AK2 Antibodies
Background
AK2, as a key metabolic enzyme, is mainly distributed in the mitochondrial membrane space and maintains cellular energy homeostasis by catalyzing the mutual conversion of adenine nucleotides. This enzyme not only ensures the stability of intracellular energy supply and signal transduction by regulating the dynamic balance of ATP/ADP/AMP, but also directly participates in the mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis regulatory pathway. In human cells, the loss of function of AK2 has been confirmed to lead to hereditary deafness and immunodeficiency syndrome, highlighting its core role in energy metabolism and cell fate determination. Since its biochemical characteristics were initially clarified in the 1970s, this enzyme has become an important model for studying the association between nucleotide metabolism and human diseases. Its unique spatial conformation composed of four domains provides a key theoretical basis for revealing the enzyme's kinetic mechanism and developing drug targets.
Structure of AK2
AK2 (adenylate kinase 2) is an intracellular enzyme with a molecular weight of approximately 25 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species, mainly due to the specific changes in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 25.4 | 25.2 | 25.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Highly conserved structure of catalytic domain | The sequence homology is extremely high and the functions are consistent | The key active sites are exactly the same as those in humans |
This protein is composed of approximately 220 amino acids, forming a characteristic adenylate kinase folding structure. The core of its three-dimensional structure is a central parallel $\beta$ -lamellar layer, surrounded by multiple $\alpha$ -helices, which together form nucleotide binding pockets. The active center contains two key substrate binding domains: the LID domain achieves ATP binding and release through conformational changes, while the CORE domain is responsible for recognizing AMP. The coordinated opening and closing of these two domains during the catalytic process, like "molecular tweezers", efficiently drive the reversible transfer of phosphate groups between ATP and ADP, thereby maintaining cellular energy homeostasis.
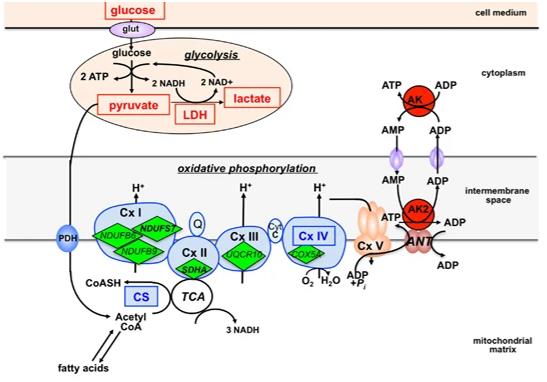 Fig. 1 AK2: A Metabolic Hub Linking Glycolysis and Oxidative Phosphorylation.1
Fig. 1 AK2: A Metabolic Hub Linking Glycolysis and Oxidative Phosphorylation.1
Key structural properties of AK2:
- Typical sandwich folding structure of adenylate kinase
- The central parallel $\beta$ -layer constitutes the catalytic core
- LID and CORE domains drive substrate binding and release through conformational changes
- The highly conserved nucleotide binding motif (P-loop) is responsible for anchoring the phosphate group
Functions of AK2
The main function of AK2 is to catalyze the energy transfer between adenosine monophosphate within mitochondria to maintain cellular energy homeostasis. In addition, this enzyme is also involved in key physiological and pathological processes such as apoptosis signal transduction.
| Function | Description |
| Maintenance of energy steady state | Catalyze the reaction between ATP and AMP to generate two molecules of ADP, rapidly balancing the adenylate pool and ensuring a continuous energy supply within the cell. |
| Metabolic signal transduction | By sensing changes in the AMP/ATP ratio, it indirectly affects energy sensing pathways such as AMPK and regulates the metabolic state of cells. |
| Regulation of apoptosis | In the mitochondrial membrane space, changes in its activity can affect the opening of membrane permeability transition pores, thereby participating in the initiation of intrinsic apoptotic pathways. |
| Nucleotide precursor supply | Maintaining ADP levels is crucial for mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and also provides the necessary precursor molecules for nucleic acid synthesis. |
| Adaptation to hypoxia stress | Under energy stress conditions, it supports the short-term survival of cells in a hypoxic environment by accelerating the ATP regeneration reaction. |
The reaction catalyzed by AK2 is in a dynamic equilibrium, and its reaction direction and rate are strictly dependent on the local substrate concentration. This enables it to sensitively respond to the instantaneous fluctuations in the cell's energy state and play a core regulatory role.
Applications of AK2 and AK2 Antibody in Literature
1. Kim, Hyunjoo, et al. "AK2 is an AMP-sensing negative regulator of BRAF in tumorigenesis." Cell death & disease 13.5 (2022): 469. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04921-7
The article indicates that adenylate kinase 2 (AK2) plays a tumor suppressor role in liver cancer by sensing the intracellular AMP level, binding to BRAF and inhibiting its activity and the downstream ERK signaling pathway, thereby correlating the metabolic state with tumor proliferation.
2. Lapacz, Kim J., et al. "DPP8/9 processing of human AK2 unmasks an IAP binding motif." EMBO reports (2025): 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44319-025-00455-z
The article indicates that after the mitochondrial protein AK2 enters the cytoplasm, its stability is antagonistically regulated by DPP8/9 digestion and NatA acetylation. Enzymatic digestion exposes the degradation signal and it is recognized by IAPs, leading to its ubiquitination and degradation. Acetylation prevents this process, thereby stabilizing AK2. This mechanism may be universal.
3. Cai, Fangfang, et al. "AK2 promotes the migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by activating TGF-β/smad pathway in vitro and in vivo." Frontiers in pharmacology 12 (2021): 714365. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.714365
Research has found that adenylate kinase 2 (AK2) can promote the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma. High expression of AK2 is associated with poor prognosis in patients. It induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by activating the Smad pathway, thereby enhancing the invasion and metastasis ability of cancer cells, suggesting that it can serve as a potential therapeutic target.
4. Six, E., et al. "AK2 deficiency compromises the mitochondrial energy metabolism required for differentiation of human neutrophil and lymphoid lineages." Cell death & disease 6.8 (2015): e1856-e1856. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.211
Research has found that mutations in the adenylate kinase 2 (AK2) gene lead to its functional loss, causing severe combined immunodeficiency disease - reticulodysplasia. AK2 deficiency can impair mitochondrial energy metabolism, block the differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells into lymphocytes and granulocytes, and lead to severe deficiency of neutrophils and lymphocytes.
5. Waldmann, Rebekka, et al. "AK2‐Deficient Mice Recapitulate Impaired Lymphopoiesis of Reticular Dysgenesis Patients, but Also Lack Erythropoiesis." European journal of immunology 55.7 (2025): e51466. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.202451466
The research found through the construction of mouse models that the deficiency of AK2 would block the development of embryonic red blood cells, leading to severe anemia and embryonic death. This is specie-different from the phenotype of human reticulodysplasia, revealing the key role of AK2 in hematopoiesis.
Creative Biolabs: AK2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality AK2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom AK2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our AK2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Six, E., et al. "AK2 deficiency compromises the mitochondrial energy metabolism required for differentiation of human neutrophil and lymphoid lineages." Cell death & disease 6.8 (2015): e1856-e1856. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.211
Anti-AK2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CECR2 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2465) (CBMAB-C3533WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1B1 Antibody (V2-2449) (CBMAB-1001CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






