ARID1B Antibodies
Background
The ARID1B gene is an important component subunit of the chromatin remodeling complex SWI/SNF and mainly functions within the nucleus of eukaryotes. This gene controls the transcriptional expression of multiple target genes by regulating chromatin structure, thereby participating in key biological processes such as embryonic development, neural differentiation and cell proliferation. The loss of function of the ARID1B gene is closely related to autosomal dominant Coffin-Siris syndrome, and patients often show symptoms such as intellectual disability and developmental delay. Since its function was first clarified in 2004, this gene has continuously attracted attention due to its core position in epigenetic regulation. Related research has not only revealed its significant role in cancer occurrence and neurodevelopmental disorders, but also deepened the scientific community's understanding of the association between chromatin remodeling mechanisms and human diseases.
Structure of ARID1B
ARID1B is a large nucleoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 250 kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies among different transcript isomers. As the core subunit of the chromatin remodeling complex SWI/SNF, its molecular size is directly related to the functional complexity.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~250 | ~245 | ~248 | ~230 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contain ARID structure domain and the more conservative functional domains | Highly homologous structure, functional domains | High similarity to human sequence | Have the homologous structure domain, but low sequence conservative |
This protein is composed of approximately 2,000 amino acid residues, and its core feature is the inclusion of a highly conserved AT-rich interaction domain (ARID), which mediates its binding to a specific DNA sequence. The ARID domain is mainly composed of a series of β -folds, forming a typical helical - turning - helical motif, which is responsible for recognizing the AT-rich sequence in the promoter region of the target gene. Its C-terminal also contains multiple functional domains that interact with other subunits of SWI/SNF, jointly assembling into a large complex. By hydrolyzing ATP, it alters the position of the nucleosome, thereby regulating the accessibility and transcriptional activity of the gene.
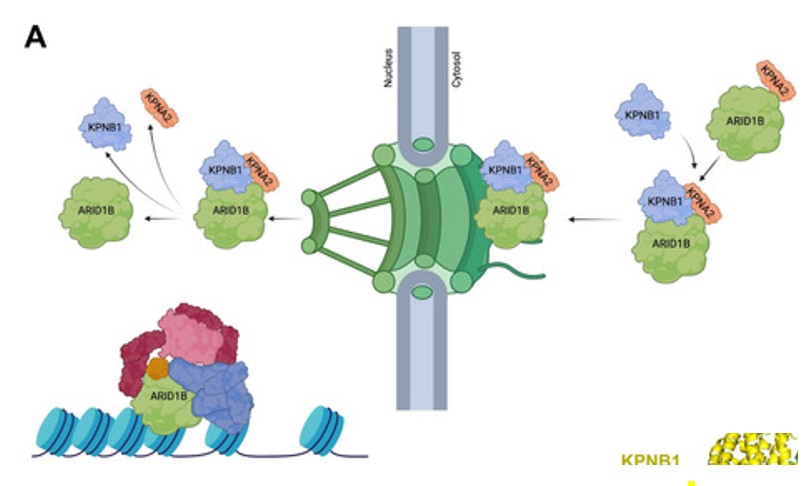 Fig. 1 The Protein Network Driving ARID1B into the Nucleus.1
Fig. 1 The Protein Network Driving ARID1B into the Nucleus.1
Key structural properties of ARID1B:
- Contains highly conserved AT-rich interaction domains (ARID domains)
- Unordered regions with multiple long fragments
- The C-terminal region contains a number of functional mods responsible for assembly with other subunits of the SWI/SNF complex
- Molecular switch functions that drive chromatin remodeling through a wide range of conformational changes
Functions of ARID1B
The main function of ARID1B protein is to act as a DNA-binding subunit of chromatin remodeling complexes and regulate gene transcription. In addition, it is also widely involved in key biological processes such as embryonic development, cell differentiation and tumor suppression.
| Function | Description |
| Transcriptional regulation | As a DNA-targeted subunit of the SWI/SNF complex, it binds to specific gene promoters and activates or inhibits transcription by reshaping chromatin structure. |
| Neural development | In play a key role in the development of the central nervous system, regulation and neuronal differentiation, migration and synapse formation a series of related genes. |
| Tumor suppression | Its functional inactivation is associated with various cancers (such as ovarian cancer, liver cancer, and neuroblastoma), promoting tumorigenesis by dysregulating genes related to the cell cycle and proliferation. |
| Disease caused by developmental disorders | Insufficient haplodose (inactivation of one copy) is the main cause of Coffin-Siris syndrome, in which patients present with intellectual disability, developmental delay and characteristic facial features. |
| Cell fate determination | By dynamically altering chromatin accessibility, it participates in the fate determination process of maintaining stem cell pluripotency and differentiating into specific lineages. |
The function of ARID1B depends on the SWI/SNF complex it is located in, which alters the nucleosome position by hydrolyzing ATP. Its regulation is highly gene-specific and environmentally dependent, in sharp contrast to the single and clear functional pattern of myoglobin.
Applications of ARID1B and ARID1B Antibody in Literature
1. Clayton-Smith, Jill. "The ARID1B spectrum in 143 patients: from nonsyndromic intellectual disability to Coffin–Siris syndrome." Genetics in Medicine (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41436-018-0330-z
The article indicates that the intellectual disability (ID) caused by the pathogenic variant ARID1B is highly similar to the phenotypic spectrum of patients with Coffin-Siris syndrome (CSS), with only the occurrence frequency of some CSS-related facial features differing. Research suggests that phenotypic collection methods should include negative feature records to avoid underestimating gene-associated phenotypes.
2. Zhang, Mingyi, et al. "ARID1B maintains mesenchymal stem cell quiescence via inhibition of BCL11B-mediated non-canonical Activin signaling." Nature Communications 15.1 (2024): 4614. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48285-2
This study reveals that ARID1B maintains the homeostasis of mesenchymal stem cells by directly inhibiting the expression of Bcl11b and regulating the non-classical Activin signaling pathway. The research clarified the key role and molecular mechanism of ARID1B as an epigenetic modifier in the fate determination of stem cells.
3. Bosch, Elisabeth, et al. "The missing link: ARID1B non-truncating variants causing Coffin-Siris syndrome due to protein aggregation." Human Genetics 143.8 (2024): 965-978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-024-02688-9
This study confirmed that non-truncated variations in the EHD2 and ARID domains of the ARID1B protein can lead to abnormal protein aggregation and loss of function. The methylation pattern is consistent with the classical pathogenic mechanism of insufficient haplodose, providing a new basis for the determination of the pathogenicity of related variations.
4. Odnokoz, Olena, et al. "Disruption of ARID1B Recruitment to the Nuclear Pore Complex as a New Anticancer Therapeutic Strategy." Advanced Science 12.36 (2025): e15585. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202415585
Research has found that ARID1B overenters the nucleus through the KPNA2-KPNB1 nuclear transport complex, negatively regulating ARID1A and driving tumor growth in triple-negative breast cancer. Blocking this nuclear transport can inhibit tumors and enhance the efficacy of PARP inhibitors, providing a new target for treatment.
5. Martins-Costa, Catarina, et al. "ARID1B controls transcriptional programs of axon projection in an organoid model of the human corpus callosum." Cell stem cell 31.6 (2024): 866-885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2024.04.014
Research has found that ARID1B is the core DNA-binding subunit of the key neurodevelopmental complex mSWI/SNF, and its mutation is the main genetic cause of corpus callosum hypoplasia and related intellectual disabilities and autism.
Creative Biolabs: ARID1B Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ARID1B antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ARID1B Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ARID1B antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Odnokoz, Olena, et al. "Disruption of ARID1B Recruitment to the Nuclear Pore Complex as a New Anticancer Therapeutic Strategy." Advanced Science 12.36 (2025): e15585. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202415585
Anti-ARID1B antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DHFR Recombinant Antibody (D0821) (CBMAB-D0821-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








