SYCN Antibodies
Background
Serine protease inhibitor B (SerpinB1) encoded by the SYCN gene is an intracellular protease inhibitor mainly expressed in various tissues of mammals. This protein protects cells from excessive proteolytic damage by specifically inhibiting neutrophil serine proteases, thereby maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating inflammatory responses. Studies have shown that the SYCN gene plays a crucial role in immune regulation and apoptosis, and its functional abnormalities are closely related to the occurrence of certain immune deficiencies and inflammatory diseases. This gene was first identified in human genome research in the 1990s. The protein structure it encodes belongs to the serine protease inhibitor superfamily and has a typical serpin folding conformation. In-depth research on SYCN not only reveals its regulatory mechanism in innate immunity, but also provides an important model for understanding the role of protease-antiprotease balance in physiological and pathological processes, promoting the development of treatment strategies for related diseases.
Structure of SYCN
Serine protease inhibitor B1 (SerpinB1) encoded by the SYCN gene is an intracellular protease inhibitor with a molecular weight of approximately 42.7 kDa. There are slight differences in this molecular weight among different mammals, mainly due to the amino acid sequence variations in the reaction center loop region.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 42.7 | 42.5 | 42.6 | 42.8 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Typical serpin domain | The reaction center ring have 3 amino acid replacement | Highly homologous to humans | There is a conservative variation in the C-terminal domain |
This protein is composed of 379 amino acids and presents a typical serine protease inhibitor (serpin) folding conformation. Its three-dimensional structure core is composed of 3 β sheets and 8-9 α helical encircling layers, forming a highly conserved reaction center ring. This cyclic segment, as a protease bait substrate, undergoes conformational rearrangement after binding to the target protease and irreversibly inhibits protease activity through the "spring mechanism". This molecular mechanism is crucial for maintaining the intracellular protease-antiprotease balance, and its functional defect is closely related to neutrophil-mediated tissue damage.
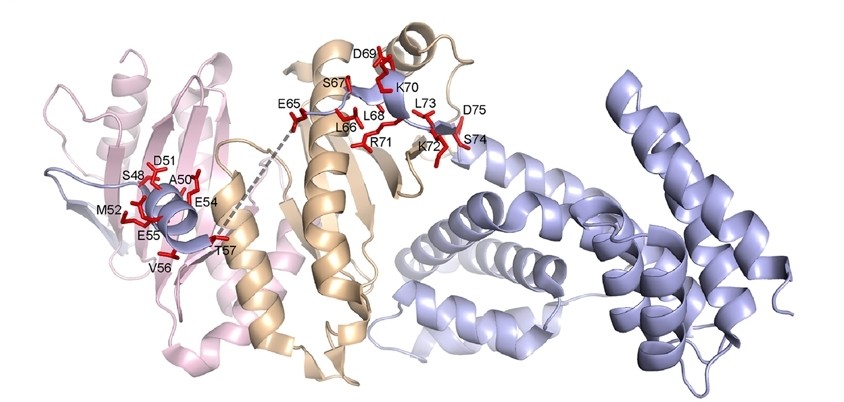 Fig. 1 Ribbon model of the ternary complex of YopN and the SycN/YscB chaperone.1
Fig. 1 Ribbon model of the ternary complex of YopN and the SycN/YscB chaperone.1
Key structural properties of SYCN:
- Typical folded conformation of serpin
- Highly conservative reaction center ring area as protease recognition and binding sites
- Variable hinge region mediated conformation rearrangement mechanism
Functions of SYCN
The core function of the SYCN gene-encoded protein is to regulate serine protease activity to maintain cellular homeostasis. This protein participates in a variety of physiological and pathological processes through its unique molecular mechanism.
| Function | Description |
| Protease inhibition | Specifically inhibit serine proteases such as neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G to prevent excessive proteolytic damage. |
| Inflammatory regulation | Regulate protease activity at the infection site to balance the intensity and duration of the inflammatory response. |
| Cell protection | Protect important intracellular proteins from protease degradation and maintain the structural integrity and function of cells. |
| Apoptosis regulation | The programmed cell death process is affected by the caspase interaction pathway. |
| Immune defense | In the innate immune response, restrict protease-mediated tissue damage and promote tissue repair. |
This protein forms a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with the target protease, and its inhibitory efficiency is not affected by the substrate concentration. This characteristic enables it to rapidly establish an effective protease inhibition barrier in acute inflammatory responses. Its abnormal function is closely related to the occurrence and development of diseases such as early-onset emphysema and neutrophil dysfunction.
Applications of SYCN and SYCN Antibody in Literature
1. Makawita, Shalini, et al. "Validation of four candidate pancreatic cancer serological biomarkers that improve the performance of CA19. 9." BMC cancer 13.1 (2013): 404. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-404
This study verified novel serum markers such as SYCN and REG1B. Research has found that the combination of SYCN and REG1B with CA19-9 can significantly improve the diagnostic accuracy of pancreatic cancer, especially for early-stage patients. Its diagnostic performance is superior to that of single CA19-9 detection and has important clinical transformation value.
2. Joseph, Sabrina S., and Gregory V. Plano. "The SycN/YscB chaperone-binding domain of YopN is required for the calcium-dependent regulation of Yop secretion by Yersinia pestis." Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 3 (2013): 1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2013.00001
The article indicates that in Yersinia pestis, the SycN/YscB molecular chaperone and the CBD region of the YopN protein it binds to are crucial for regulating the type III secretion system. Research has found that this CBD area has novel regulatory functions independent of its mating partner function, revealing its previously unknown secretory regulatory mechanism.
3. Feng, Xikang, et al. "Scyn: single cell cnv profiling method using dynamic programming." BMC genomics 22.Suppl 5 (2021): 651. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07941-3
This study proposes SCYN, a single-cell DNA copy number variation (CNV) segmentation method based on dynamic programming. This tool has demonstrated high precision and robustness on multiple datasets, effectively identifying rare tumor cells. Its computational efficiency is approximately 150 times higher than that of existing methods, which is helpful for analyzing intratuminal heterogeneity.
4. Zhou, Yang-Yang, et al. "Integrated transcriptomic analysis reveals hub genes involved in diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer." Molecular medicine 25.1 (2019): 47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-019-0113-2
This study identified a 19 gene module containing SYCN through integrated transcriptome analysis, which can serve as a specific diagnostic marker for pancreatic cancer. Based on this, the team further developed a simplified and highly feasible four-gene diagnostic model. This discovery provides a new perspective and potential tools for the clinical diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
5. Yau, Belinda, et al. "A fluorescent timer reporter enables sorting of insulin secretory granules by age." Journal of Biological Chemistry 295.27 (2020): 8901-8911. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.012432
In this study, the novel fluorescent timing protein Syncollin-dsRedE5TIMER was utilized to achieve precise "age" labeling of insulin secretion granules for the first time. Research has found that β cells regulate the age composition of the granulosa population in different environments such as hyperglycemia, and younger granulosa are more likely to be secreted preferentially under glucose stimulation, which provides a new perspective for understanding the mechanism of insulin secretion.
Creative Biolabs: SYCN Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SYCN antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SYCN Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SYCN antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Joseph, Sabrina S., and Gregory V. Plano. "The SycN/YscB chaperone-binding domain of YopN is required for the calcium-dependent regulation of Yop secretion by Yersinia pestis." Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 3 (2013): 1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2013.00001
Anti-SYCN antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARIH1 Recombinant Antibody (C-7) (CBMAB-A3563-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








