KLRG1 Antibodies
Background
KLRG1 (killer lectin-like receptor G1) is a transmembrane inhibitory receptor mainly expressed on the surface of natural killer cells (NK cells) and effector/memory T cells. This protein transmits inhibitory signals by recognizing ligands such as e-cadherin, thereby regulating the activation threshold of immune cells, preventing excessive immune responses and maintaining autoimmune tolerance. Research has found that KLRG1 is highly expressed in chronic infections and tumor microenvironments, and its signaling pathway can lead to T cell exhaustion. This mechanism provides an important direction for immune regulation research. Since its first identification in 1998, KLRG1 has become one of the key molecules in immune checkpoint research due to its regulatory role in immune senescence, antiviral response and tumor immunity, providing a new perspective for understanding the maintenance mechanism of immune homeostasis and the treatment of related diseases.
Structure of KLRG1
KLRG1 is a type I transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 26-28 kDa. This value shows subtle differences among different species, mainly due to the varying degrees of glycosylation modification in extracellular domains.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Rhesus monkey | Pig |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 28 | 26 | 26.5 | 27.5 | 27 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains three C2 type lectin-like domains | Extracellular region and human homology of 65% | Highly conserved across the membrane area | Extracellular domain glycosylation pattern similar to humans | Signal peptide sequence has species specificity |
This protein is composed of three extracellular C2-type lectin-like domains, transmembrane regions and intracellular segments. Its extracellular segment functions through a Ca²⁺-dependent mechanism that specifically recognizes ligands such as e-cadherin, while the intracellular segment carries an inhibitory motif (ITIM) based on immune receptor tyrosine. After ligand binding, it recruits SHP-1 phosphatase to transmit inhibitory signals. This unique structural layout enables it to play a key role in immune regulation.
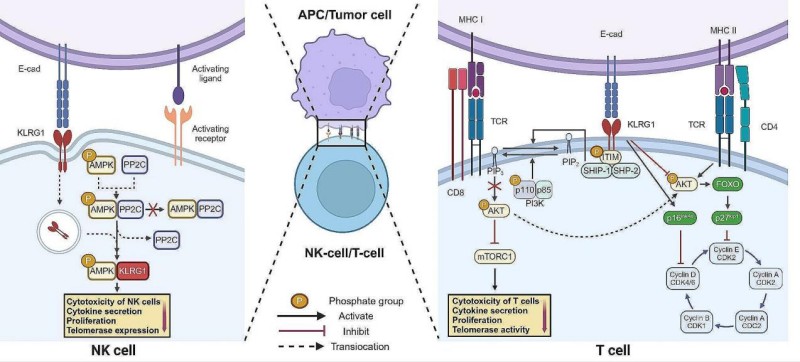 Fig. 1 KLRG1 signaling pathway.1
Fig. 1 KLRG1 signaling pathway.1
Key structural properties of KLRG1:
- Extracellular section contains three sample C2 type lectin structural domain
- The transmembrane region binds to the aptamer via a positively charged lysine residue
- Intracellular section carrying immune receptor tyrosine inhibit motif (ITIM)
- Homodimers are formed through disulfide bonds to enhance ligand recognition
Functions of KLRG1
The main function of KLRG1 is to transmit immunosuppressive signals to maintain immune homeostasis. However, this receptor is also involved in the regulation of various immunopathological processes, including cellular exhaustion, immunosenescence and autoimmune tolerance.
| Function | Description |
| Immunosuppression | SHP-1/SHP-2 phosphatases were recruited through intracellular ITIM motifs to inhibit the activation signaling pathways of T cells and NK cells. |
| Immunosenescence markers | During chronic infection and aging, the proportion of KLRG1high CD8+ T cells significantly increases, characterizing the terminal state of cell differentiation. |
| Tolerance maintenance | By recognizing E-cadherin expressed in normal tissues, the attack of effector T cells on autologous tissues is prevented. |
| Metabolic regulation | Inhibitory signals down-regulate the expression of the glucose transporter GLUT1 and limit the glycolytic ability of effector T cells. |
| Differentiation regulation | KLRG1 expression is related to the differentiation of effector memory T cells and affects the homing ability of secondary lymphoid organs. |
The ligand recognition characteristics of KLRG1 are manifested as specific binding to members of the E-cadherin family, and its affinity is significantly higher than that of other immune receptors, which is consistent with the core role of this receptor in maintaining tissue immune homeostasis.
Applications of KLRG1 and KLRG1 Antibody in Literature
1. Zhang, Yakun, et al. "The role of KLRG1: a novel biomarker and new therapeutic target." Cell Communication and Signaling 22.1 (2024): 337. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-024-01714-7
The article indicates that KLRG1 is an immune checkpoint receptor mainly expressed in NK cells and T cells, which can inhibit the activity of immune cells and participate in the regulation of immune responses. This article reviews the expression patterns and mechanisms of action of KLRG1 in autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases and tumors, and explores its potential as a target for tumor immunotherapy.
2. Borys, Samantha M., et al. "The yin and yang of targeting KLRG1+ Tregs and effector cells." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 894508. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.894508
This article focuses on the Treg cell subpopulation expressing KLRG1. Although the role of KLRG1 in NK and effector T cells has been widely studied, its function in immunosuppressive Tregs has long been overlooked. This article reviews the role of KLRG1+ Treg in tumors and autoimmunity, and emphasizes that future therapies targeting KLRG1 must simultaneously consider its dual effects on effector cells and Treg.
3. Hui, Zhenzhen, et al. "PD-1 blockade potentiates neoadjuvant chemotherapy in NSCLC via increasing CD127+ and KLRG1+ CD8 T cells." NPJ Precision Oncology 7.1 (2023): 48. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-023-00384-x
In this study, through techniques such as single-cell sequencing, it was found that in neoadjuvant therapy for non-small cell lung cancer, the combination of PD-1 inhibitors can significantly increase the infiltration of CD8⁺T cells and their KLRG1⁺subsets within the tumor, and promote their spatial aggregation with B cells and CD4⁺T cells, thereby enhancing the anti-tumor immune response and improving the therapeutic effect.
4. Soto-Heredero, Gonzalo, et al. "KLRG1 identifies regulatory T cells with mitochondrial alterations that accumulate with aging." Nature Aging (2025): 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-025-00855-9
This study identified a subpopulation of KLRG1+ Treg cells that accumulates with aging. This group of cells exhibits senescent characteristics such as abnormal mitochondrial function and DNA damage, and has a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Their immunosuppressive function is significantly weakened in the body. This indicates that KLRG1+ Treg cells are the key factor connecting immunosenescence with tissue inflammation (inflammatory senescence).
5. Wang, Li, et al. "KLRG1-expressing CD8+ T cells are exhausted and polyfunctional in patients with chronic hepatitis B." Plos one 19.5 (2024): e0303945. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303945
In chronic hepatitis B virus infection, CD8⁺T cells expressing KLRG1, although presenting an consumption-related molecular phenotype, can produce effector factors such as TNF-α and IFN-γ, demonstrating functional activity. Studies have shown that the binding of KLRG1 to E-cadherin inhibits its antiviral efficacy, suggesting that this cell population has functional diversity.
Creative Biolabs: KLRG1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality KLRG1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom KLRG1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our KLRG1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zhang, Yakun, et al. "The role of KLRG1: a novel biomarker and new therapeutic target." Cell Communication and Signaling 22.1 (2024): 337. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-024-01714-7
Anti-KLRG1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CCDC25 Recombinant Antibody (CBLC132-LY) (CBMAB-C9786-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CHRNA9 Recombinant Antibody (8E4) (CBMAB-C9161-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CAT Recombinant Antibody (724810) (CBMAB-C8431-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








