP1 gene regulates its expression through an enhancer region. The transcription factor SNAIL can specifically bind to this risk allele, thereby inhibiting the expression of LRP1. The deletion of LRP1 alters the extracellular matrix of smooth muscle cells and enhances the TGF-β signaling pathway, which provides a potential mechanism for explaining why the LRP1 locus is a common risk factor for various vascular diseases.
Creative Biolabs: LRP1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality LRP1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom LRP1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our LRP1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Shinohara, Mitsuru, et al. "Role of LRP1 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: evidence from clinical and preclinical studies: Thematic Review Series: ApoE and Lipid Homeostasis in Alzheimer's Disease." Journal of lipid research 58.7 (2017): 1267-1281. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R075796
Anti-LRP1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CORO1A Recombinant Antibody (4G10) (V2LY-1206-LY806)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTN4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-6075) (CBMAB-0020CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








