CD70 Antibodies
Background
CD70 is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily, mainly expressed on the surface of activated immune cells, such as T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes. This protein plays a key role in adaptive immune responses by specifically binding to the receptor CD27 and participating in the transmission of co-stimulatory signals. The abnormal activation of the CD70-CD27 signaling pathway is closely related to the occurrence and development of various autoimmune diseases and malignant tumors and has received extensive attention especially in lymphoma and renal cell carcinoma. Since its discovery in the 1990s, targeted therapy research on this pathway has become a hot topic in the field of immunotherapy. The study of its mechanism of action not only deepens the understanding of the immune co-stimulatory molecular network but also provides a new direction for immune intervention strategies for related diseases.
Structure of CD70
CD70 is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 26-29 kDa, and its differences mainly stem from the varying degrees of glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 28-29 | 26-28 | 28-29 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Extracellular domain contains conservative TNF homologous region | With the human CD70 about 65% amino acid sequence homology | Highly similar to the human CD70 sequence, it is often used in preclinical research |
This protein is composed of 193 amino acids, and its spatial structure forms a typical "β -sandwich" fold through the extracellular domain. The active form of CD70 is a trimer, and this advanced structure is crucial for its binding to the receptor CD27. Its extracellular domain contains specific receptor binding sites, among which conserved amino acid residues are responsible for specific interactions with the ligand binding slot of the CD27 receptor, thereby activating the downstream NF-κB signaling pathway.
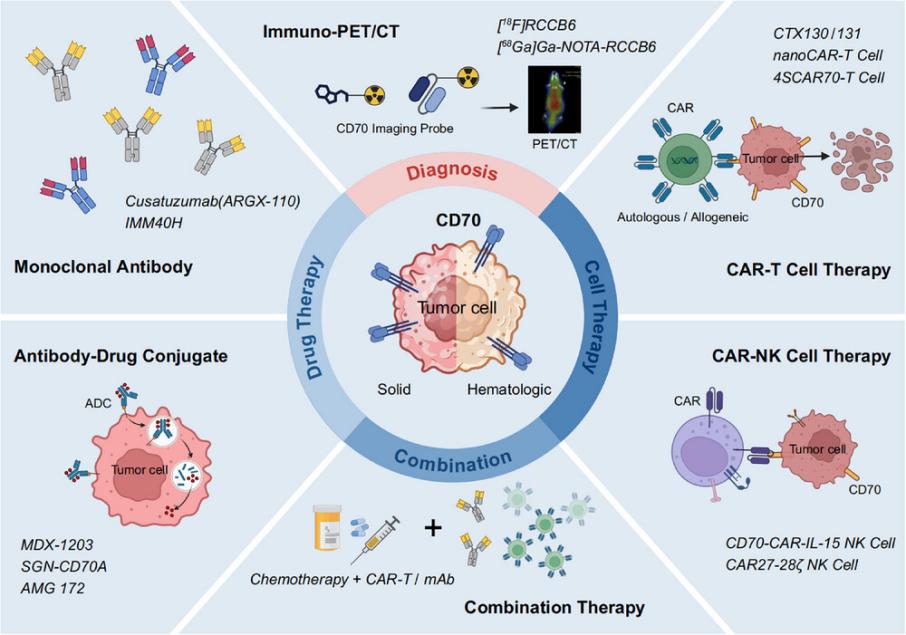 Fig. 1 Overview of CD70-targeted strategies in cancer diagnosis and therapy.1
Fig. 1 Overview of CD70-targeted strategies in cancer diagnosis and therapy.1
Key structural properties of CD70:
- Type II transmembrane glycoprotein structure
- Extracellular section contains conservative TNF homologous structure domain
- Anchored to the cell membrane through the N-terminal of the intracellular segment
- Dependent on cysteine residues to form stable homologous trimers
Functions of CD70
The main function of CD70 is to act as an immune co-stimulatory molecule, but its signal dysregulation is also involved in various pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Immune activation | Binding to CD27 receptors on the surface of T cells provides costimulatory signals that promote T cell proliferation, differentiation and cytokine secretion. |
| B-cell regulation | In germinal center reaction, adjust antibody category B cell activation and conversion, affect the humoral immune response. |
| Regulation of immune tolerance | Abnormal and persistent activation of signaling pathways can disrupt immune homeostasis and is associated with the occurrence and development of autoimmune diseases. |
| Tumor immune escape | Persistent expression in a variety of tumors may mediate T-cell depletion and promote tumor immune escape. |
| Immune memory formation | By regulating T cell activation, it affects the differentiation of effector T cells into memory T cells and participates in the formation of long-term immune memory. |
The interaction affinity between CD70 and CD27 is relatively high, but its signal intensity and effect strictly depend on its transient expression pattern on activated immune cells, which contrasts with the constitutive expression of CD27 and reflects the precise regulation of immune co-stimulatory signals.
Applications of CD70 and CD70 Antibody in Literature
1. Flieswasser, Tal, et al. "The CD70-CD27 axis in oncology: the new kids on the block." Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research 41.1 (2022): 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-02215-y
The article indicates that the CD70-CD27 axis is abnormally expressed in various hematological malignancies and solid tumors. Unlike its physiological immunomodulatory effect, the dysregulation of this axis promotes tumor progression and immunosuppression. Therefore, CD70 has become a new target in the field of tumor treatment, and related research and treatment strategies are being actively explored.
2. Wu, Gongqiang, et al. "Preclinical evaluation of CD70-specific CAR T cells targeting acute myeloid leukemia." Frontiers in Immunology 14 (2023): 1093750. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1093750
The article indicates that CD70 is specifically expressed on acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells but not on normal hematopoietic stem cells, making it an ideal target for CAR-T therapy. Studies have shown that CAR-T cells targeting CD70 can effectively kill AML cells both in vivo and in vitro, demonstrating good therapeutic potential.
3. Gong, Lanqi, et al. "Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells promote regulatory T cell development and suppressive activity via CD70-CD27 interaction." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 1912. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37614-6
This study reveals that in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, tumor cells promote the development of immunosuppressive Treg cells through the CD70-CD27 signaling axis, thereby weakening the function of CD8+ T cells and leading to immune escape. The combination of CD70 blockers and anti-PD-1 therapy can synergistically enhance anti-tumor immunity, providing a new treatment strategy.
4. Van den Eynde, Astrid, et al. "IL-15-secreting CAR natural killer cells directed toward the pan-cancer target CD70 eliminate both cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts." Journal of hematology & oncology 17.1 (2024): 8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-024-01525-w
The article indicates that CD70 is expressed on tumor cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts of solid tumors such as colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer. Studies have shown that CAR-NK cells targeting CD70 stimulated by IL-15 can effectively clear these target cells, providing a new strategy for the treatment of such matrix-rich solid tumors.
5. Hu, Jiatao, et al. "CD70: An emerging target for integrated cancer diagnosis and therapy." Clinical and Translational Medicine 15.7 (2025): e70400. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.70400
The article indicates that CD70 is overexpressed in various hematological malignancies and solid tumors and has become an important tumor target. Targeted diagnosis and treatment strategies based on CD70 have developed rapidly, including immune PET imaging, antibody-drug conjugates, CAR-T/NK cell therapy, etc., and have shown broad prospects in both diagnosis and treatment fields.
Creative Biolabs: CD70 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CD70 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CD70 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CD70 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Hu, Jiatao, et al. "CD70: An emerging target for integrated cancer diagnosis and therapy." Clinical and Translational Medicine 15.7 (2025): e70400. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.70400
Anti-CD70 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (61-3E7) (CBMAB-1183-CN)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AOC3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0014) (CBMAB-0014-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






