NRG1 Antibodies
Background
The NRG1 gene encodes neuromodulin 1, a cytokine protein widely expressed in tissues such as the nervous system, cardiovascular system and breast. This gene participates in intercellular signal transduction by activating ERBB receptor tyrosine kinase, regulating key physiological processes such as synaptic formation, cardiomyocyte differentiation, and mammary duct development. Abnormalities in the NRG1 signaling pathway are often found in patients with schizophrenia, which is closely related to the core role of this gene in neural development and myelin formation. The precursor protein of NRG1, which was simultaneously discovered by multiple research teams in 1992, needs to be processed by protease hydrolysis to form a biologically active subtype. The molecular characteristics of over 30 isomers produced by selective splicing of this gene provide an important model for studying the functional diversity of growth factors, cellular communication mechanisms, and neuro-immune interactions.
Structure of NRG1
NRG1 is a transmembrane protein with a relatively large molecular weight, and the molecular weight of its precursor protein is approximately 110-135 kDa. This value will vary significantly due to different splicing isomers.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~110-135 | ~105-130 | ~110-132 | ~108-133 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Egf-like domains and immunoglobulin-like domains are present | Conservative high homology with humans, the core functional areas | Extracellular domain structure of similar height | There are subtle interspecific differences in the transmembrane region sequence |
This protein contains approximately 640 amino acid residues (taking the most common NRG1-β1 subtype as an example), and its primary structure determines its characteristics as a transmembrane protein. The core functional structure of the NRG1 protein is an EGF-like domain, which is responsible for specifically binding to the ERBB receptor and activating downstream signals. Its secondary structure forms characteristic β -folding and three pairs of disulfide bonds within the EGF-like domain, which are crucial for maintaining the correct three-dimensional conformation and biological activity. A unique structural feature is that the NRG1 precursor needs to undergo proteolytic processing (such as being cleaved by TACE/ADAM17) to release extracellular fragments with signal transduction activity.
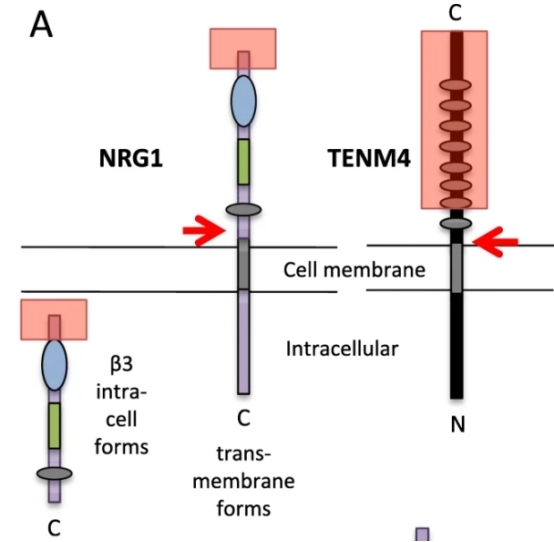 Fig. 1 Normal structures: a typical transmembrane NRG1 and a β3 isoform, and TENM4.1
Fig. 1 Normal structures: a typical transmembrane NRG1 and a β3 isoform, and TENM4.1
Key structural properties of NRG1:
- With functions of EGF sample structure domain
- There are multiple transmembrane subtypes and soluble subtypes
- Immunoglobulin - like domains mediate protein interactions
Functions of NRG1
The core function of the NRG1 gene is to serve as a key ligand for intercellular signal transduction, regulating various biological processes by activating the ERBB receptor.
| Function | Description |
| Neurodevelopmental regulation | Promoting neuronal migration, myelin formation and synaptic plasticity is crucial for the development of the central and peripheral nervous systems. |
| Cardiac development support | Guide the formation of endocardial pads and the differentiation of cardiomyocytes during cardiac embryonic development to ensure the establishment of normal cardiac structure and function. |
| Breast ductal formation | By mediating epithelial-mesenchymal interactions, it guides the morphogenesis of breast ducts and alveolar development. |
| Association of disease mechanisms | Abnormalities in its signaling pathways are closely related to the occurrence and development of schizophrenia, breast cancer and various heart diseases. |
| Cell fate determination | Regulate the survival, proliferation, differentiation or apoptosis and other fate decisions of cells in different microenvironments. |
NRG1 binds to ERBB receptors (mainly ERBB3/ERBB4) through its EGF-like domain, triggering receptor dimerization and tyrosine kinase activation, thereby activating multiple downstream signaling pathways (such as PI3K-AKT, RAS-MAPK). This pleiotropic signal transduction mode enables it to precisely regulate distinct physiological and pathological processes in different tissues.
Applications of NRG1 and NRG1 Antibody in Literature
1. Howarth, Karen D., et al. "NRG1 fusions in breast cancer." Breast Cancer Research 23.1 (2021): 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-020-01377-5
This study reveals that NRG1 gene rearrangement in breast cancer is highly complex. A novel triple fusion of PPP6R3-TENM4-NRG1 was discovered in the MDA-MB-175 cell line, and multiple NRG1 fusion types were identified in 571 cases of breast cancer. It is worth noting that partial rearrangement can lead to the inactivation rather than activation of NRG1 function, which has significant guiding significance for clinical treatment decisions.
2. Navarro-González, Carmen, Alba Huerga-Gómez, and Pietro Fazzari. "Nrg1 intracellular signaling is neuroprotective upon stroke." Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2019.1 (2019): 3930186. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3930186
This study reveals a new intracellular signaling function of neuroregulatory protein 1 (NRG1). Experiments have shown that activating the intracellular domain (ICD) of NRG1 can effectively protect neurons and significantly increase their survival rate in hypoxia and hypoglycemia (in vitro stroke models) and in vivo stroke models. This discovery suggests that targeting the intracellular signaling pathway of NRG1 may become a new strategy for treating stroke.
3. Berdiel-Acer, Mireia, et al. "Stromal NRG1 in luminal breast cancer defines pro-fibrotic and migratory cancer-associated fibroblasts." Oncogene 40.15 (2021): 2651-2666. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01719-3
This study found that the activation of HER3 in luminal breast cancer stems from NRG1 produced by cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) through paracrine means. Meanwhile, NRG1 itself can also directly act on CAF, inducing it to produce strong migration and pro-fibrotic phenotypes. Targeting the NRG1 signal or its key molecules (such as HAS2) may become a new therapeutic strategy.
4. Zhu, Jun-Ming, et al. "Increased NRG1-ErbB4 signaling in human symptomatic epilepsy." Scientific Reports 7.1 (2017): 141. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00207-7
This study reveals the new role of the NRG1-ErbB4 signaling pathway in symptomatic epilepsy. This pathway may act as an homeostatic regulatory mechanism by inhibiting the phosphorylation of GluN2B protein by Src kinase, thereby reducing epileptiform activity in the brain and exerting a protective effect.
5. Gunadi, et al. "NRG1 variant effects in patients with Hirschsprung disease." BMC pediatrics 18.1 (2018): 292. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1265-x
This study was the first to identify the rare variant p.V133L of the NRG1 gene in Southeast Asian patients with congenital megacolon (HSCR), and confirmed that the common variant rs7834206 is associated with the disease, revealing the significant role of NRG1 in the pathogenesis of HSCR.
Creative Biolabs: NRG1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality NRG1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom NRG1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our NRG1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Howarth, Karen D., et al. "NRG1 fusions in breast cancer." Breast Cancer Research 23.1 (2021): 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-020-01377-5
Anti-NRG1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-NSUN6 Recombinant Antibody (D-5) (CBMAB-N3674-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






