ART4 Antibodies
Background
The ART4 gene encodes a membrane-anchored adenosine diphosphate ribosyltransferase protein, which is mainly expressed in immune cells (such as T lymphocytes) and some tumor tissues. This protein participates in immunomodulatory signal transduction by modifying cell surface molecules, influencing T cell activation and tolerance balance. Meanwhile, it shows abnormally high expression in various cancers and is closely related to the tumor immune escape mechanism. First discovered in 1994 through the screening of T-cell cDNA libraries, its unique glycosylation modification function provides a new perspective for the study of immune checkpoints, and the related mechanism research has promoted the development of tumor immunotherapy targets. The research on the pathophysiological function of this gene has continuously driven the progress in the fields of autoimmune diseases and cancer treatment.
Structure of ART4
ART4 is a membrane-anchored glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 36-42 kDa. This difference mainly stems from the varying degrees of glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 39.5 | 38.2 | 40.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | With longer extracellular domain structure | Extracellular area highly homologous with humans | Glycosylation pattern similar to humans |
This protein is composed of 293 amino acids, and its primary structure forms a typical extracellular ADP-ribosyltransferase domain. The secondary structure of ART4 is mainly of a mixed type, where the β -fold constitutes the enzyme's active center, while the α -helix participates in the formation of the interface for protein-protein interactions. Its active site contains a conserved Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) motif, which plays a key role in mediating intercellular adhesion signal transduction.
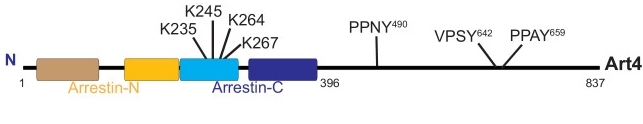 Fig. 1 Art4 domain architecture.1
Fig. 1 Art4 domain architecture.1
Key structural properties of ART4:
- Extracellular ADP-ribosyltransferase domain
- Transmembrane anchoring sites and glycosylation modification sites
- Conserved RGD motifs mediate cell adhesion
Functions of ART4
ART4 is a membrane-anchored ADP-ribosyltransferase, whose main function is to mediate immune regulation and influence the tumor microenvironment. Specific functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Immune regulation | By modifying T cell surface proteins through ADP-ribosylation, T cell activation and the intensity of immune response are regulated to maintain autoimmune tolerance. |
| Tumor immune escape | In a wide variety of cancer cells increased, by interfering with participate in the process of tumor immune escape immune recognition, promotes cancer progression. |
| Regulation of cell adhesion | The conservative RGD motif with integrin molecules such as interaction, affect the immune cells in tissue between the migration and positioning. |
| Potential of drug targets | As an emerging target for tumor immunotherapy, its specific expression pattern offers the possibility for the development of targeted drugs. |
| Diagnostic markers | In acute myeloid leukemia and other present specificity high expression in malignant tumor, can be used as a potential disease diagnosis and classification of markers. |
ART4 plays a complex dual role in immune homeostasis and pathological processes through its enzymatic activity and protein-protein interactions, and its functional mechanism remains a cutting-edge field in current tumor immunology research.
Applications of ART4 and ART4 Antibody in Literature
1. Halawani, Amr J., et al. "Investigation of dombrock blood group alleles and genotypes among Saudi Blood Donors in Southwestern Saudi Arabia." Genes 13.6 (2022): 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061079
This study conducted Dombrock blood group system genotyping on 150 blood donors in Jizan Province, Saudi Arabia, based on the rs11276 polymorphism of the ART4 gene. The results showed that the allele frequencies of DOA and DOB were 40.67% and 59.33% respectively, among which the proportion of the DOA/DOB genotype was the highest (54.67%). This research provides important data support for establishing a regional blood donor database and preventing transfusion reactions.
2. Wang, Xinyue, et al. "Rescue RM/CS-AKI by blocking strategy with one-dose anti-myoglobin RabMAb." Nature Communications 16.1 (2025): 1044. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0242168
This study assesses the feasibility of whole-genome sequencing for red blood cell antigen typing, covering nine systems including ART4. The results show that the consistency with the conventional method reaches 93%, but the sequencing depth must be strictly greater than 15x. Studies show that WGS technology is expected to be applied in the screening of rare blood types and promote precise blood transfusion management.
3. Olivieri, Anna, et al. "Structural organization of erythrocyte membrane microdomains and their relation with malaria susceptibility." Communications Biology 4.1 (2021): 1375. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02900-w
This study analyzed the cholesterol-rich microregion structure on human erythrocyte membranes and found that proteins such as ART4 are closely related to malaria invasion. ART4 was not only recruited to the site of malaria parasite invasion, but experiments also confirmed that its functional deficiency would affect the invasion of malaria parasites. Population genetic analysis further indicated that variations in the ART4 gene were associated with malaria susceptibility.
4. Zhu, Lu, et al. "Adaptor linked K63 di-ubiquitin activates Nedd4/Rsp5 E3 ligase." Elife 11 (2022): e77424. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.77424
This study reveals that Rsp5 E3 ligase adaptors such as Art4 undergo dimerization ubiquitination linked by K63. This modification can enhance the recruitment of Rsp5 to the plasma membrane as a ubiquitinating substrate, and its HECT domain can protect this dimeric ubiquitin from being cleaved by deubiquitinating enzymes. This clarifies a new mechanism by which adaptor proteins regulate the activity of Rsp5.
5. Grahnert, Andreas, et al. "The orthologue of the" acatalytic" mammalian ART4 in chicken is an arginine-specific mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase." BMC Molecular Biology 9.1 (2008): 86. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-9-86
This study first discovered that chicken ART4 is a functional direct homolog of mammalian ART4. Unlike ART4 which is inactivated due to active site mutations in mammals, chicken ART4 has a complete R-S-EXE motif and is expressed as a GPI-anchored protein on the cell surface, demonstrating arginine-specific ADP-ribosyl transferase activity.
Creative Biolabs: ART4 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ART4 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ART4 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ART4 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zhu, Lu, et al. "Adaptor linked K63 di-ubiquitin activates Nedd4/Rsp5 E3 ligase." Elife 11 (2022): e77424. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.77424
Anti-ART4 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CORO1A Recombinant Antibody (4G10) (V2LY-1206-LY806)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








