TLR4 Antibodies
Background
TLR4 is an important transmembrane pattern recognition receptor, mainly expressed on the surface of immune cells, capable of recognizing pathogen-related molecular patterns (such as lipopolysaccharides) and activating innate immune responses. The protein encoded by this gene induces the release of inflammatory factors by triggering signaling pathways such as NF-κB, playing a core role in host defense and the regulation of inflammatory responses. In 1997, the team led by Bruce Beutler first discovered the recognition function of TLR4 for LPS. This breakthrough discovery won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2011. The unique structural features of TLR4 - the extracellular domain rich in leucine repeat sequences and the intracellular segment of the TIR domain - make it a classic model for studying the molecular mechanisms of innate immunity. Its functional abnormalities are closely related to various pathological processes such as sepsis, autoimmune diseases, and metabolic diseases.
Structure of TLR4
TLR4 is a transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 95-100 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species, mainly due to glycosylation modifications and interspecific variations in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine | Pig |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 95-100 | 94-99 | 96-101 | 97-102 | 95-100 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Rich in LRR domains and TIR conserved | The number of LRS is slightly smaller | Intracellular period of similar height | The glycation sites are different | The transmembrane region is highly conserved |
TLR4 is composed of approximately 839 amino acids, and its structure consists of three key parts: the leucine-rich repeat sequence (LRR) in the extracellular region is responsible for recognizing lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the transmembrane region is anchored to the cell membrane, and the TIR domain (Toll/IL-1 receptor homologous region) in the intracellular segment mediates downstream signal transduction. Its function depends on the synergistic effect with the helper proteins MD-2 and CD14 to form the LPS receptor complex. The activation of TLR4 triggers MyD88-dependent or non-dependent signaling pathways, ultimately activating NF-κB and interferon regulatory factor (IRF), and inducing the release of inflammatory factors. The study of the structure-function relationship of this receptor provides an important target for the development of immunomodulatory drugs.
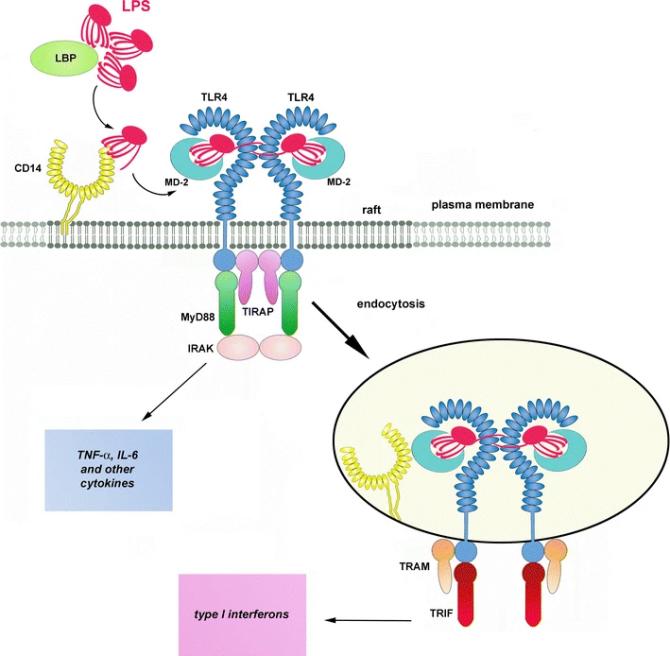 Fig. 1 Activation of TLR4 by LPS.1
Fig. 1 Activation of TLR4 by LPS.1
Key structural properties of TLR4:
- Extracellular domains rich in leucine repeat sequences (LRR)
- Transmembrane helical structure
- TIR (Toll/IL-1 receptor homology) domain
- Conservative CXXC motif
- Glycosylation modification site
Functions of TLR4
The core function of the TLR4 gene is to recognize pathogen-related molecular patterns and activate innate immune responses, while also participating in multiple immune regulatory processes.
| Function | Description |
| Pathogen identification | Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) specifically recognizes Gram-negative bacteria and triggers inflammatory signaling pathways. |
| Immune activation | NF-κB and IRF are activated through the MyD88-dependent/non-dependent pathway, inducing the release of pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-6. |
| Inflammatory regulation | Balance pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses to prevent excessive immune damage. |
| Participation in tissue repair | Activate fibroblasts and stem cells to promote tissue regeneration after injury. |
| Metabolic regulation | Associated with insulin resistance and obesity, and effecting the metabolism of fat and sugar steady state. |
| Regulation of the tumor microenvironment | Regulate immune escape or anti-tumor response in tumor-associated macrophages. |
The signal activation of TLR4 shows a threshold effect - low concentrations of LPS induce protective immunity, while high concentrations lead to excessive inflammatory responses such as sepsis. Its functional diversity stems from the combined effects with different helper proteins (such as MD-2, CD14), as well as the regulation of cell type-specific downstream pathways. This receptor has become an important target for the treatment of infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Applications of TLR4 and TLR4 Antibody in Literature
1. Kim, Hyo, et al. "Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4): new insight immune and aging." Immunity & Ageing 20.1 (2023): 67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12979-023-00383-3
The article indicates that TLR4, as a key receptor for innate immunity, mediates inflammatory responses through the MyD88 and TRIF pathways and participates in the occurrence and development of aging-related diseases. Its excessive activation leads to chronic inflammation, which is closely related to Alzheimer's disease, osteoarthritis and other conditions, and is a potential therapeutic target.
2. Płóciennikowska, Agnieszka, et al. "Co-operation of TLR4 and raft proteins in LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling." Cellular and molecular life sciences 72.3 (2015): 557-581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1762-5
The article indicates that TLR4 recognizes LPS through lipid raft microregions (such as CD14/CD36) and activates the MyD88/TRIF pathway, triggering an inflammatory response. This signal transduction relies on the coordinated regulation of membrane raft proteins (such as Lyn, Hsp70, etc.), and abnormal activation can lead to pathological processes such as sepsis.
3. Halajian, Emily A., et al. "Activation of TLR4 by viral glycoproteins: A double-edged sword?." Frontiers in Microbiology 13 (2022): 1007081. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1007081
The article indicates that TLR4 can be activated by viral glycoproteins such as the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, triggering excessive inflammatory responses and cytokine storms. This mechanism is similar to bacterial LPS and plays a key pathogenic role in viral infections such as COVID-19 and dengue fever.
4. Gabr, Mai Mahmoud, et al. "Interaction of opioids with TLR4—mechanisms and ramifications." Cancers 13.21 (2021): 5274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215274
The article indicates that TLR4 is not only a potential target for opioid drugs but can also be non-stereoselectively regulated by them - it can weakly activate and inhibit LPS-induced inflammatory responses. This discovery provides a new perspective for studying the role of opioid drugs in cancer.
5. Heine, Holger, and Alla Zamyatina. "Therapeutic targeting of TLR4 for inflammation, infection, and cancer: a perspective for disaccharide lipid A mimetics." Pharmaceuticals 16.1 (2022): 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010023
The article indicates that TLR4 is a key receptor for innate immunity, which can not only recognize LPS to trigger inflammatory defense but also may cause overreactions such as sepsis. Its dual effects make it a target for the development of anti-inflammatory drugs and vaccine adjuvants. Currently, there are studies on highly efficient carbohydrate-based agonists/antagonists.
Creative Biolabs: TLR4 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality TLR4 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom TLR4 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our TLR4 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Płóciennikowska, Agnieszka, et al. "Co-operation of TLR4 and raft proteins in LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling." Cellular and molecular life sciences 72.3 (2015): 557-581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1762-5
Anti-TLR4 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADV Recombinant Antibody (V2-503423) (CBMAB-V208-1364-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARIH1 Recombinant Antibody (C-7) (CBMAB-A3563-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BZLF1 Recombinant Antibody (BZ.1) (CBMAB-AP705LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








