SNRK Antibodies
Background
The SNRK gene encodes a serine/threonine protein kinase, which is mainly distributed in metabolically active tissues of mammals such as fat, muscle and the brain. This gene promotes mitochondrial biosynthesis by activating the AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway and participates in energy balance regulation by regulating insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism homeostasis. Its most notable feature lies in its high sensitivity to energy stress - when cells are in a state of glucose deprivation or energy depletion, SNRK can be activated through autophosphorylation and guide cells to transition from anabolism to catabolism. In 2014, researchers discovered through gene knockout models that the deletion of SNRK can cause abnormal hypertrophy of white fat, insulin resistance and systemic energy metabolism disorders, which provides a new molecular explanation for the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes. As a core regulatory node of metabolic homeostasis, SNRK not only reveals the deep connection between energy perception and metabolic reprogramming, but also opens up a new perspective for the targeted treatment of metabolic syndrome.
Structure of SNRK
SNRK is a serine/threonine protein kinase, and its molecular weight varies significantly among different species, mainly due to its unique alternative splicing mode and domain composition.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Zebrafish | African clawed toad |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~115 | ~112 | ~114 | ~98 | ~102 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains the complete N-terminal kinase domain and C-terminal extension | There are three amino acid deficiencies in the C-terminal regulatory region | Highly homologous to humans, with only a few conservative substitutions | Lacking the mammalian C-terminal self-inhibition sequence | Contains a unique hydrophobic insert |
This protein is composed of approximately 1,000 amino acids, with a highly conserved N-terminal kinase domain at its core, which is connected to the C-terminal regulatory module via a flexible hinge. This C-terminal region contains multiple phosphorylation sites and protein-protein interaction motifs, which can respond to cellular energy states (such as the AMP/ATP ratio) and relieve self-inhibition of kinase activity through conformational changes. Its unique "dual-lock" activation mechanism - which requires both phosphorylation of the activation loop and allosteric regulation of the C-terminal inhibitory domain - makes it a core sensor for cellular energy homeostasis.
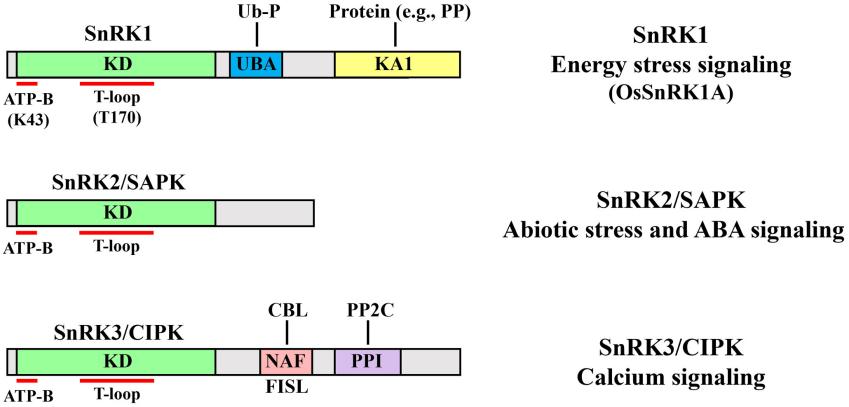 Fig. 1 Structural domains and major functions of the three SnRK subfamilies.1
Fig. 1 Structural domains and major functions of the three SnRK subfamilies.1
Key structural properties of SNRK:
- Modular kinase domains and unique C-terminal extension regions
- Autonomous inhibition rings and allosteric regulatory pockets
- Highly conserved ATP-binding motifs and substrate recognition channels
Functions of SNRK
The core function of SNRK is to serve as an integrated regulatory hub for cellular energy metabolism. Its main physiological roles are as follows:
| Function | Description |
| Energy steady-state regulation | As an upstream regulatory factor of AMPK, it activates catabolic pathways and inhibits anabolism when energy is scarce by sensing changes in the AMP/ATP ratio within cells. |
| Maintenance of insulin sensitivity | Specific knockout of SNRK in adipose tissue can cause severe systemic insulin resistance, which enhances insulin signaling by phosphorylating the PI3K regulatory subunit. |
| Promotion of mitochondrial biosynthesis | Direct phosphorylation and activation of PGC-1α induce mitochondrial proliferation and functional remodeling. This mechanism is particularly crucial in brown adipose thermogenesis and myocardial energy adaptation. |
| Autophagic flow regulation | Through the phosphorylation modification of the ULK1 complex, the autophagy process is precisely initiated under nutrient deprivation conditions, and damaged organelles are cleared to maintain energy supply. |
| Adipocyte differentiation is balanced | Through the phase transition mechanism, biomolecular condensates are formed to dynamically regulate the transcriptional activity of PPARγ, thereby inhibiting excessive white fat hypertrophy and ectopic lipid deposition. |
Unlike the acute energy stress response of AMPK, the activation kinetics of SNRK is slower and more persistent. It achieves "strategic" regulation of the long-term energy balance of the body by constructing a multi-component signaling network including transcriptional co-activators, metabolic enzymes and organelle membrane proteins. This functional division of labor at the energy sensing and metabolic execution levels makes it a core pathological node for metabolic syndromes such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Applications of SNRK and SNRK Antibody in Literature
1. Son, Seungmin, and Sang Ryeol Park. "The rice SnRK family: biological roles and cell signaling modules." Frontiers in Plant Science 14 (2023): 1285485. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1285485
The article indicates that SnRK protein kinase is a conserved regulatory factor in plants. It participates in multiple signal transduction processes through phosphorylation modification, regulating the growth, development and stress response of rice, which is of great significance for improving the stress resistance of crops.
2. Wang, Zhi-Yan, Xiao-Xiao Liu, and Yun-Fei Deng. "Negative feedback of SNRK to circ-SNRK regulates cardiac function post-myocardial infarction." Cell Death & Differentiation 29.4 (2022): 709-721. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00885-x
Studies have found that the circular RNA circ-SNRK derived from the SNRK gene enhances SNRK expression by adsorbing miR-33, thereby improving the energy metabolism of myocardial cells and protecting ischemic cardiac function. The negative feedback mechanism in this pathway makes it a potential new target for heart disease treatment.
3. Thirugnanam, Karthikeyan, and Ramani Ramchandran. "SNRK: a metabolic regulator with multifaceted role in development and disease." Vessel plus 4 (2020): 26. http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2020.18
The article indicates that SNRK is a serine/threonine kinase that can regulate the metabolic homeostasis of the heart and adipose tissue and inhibit inflammation, demonstrating potential therapeutic value in metabolism-related diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and obesity.
4. Meng, Fanhang, et al. "Inhibition of Circ-Snrk ameliorates apoptosis and inflammation in acute kidney injury by regulating the MAPK pathway." Renal Failure 44.1 (2022): 672-681. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2022.2032746
Studies have found that the circular RNA circ-Snrk is upregulated in acute kidney injury. In renal tubular epithelial cells, knockdown of circ-Snrk can reduce apoptosis and the release of inflammatory factors by inhibiting the activation of MAPK signaling pathways (such as p-JNK and p-38), indicating that it plays an important role in the process of AKI.
5. Wang, Guoming, et al. "Comprehensive genomic analysis of SnRK in Rosaceae and expression analysis of RoSnRK2 in response to Abiotic Stress in Rubus occidentalis." Plants 12.9 (2023): 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12091784
In this study, 209 SnRK genes were identified in Rosaceae plants, systematically revealing their evolutionary history and expression patterns in black raspberry tissues. Research has confirmed that five RoSnRK2 genes are located in the cytoplasm and nucleus and are involved in abiotic stress responses, providing a new basis for analyzing their molecular mechanisms.
Creative Biolabs: SNRK Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SNRK antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SNRK Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SNRK antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Son, Seungmin, and Sang Ryeol Park. "The rice SnRK family: biological roles and cell signaling modules." Frontiers in Plant Science 14 (2023): 1285485. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1285485
Anti-SNRK antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CECR2 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2465) (CBMAB-C3533WJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






