TRAIP Antibodies
Background
The TRAIP gene encodes an E3 ubiquitin ligase, a protein that plays a core role in DNA damage response and cell cycle regulation. It participates in regulating the stability of DNA replication forks and replication stress responses through ubiquitination modification, thereby maintaining genomic integrity. Mutations in this gene are associated with various genetic diseases and cancer susceptibility, and have been particularly deeply studied in microcephaly and melanoma. Since its function was simultaneously identified by multiple research teams in 2015, TRAIP has rapidly become an important molecule in the field of cell stress research due to its key position in connecting DNA repair and cell cycle checkpoints. Its multi-domain characteristics and complex protein-protein interaction network provide a new perspective for understanding the molecular mechanisms by which eukaryotic cells respond to replication stress.
Structure of TRAIP
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the TRAIP gene is approximately 46 kDa, and its precise size varies slightly among different species due to sequence differences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Fruit fly |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 46.2 | 45.8 | 44.5 | 42.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Domain and coiled coil area contains RING structure | RING structure domain highly conservative | The core functional areas are similar | Only retain the most core RING domain |
This protein is composed of 416 amino acids and forms a typical E3 ubiquitin ligase spatial conformation. The N-terminal in its primary structure is a typical RING domain, which is the key active center for catalyzing ubiquitin transfer. The C-terminal contains a coiled-coil protein-protein interaction module, which is responsible for mediating specific protein-protein interactions. The three-dimensional structure of the entire molecule is constructed around the RING domain stably formed by zinc ions, in which multiple conserved cysteine and histidine residues are responsible for the coordinated binding of zinc ions. A hydrophobic groove located on the surface of the RING domain provides a specific binding interface for the ubiquitin-binding enzyme (E2), while the coiled-coil region acts like a molecular scaffold, precisely recruiting specific substrates such as DNA replication stress factors downstream, thereby achieving efficient ubiquitination modification.
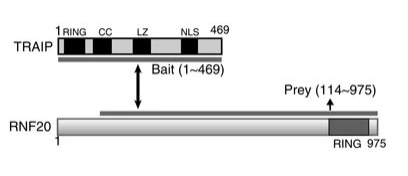 Fig. 1 Schematic structure of TRAIP and RNF20.1
Fig. 1 Schematic structure of TRAIP and RNF20.1
Key structural properties of TRAIP:
- The typical RING domain is responsible for E2 ubiquitin-binding enzyme recruitment
- Central coiled-coil models mediate specific protein interactions
- C-terminal nuclear localization signals regulate nuclear localization and function
Functions of TRAIP
The core function of the TRAIP gene is to maintain genomic stability and regulate the progress of the cell cycle. In addition, it is also widely involved in key cellular activities such as DNA replication stress response and telomere maintenance.
| Function | Description |
| DNA damage response | As an E3 ubiquitin ligase, it initiates the repair signaling pathway for DNA replication fork damage through ubiquitination modification. |
| Cell cycle regulation | Checkpoints in the S phase and G2/M phase function to prevent cells with DNA damage from entering the division phase. |
| Copy fork stability | Recruited to the stalled replication forks during DNA replication stress to prevent fork collapse and promote repair and restart. |
| Telomere maintenance | Participate in addressing replicative telomere stress to ensure the complete replication and stability of the telomere region. |
| Tumor suppression | Its functional inactivation can lead to genomic instability, increase cancer susceptibility, and play an important role in tumor suppression. |
TRAIP catalyzes the formation of specific ubiquitin chain signals through its RING domain. This signal cascade is completely different from the synergistic effect of hemoglobin, demonstrating its unique mechanism as a specific molecular switch to precisely control the activation of repair pathways and cell fate determination in the DNA damage response network.
Applications of TRAIP and TRAIP Antibody in Literature
1. Scaramuzza, Shaun, et al. "TRAIP resolves DNA replication-transcription conflicts during the S-phase of unperturbed cells." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 5071. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40695-y
In this study, using the induced degradation system, it was found that the rapid loss of TRAIP protein in the S phase would lead to the arrest of cell proliferation and the entry into senescence. The mechanism lies in that TRAIP maintains genomic stability in the S phase by preventing replication and transcription conflicts and protecting the transcription initiation site from DNA damage.
2. Zheng, Yan, et al. "Silencing TRAIP suppresses cell proliferation and migration/invasion of triple negative breast cancer via RB-E2F signaling and EMT." Cancer Gene Therapy 30.1 (2023): 74-84. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-022-00517-7
This study confirmed that TRAIP is highly expressed in triple-negative breast cancer and promotes the proliferation and metastasis of cancer cells through the RB-E2F signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. microRNA miR-590-3p can target and inhibit TRAIP, indicating that TRAIP is a potential carcinogenic factor and therapeutic target for this disease.
3. Kochenova, Olga V., et al. "USP37 prevents premature disassembly of stressed replisomes by TRAIP." Nature Communications 16.1 (2025): 5333. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-60139-z
This study reveals that the deubiquitinating enzyme USP37 protects genomic stability by binding to CDC45 and inhibiting the premature ubiquitination and dissociation of CMG helicase by E3 ligase TRAIP under replication pressure. Abnormal activation of TRAIP can lead to the inappropriate disintegration of replicas.
4. Piloto, Ana Margarida, et al. "Plastic antibodies tailored on quantum dots for an optical detection of myoglobin down to the femtomolar range." Scientific reports 8.1 (2018): 4944. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10463
This study reveals that E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAIP, as a novel binding protein of RAP80, targets DNA damage sites through its C-terminal interaction with RNF20-RNF40, thereby guiding the aggregation of the RAP80-BRCA1 complex, which is crucial for activating homologous recombination repair.
5. Sonneville, Remi, et al. "TRAIP drives replisome disassembly and mitotic DNA repair synthesis at sites of incomplete DNA replication." Elife 8 (2019): e48686. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48686
This study reveals that TRAIP ubiquitin ligase is the key for cells to shift from conventional replication to mitotic DNA repair (MiDAS). It provides pathways for repair factors by depolymerizing stagnant replicas, thereby preventing chromosomal misseparation and ensuring genomic stability.
Creative Biolabs: TRAIP Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality TRAIP antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom TRAIP Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our TRAIP antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Soo Lee, Nam, et al. "TRAIP/RNF206 is required for recruitment of RAP80 to sites of DNA damage." Nature communications 7.1 (2016): 10463. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10463
Anti-TRAIP antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DHFR Recombinant Antibody (D0821) (CBMAB-D0821-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AOC3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0014) (CBMAB-0014-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






