SMARCA2 Antibodies
Background
SMARCA2 is a gene encoding the catalytic subunit of ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes and is widely expressed in various tissues of the human body. This gene participates in important biological processes such as cell differentiation, development and DNA damage repair by regulating chromatin structure and gene transcription. Studies have shown that SMARCA2 and SMARCA4 complement each other functionally. In various cancers, their mutations or abnormal expressions are closely related to tumorigenesis and development. Since its identification in the 1990s, this gene has become a key object in epigenetic regulation and tumor biology research. The study of its structural and functional mechanisms has continuously promoted the understanding of chromatin remodeling and disease-related signaling pathways.
Structure of SMARCA2
SMARCA2 is a gene that encodes the catalytic subunit of ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes, and the molecular weight of its encoded protein is approximately 180 kDa. This protein is highly conserved among species, and its core function depends on the synergistic effect of multiple key domains.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~180 | ~180 | ~180 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Highly conserved, with the core containing the ATPase domain, helicase domain and bromine domain | The sequence homology with human protein is extremely high, and the functional domain is completely identical | The core functional domain is also conservative, but there are sequence differences in non-critical areas |
The ATPase domain of this protein is the engine for its chromatin remodeling function, providing energy by hydrolyzing ATP. The helicase domain helps handle DNA-histone interactions, while the bromine domain specifically recognizes acetylated histone markers, targeting remodeling complexes to specific genomic regions. These domains work together to regulate the transcriptional activity of genes by sliding or replacing nucleosomes, playing a key role in development, cell differentiation and DNA damage repair.
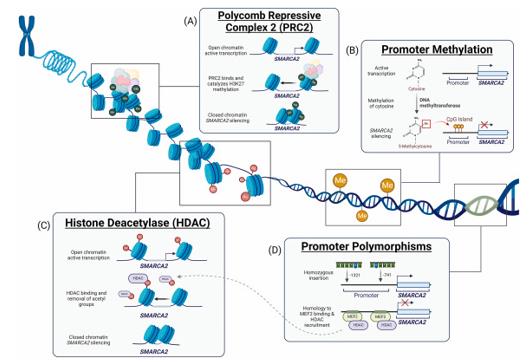 Fig. 1 Four epigenetic mechanisms linked to SMARCA2 silencing in cancer.1
Fig. 1 Four epigenetic mechanisms linked to SMARCA2 silencing in cancer.1
Key structural properties of SMARCA2:
- The conserved ATPase/helicase core domain provides the biochemical impetus for chromatin remodeling
- Unique bromine domain that specifically recognizes histone acetylation modification
- More protein interaction interface, mediated and other BAF complex assembly
Functions of SMARCA2
The BRM protein encoded by SMARCA2, as the core catalytic subunit of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, mainly functions to regulate chromatin structure and gene transcription by relying on ATP hydrolysis. However, this gene is also widely involved in a variety of key cellular physiological and pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Chromatin remodeling | By utilizing the energy of ATP hydrolysis, nucleosomes are slid or replaced, altering DNA accessibility and thereby enabling or disabling gene transcription. |
| Transcriptional regulation | As a transcriptional co-activator or co-inhibitor, it precisely regulates the expression of target genes by working in synergy with multiple transcription factors and histone modification enzymes. |
| Development and Differentiation | In embryonic development, cell lineage decision and the key role in the tissue specificity of differentiation, its dysfunction can cause birth defects. |
| Tumor suppression | In many types of cancer, SMARCA2 is functionally redundant with the homologous gene SMARCA4. When SMARCA4 is inactivated, SMARCA2 becomes a key "synthetic lethal" target for maintaining the normal state of cells and inhibiting tumor occurrence. |
| DNA damage repair | Fracture repair pathways, involved in double-stranded DNA damage by reshaping locus of chromatin structure, promote the repair proteins to recruit. |
The function of SMARCA2 is highly dependent on the subtype of the BAF complex it belongs to. Under different tissue or cell states, there are significant differences in the specific target genes it regulates and its biological effects.
Applications of SMARCA2 and SMARCA2 Antibody in Literature
- Wang, Xinyue, et al. "A novel rabbit anti-myoglobin monoclonal antibody's potential application in rhabdomyolysis associated acute kidney injury." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.9 (2023): 7822. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34562-5
The article indicates that SmarCa4-inactivated tumors depend on SMARCA2, but its high homology makes selective inhibition difficult. The A947 PROTAC developed in this study can selectively degrade SMARCA2, demonstrating significant in vitro and in vivo activity in the SMARCA4 mutation model, and no expected off-target degradation was found, providing a new strategy for the treatment of related tumors.
- Kofink, Christiane, et al. "A selective and orally bioavailable VHL-recruiting PROTAC achieves SMARCA2 degradation in vivo." Nature Communications 13.1 (2022): 5969. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33430-6
This study developed a novel oral bioavailable PROTAC molecule, ACBI2, which can selectively recruit VHL E3 ligase to degrade SMARCA2 protein. The synthetic lethal efficacy was verified in a SmarCA4-deficient tumor model, providing a new strategy for expanding targeted protein degradation therapies.
- Field, Natisha R., et al. "SMARCA4 and SMARCA2 co-deficiency: An uncommon molecular signature defining a subset of rare, aggressive and undifferentiated malignancies associated with defective chromatin remodeling." Cancer letters 605 (2024): 217282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217282
This study indicates that the double deletion of SMARCA4 and SMARCA2 is a characteristic feature of some rare undifferentiated tumors. This article systematically reviews the clinical and molecular commonalities of this type of cancer, the mechanisms of functional loss, and the resulting cellular dysfunction, and explores the current potential selective treatment strategies.
- Zhang, Wei, et al. "SETMAR Facilitates the Differentiation of Thyroid Cancer by Regulating SMARCA2‐Mediated Chromatin Remodeling." Advanced Science 11.32 (2024): 2401712. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202401712
This study reveals that SETMAR promotes its transcription by methylating the SMARCA2 promoter, thereby enhancing the expression of thyroid differentiation transcription factors and influencing cancer differentiation and treatment sensitivity. METTL3 can regulate this pathway through m6A modification, providing a new target for promoting the redifferentiation of thyroid cancer.
- Urer, Halide Nur, Nurcan Unver, and Neslihan Fener. "Analysis of SMARCA4 and SMARCA2 loss in lung sarcomatoid carcinomas." Turkish Journal of Pathology 39.2 (2023): 147. https://doi.org/10.5146/tjpath.2022.01590
This study found through immunohistochemical analysis that the absence of SMARCA4 (25.8%) and SMARCA2 (44.8%) expression is common in lung sarcomatoid carcinomas, among which the absence rate is the highest in pleomorphic carcinomas. This absence may be related to the heterogeneity of tumor morphology and is independent of conventional pathological parameters.
Creative Biolabs: SMARCA2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SMARCA2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SMARCA2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SMARCA2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Field, Natisha R., et al. "SMARCA4 and SMARCA2 co-deficiency: An uncommon molecular signature defining a subset of rare, aggressive and undifferentiated malignancies associated with defective chromatin remodeling." Cancer letters 605 (2024): 217282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217282
Anti-SMARCA2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1B1 Antibody (V2-2449) (CBMAB-1001CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






