SDHA Antibodies
Background
The SDHA gene encodes the flavoprotein subunit of the succinate dehydrogenase complex, which is embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane as a core component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain (complex II). It catalyzes the oxidation reaction of succinic acid to fumaric acid, while transferring electrons to ubiquinone, playing a bridging role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Mutations in this gene can disrupt cellular energy metabolism, leading to genetic diseases such as Leigh syndrome and paraganglioma. In the 1980s, researchers gradually analyzed its structure through protein purification and gene cloning techniques. In 2010, crystallographic studies revealed the precise conformation of its [2Fe-2S] cluster and FAD cofactor. Continuous research on SDHA not only deepens the understanding of mitochondrial disease mechanisms but also promotes the progress of cross-disciplinary research in the fields of metabolic regulation and tumorigenesis.
Structure of SDHA
The succinate dehydrogenase subunit A encoded by the SDHA gene is a flavoprotein of approximately 72.8 kDa. The molecular weight of this protein may vary slightly due to differences in species-specific post-translational modifications and mitochondrial targeting sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine | Yeast |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 72.8 | 72.6 | 72.9 | 69.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing FAD covalent binding sites | High homology with humans | Catalytic core highly conservative | There exist unique mitochondrial signaling peptides |
This protein is composed of approximately 620 amino acids, and its tertiary structure forms a typical Rossmann fold for binding to FAD cofactors. The active center contains highly conserved cysteine residues that are covalently bonded to FAD molecules, which is the key to its catalytic oxidation of succinic acid. The C-terminal domain of the protein is responsible for electron transfer with the [Fe-S] cluster of subunit B, while the N-terminal participates in the formation of substrate channels, and its opening and closing state is regulated by adjacent charged amino acids.
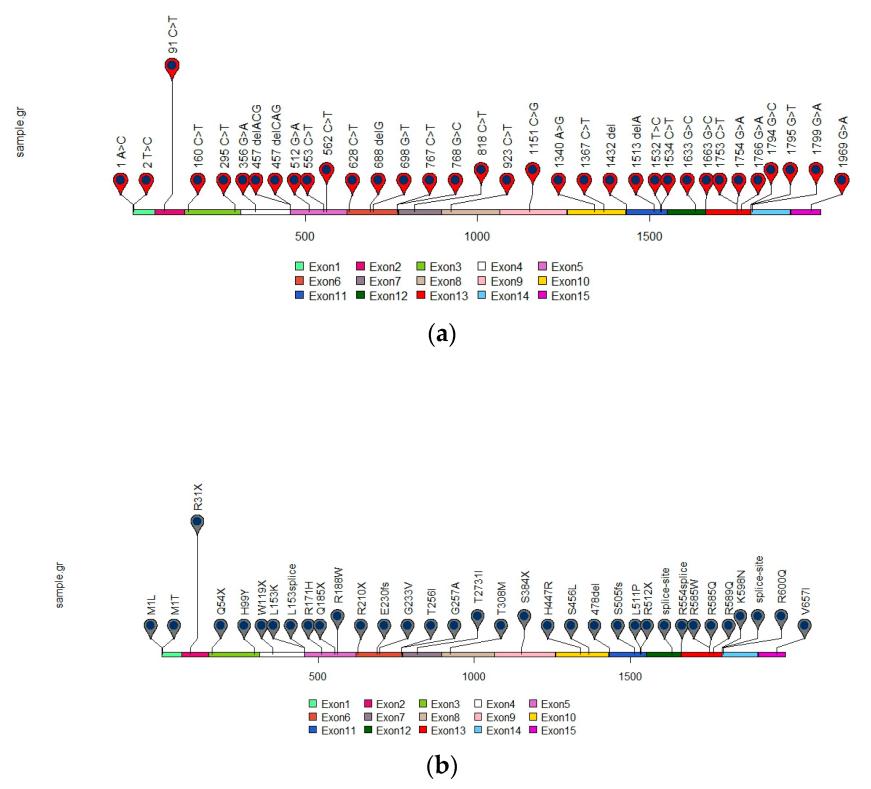 Fig. 1 Distribution of reported SDHA gene mutations in GIST.1
Fig. 1 Distribution of reported SDHA gene mutations in GIST.1
Key structural properties of SDHA:
- Typical Rossmann folded domains are used to bind FAD prosthetic groups
- Conserved cysteine residues form covalent bonds with FAD
- The [4Fe-4S] cluster and the flavin group form an electron transport chain
Functions of SDHA
The core function of the protein encoded by the SDHA gene is to catalyze the oxidation of succinic acid and serve as a key hub connecting the tricarboxylic acid cycle with the electron transport chain. In addition, it is also involved in cellular signal transduction and the regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism.
| Function | Description |
| Oxidation of succinic acid | In the tricarboxylic acid cycle, it catalyzes the conversion of succinic acid to fumaric acid, which is the only membrane-binding step in this cycle. |
| Electron transfer | As complex II, the electrons released during the oxidation reaction are transferred to the ubiquinone cell via FAD and [Fe-S] clusters. |
| Metabolic integration | It directly connects to the two core metabolic pathways of mitochondria - the tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, coordinating energy generation. |
| Regulation of hypoxia signals | The accumulation of succinic acid can inhibit prolyl hydroxylase and stabilize HIF-1α, thereby activating the hypoxia adaptation pathway of cells. |
| Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation | Under conditions such as reverse electron transport (RET), it can become an important source of superoxide anions in mitochondria. |
Unlike single-function oxygen carriers, the reaction kinetics catalyzed by SDHA follows the classical Michaelis equation, and its activity is precisely regulated by multiple factors such as substrate concentration, oxygen partial pressure, and mitochondrial membrane potential, reflecting its complexity as a core metabolic node.
Applications of SDHA and SDHA Antibody in Literature
1. Hanson, Helen, et al. "UK recommendations for SDHA germline genetic testing and surveillance in clinical practice." Journal of Medical Genetics 60.2 (2023): 107-111. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2021-108355
Studies have shown that the tumor penetrance rate of carriers of pathogenic germline variations of SDHA is low, but the existing monitoring protocols are relatively intensive. With the popularization of genetic testing, the number of this population has increased. To balance the benefits and burdens, the expert working group has formulated new recommendations for relevant clinical testing and management.
2. Schipani, Angela, et al. "SDHA germline mutations in SDH-deficient GISTs: a current update." Genes 14.3 (2023): 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030646
Studies have shown that in SDH-deficient GIST, SDHA gene mutations are the most common. Such patients usually undergo two genetic strikes and have a high rate of germline mutation. This article reviews the relevant data and emphasizes the importance of providing genetic counseling for SDHA variant carriers and their relatives.
3. Kaplan, Adam I., et al. "SDHA-related phaeochromocytoma and paraganglioma: review and clinical management." Endocrine-Related Cancer 31.10 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-24-0111
Studies have shown that SDHA is a susceptibility gene for PPGL, and its related tumors can occur in multiple parts of the body. About 25.5% of cases will have metastasis, and it is common many years later. Due to the rarity of family history, a thorough understanding of its clinical characteristics and risks is crucial for the scientific management of patients and their families.
4. Skefos, Catherine M., et al. "SDHA secondary findings in germline testing: counseling and surveillance considerations." Endocrine Oncology 4.1 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1530/EO-23-0043
With the popularization of genetic testing, the number of secondary variations of SDHA found in individuals without a relevant medical history is increasing in clinical practice. Given its complex visibility and inconsistent screening guidelines, this article suggests that clinicians should fully inform of the risks, make joint decisions, and carefully evaluate the monitoring plan to optimize individualized management.
5. Pantaleo, Maria A., et al. "SDHA germline variants in adult patients with SDHA-mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumor." Frontiers in oncology 11 (2022): 778461. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.778461
This study confirmed that patients with SDHA-deficient GIST generally have pathogenic mutations in the SDHA germline, and the age of onset can be relatively high. All patients carried germline variations and experienced a second blow. The disease process is relatively inert. It is recommended to conduct genetic testing and long-term monitoring for carriers and their relatives.
Creative Biolabs: SDHA Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SDHA antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SDHA Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SDHA antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Schipani, Angela, et al. "SDHA germline mutations in SDH-deficient GISTs: a current update." Genes 14.3 (2023): 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030646
Anti-SDHA antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








