FOXP3 Antibodies
Background
FOXP3 is a key transcription factor protein, mainly expressed in regulatory T cells of vertebrates. This protein regulates the expression of immune-related genes by binding to specific DNA sequences, thereby maintaining immune tolerance and suppressing excessive immune responses. In fields such as autoimmune diseases and organ transplantation, FOXP3 plays a core role in the regulatory mechanism of immune balance. This gene was first identified by a research team in 2001 as a key factor in immune regulation, and its mutation can lead to serious immune disorders such as IPEX syndrome in humans. As the first confirmed transcription factor dedicated to regulating the development of regulatory T cells, its unique forkhead domain and regulatory mechanism have become a classic model in immunology research, greatly promoting the development of autoimmune disease treatment and tumor immunotherapy.
Structure of FOXP3
FOXP3 is a protein with a molecular weight of approximately 47-50 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species due to differences in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 47.3 | 48.1 | 49.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 431 amino acids, with fork structure domain | Fork structure domain highly conservative | High homology with human |
This protein is encoded by the FOXP3 gene, and its primary structure contains a characteristic C2H2 zinc finger structure and a Forkhead DNA-binding domain. This fork-head domain is composed of approximately 100 amino acids, forming a special wing-like helical structure that enables it to specifically recognize and bind to the DNA sequence of the target gene, thereby exerting transcriptional regulatory functions. The key amino acid residues in its protein structure determine the affinity and specificity for binding to DNA.
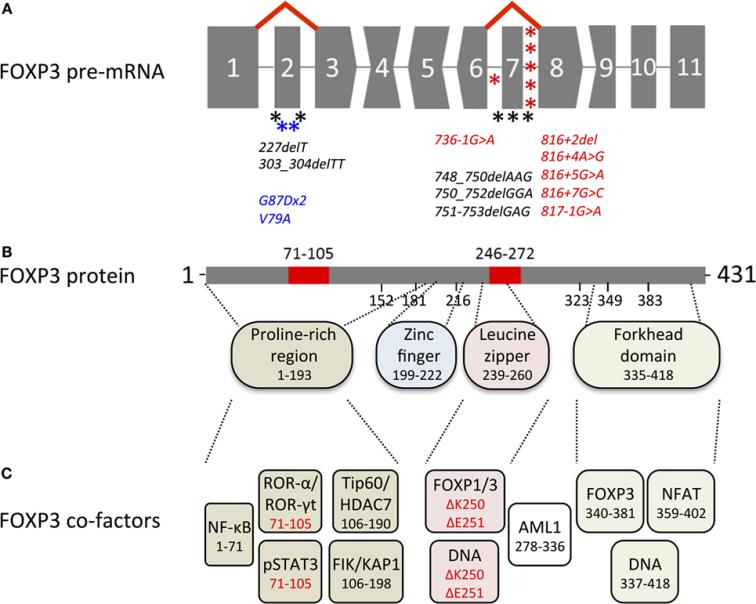 Fig. 1 Overview of genetic, transcriptional, and functional features of human FOXP3.1
Fig. 1 Overview of genetic, transcriptional, and functional features of human FOXP3.1
Key structural properties of FOXP3:
- Unique forked head-shaped DNA binding domain
- The N-terminal region rich in proline mediates protein-protein interactions
- C2H2 type zinc refers to the conformation of structurally stable proteins
- Leucine zipper motifs promote dimerization
Functions of FOXP3
The core function of the FOXP3 protein is to act as the main regulatory transcription factor for regulatory T cells (TreGs) and maintain immune tolerance. In addition, it is also involved in regulating T cell activation, proliferation and various immune response processes.
| Function | Description |
| Induction of immune tolerance | By regulating the transcription of target genes, it promotes the development of Treg cells and inhibits the activity of effector T cells, preventing autoimmune reactions. |
| Immunosuppression | Recruit histone modification complexes to the promoter region of target genes to epigenetically down-regulate the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2 and IFN-γ. |
| Regulation of T cell function | Directly inhibit signaling pathways such as NFAT and NF-κB, restricting the excessive activation and proliferation of conventional T cells. |
| Metabolic reprogramming | Influence the metabolic pathways of T cells so that they tend to adopt metabolic patterns with immunosuppressive properties. |
| Tissue repair | By regulating the immune microenvironment, it indirectly promotes the repair and regeneration of certain tissues. |
Unlike most transcription factors that widely promote gene expression, FOXP3 mainly exerts transcriptional inhibitory effects. The loss of its function will directly lead to fatal autoimmune diseases, highlighting its unique position as the "master switch" of immune homeostasis.
Applications of FOXP3 and FOXP3 Antibody in Literature
1. Ziółkowska-Suchanek, Iwona, and Magdalena Żurawek. "FOXP3: A player of immunogenetic architecture in lung cancer." Genes 15.4 (2024): 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15040493
The article indicates that FOXP3 is a key factor of regulatory T cells and has been found to be expressed in various tumors (such as lung cancer) in recent years. This article reviews the role of FOXP3 in the immune microenvironment of lung cancer, the association between its expression and prognosis, as well as its potential for targeted therapy.
2. Copland, Alastair, and David Bending. "Foxp3 molecular dynamics in treg in juvenile idiopathic arthritis." Frontiers in immunology 9 (2018): 2273. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02273
The article indicates that Foxp3 is a key factor regulating T cell function, and its dynamic expression and activity directly affect the occurrence of autoimmune diseases such as arthritis in children. This article goes beyond static cell counting to explore the transcriptional and post-translational regulatory mechanisms of Foxp3, providing a new perspective for the development of new immunotherapies for arthritis.
3. Mailer, Reiner KW. "Alternative splicing of FOXP3—Virtue and vice." Frontiers in immunology 9 (2018): 530. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00530
The article indicates that FOXP3 is a key transcription factor for regulatory T cells (Treg). Unlike mice, humans have selective splicing isomers of FOXP3. This review explores the functions of these unique isomers in health and disease, as well as their potential as therapeutic targets.
4. Yue, Yi, et al. "Epigenetic regulation of human FOXP3+ Tregs: from homeostasis maintenance to pathogen defense." Frontiers in Immunology 15 (2024): 1444533. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1444533
The article indicates that FOXP3 is the core marker of regulatory T cells (TreGs), and its expression and function are precisely regulated by epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation. This article focuses on elaborating the multi-faceted role of Treg in immune homeostasis and explores its regulatory potential in disease treatment (such as COVID-19).
5. Ma, Benxu, et al. "The role of FOXP3 on tumor metastasis and its interaction with traditional Chinese medicine." Molecules 27.19 (2022): 6706. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196706
The article indicates that FOXP3 is not only a key factor for regulatory T cells, but also expressed in various tumor cells, influencing their proliferation, metastasis and drug resistance. This article focuses on reviewing the role of FOXP3 in tumor metastasis and explores its interaction with traditional Chinese medicine, providing a new perspective for clinical research.
Creative Biolabs: FOXP3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality FOXP3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom FOXP3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our FOXP3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Mailer, Reiner KW. "Alternative splicing of FOXP3—Virtue and vice." Frontiers in immunology 9 (2018): 530. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00530
Anti-FOXP3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Rat Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (7G4.2E8) (CBMAB-C8725-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






