CAMK1 Antibodies
Background
CAMK1 is a serine/threonine protein kinase widely distributed in eukaryotic cells, mainly involved in calcium signal-mediated transcriptional regulation and neuronal function regulation. This enzyme is activated by the calcium/calmodulin complex and then phosphorylates downstream targets (such as CREB), thereby regulating key physiological processes such as cell differentiation, synaptic plasticity and hormone secretion. It was first identified by homologous cloning technology in the 1990s. The analysis of its three-dimensional structure revealed a unique interaction mechanism between the self-inhibitory domain and the kinase domain. As a core medium molecule of calcium signaling pathways, CAMK1 provides an important model for studying intracellular signal transduction, neural development and metabolic diseases, and continuously promotes the development of related fields.
Structure of CAMK1
CAMK1 is a calcium/calcinein-dependent protein kinase with a molecular weight of approximately 42 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species, mainly due to species-specific variations in amino acid sequences. This protein is composed of approximately 370 amino acids and forms a typical kinase folding structure, including an N-terminal kinase catalytic domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain. Its active center has a highly conserved ATP binding site and substrate recognition region. The crucial threonine phosphorylation at position 174 is essential for the complete activation of enzyme activity. The activation of CAMK1 strictly depends on the binding of the calcium ion-calmodulin complex: this binding induces conformational changes, causing the self-inhibitory region to detachment from the catalytic core and thereby exposing the substrate binding site. This protein plays a core role in the regulation of synaptic plasticity, hormone secretion and gene expression in neurons. The relationship between its structure and function has become an important model for studying intracellular calcium signal transduction.
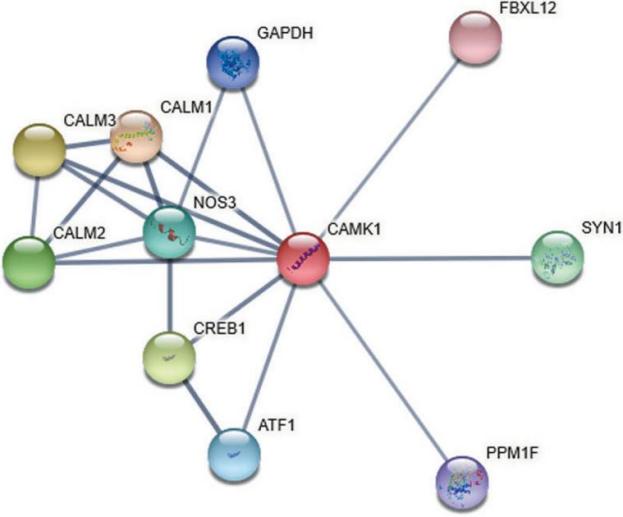 Fig. 1 The PPI information about CAMK1 evaluated by STRING database. 1
Fig. 1 The PPI information about CAMK1 evaluated by STRING database. 1
Key structural properties of CAMK1:
- The typical folding domain of protein kinases consists of a β-sheet and an α-helix to form the catalytic core
- The autoinhibitory region stably seals the ATP-binding pocket through hydrophobic interactions
- The calmodulin binding domain contains negatively charged helical structures that are responsible for sensing calcium signals
- Phosphorylation of conserved threonine (Thr-174) in the activation loop induces conformational changes and thoroughly activates enzyme activity
Functions of CAMK1
The main function of CAMK1 is to act as a key transducer of intracellular calcium signals and participate in the regulation of various physiological processes. Its specific functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Signal transduction | In response to calcium ion influx, it is activated by calmodulin and phosphorylates downstream substrates to conduct calcium signals. |
| Regulation of gene expression | By phosphorylating transcription factors (such as CREB), it affects the expression of early genes and synaptic associated proteins. |
| Neuronal plasticity | Regulate dendrite morphogenesis and synaptic strength, and participate in the formation of learning and memory. |
| Metabolic regulation | It participates in the regulation of insulin secretion and energy balance in metabolic cells such as pancreatic beta cells. |
| Cell differentiation and proliferation | Affects the differentiation process and proliferation activity of a variety of cells, such as immune cells and precursor cells. |
The activation of CAMK1 is typically calcium concentration-dependent, and its enzymatic kinetics conforms to the characteristics of biphase kinetics. It can be partially activated under low calcium pulses and maintain long-term activity through autophosphorylation under continuous calcium signals. This feature makes it a precise converter for short-term and long-term calcium signal responses within cells.
Applications of CAMK1 and CAMK1 Antibody in Literature
1. Lei, Yangyang, et al. "Expression of CAMK1 and its association with clinicopathologic characteristics in pancreatic cancer." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 25.2 (2021): 1198-1206. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16188
The article indicates that calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase 1 (CAMK1) is highly expressed in pancreatic cancer and is associated with a poor prognosis. Its interacting proteins such as CALM1 suggest that CAMK1 may serve as a potential biomarker for the prognosis assessment of pancreatic cancer.
2. Yang, Jie, et al. "Pitavastatin activates mitophagy to protect EPC proliferation through a calcium-dependent CAMK1-PINK1 pathway in atherosclerotic mice." Communications Biology 5.1 (2022): 124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-03081-w
The article indicates that statins enhance mitochondrial autophagy and improve the proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells by promoting mitochondrial calcium release and CAMK1 phosphorylation, activating the PINK1-PARK2 pathway, and providing a new target for the treatment of atherosclerosis.
3. Li, Guoqi, et al. "Characterization and functional analysis of a new Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase (CaMK1) in the citrus pathogenic fungus Penicillium italicum." Journal of Fungi 8.7 (2022): 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8070667
The article indicates that the calmodulin kinase PiCaMK1 (homologous CALM1) in citrus pathogenic fungi regulates growth, spore production, pathogenicity and environmental stress response. Its absence leads to the down-regulation of key metabolic and signaling pathway gene expression.
4. Li, Shiyang, et al. "Association between plasma proteome and pulmonary heart disease: A two‐stage Mendelian randomization analysis." The Clinical Respiratory Journal 18.6 (2024): e13775. https://doi.org/10.1111/crj.13775
The article indicates that Mendelian randomization analysis combined with cohort validation found that elevated plasma calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase I (CAMK1) levels were significantly positively correlated with the risk of pulmonary heart disease, suggesting that the calcium signaling pathway plays an important role in the pathological mechanism of this disease.
5. Szaluś-Jordanow, Olga, et al. "A primary multiple pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma of the heart in an adult dog." BMC Veterinary Research 19.1 (2023): 137. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07981
This article describes a rare case of primary multiple pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma in a dog's heart, where myoglobin antibody was used as an immunohistochemical marker to confirm the tumor's myogenic origin, demonstrating its diagnostic significance in differentiating cardiac neoplasms.
Creative Biolabs: CAMK1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CAMK1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CAMK1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CAMK1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Lei, Yangyang, et al. "Expression of CAMK1 and its association with clinicopathologic characteristics in pancreatic cancer." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 25.2 (2021): 1198-1206. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16188
Anti-CAMK1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BBS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0253) (CBMAB-0254-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC25 Recombinant Antibody (CBLC132-LY) (CBMAB-C9786-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (P67.6) (CBMAB-C10189-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-NSUN6 Recombinant Antibody (D-5) (CBMAB-N3674-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








