L1CAM Antibodies
Background
L1CAM is a transmembrane glycoprotein mainly distributed on the surface of neuronal cell membranes and belongs to the member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. The protein encoded by this gene plays a core role in the development of the nervous system, axon orientation and synaptic formation by mediating the adhesion and signal transduction between neurons. Its functional abnormalities are associated with a variety of neurodevelopmental disorders, especially in some cases of hereditary hydrocephalus syndrome and intellectual disability where L1CAM gene mutations have been found. Since its discovery in the 1980s, this protein has become a hot topic due to its key position in the research of neural plasticity and neural regeneration. The interaction mechanism between its multiple domains and ligands has been deeply analyzed, providing an important model for understanding the molecular basis of intercellular recognition, neural circuit construction and neurological diseases.
Structure of L1CAM
L1CAM is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 200-220 kDa. Its actual molecular weight shows a wide range in electrophoresis due to the varying degrees of glycosylation modification. The following table shows the typical performance in different common experimental species or cell models:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~200-220 | ~180-200 | ~180-200 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains six Ig sample structure, five FnIII repetitive structure domains | Extracellular domain highly conservative, glycosylation pattern with the human species differences | Similar to mice, it is often used in neurodevelopmental research models |
This protein is composed of 1,257 to 1,287 amino acids, and its extracellular region contains multiple immunoglobulin (Ig) -like and fibronectin III (FnIII) repeat domains, which jointly mediate homologous and heterologous intercellular adhesion interactions. Its single transmembrane domain is connected to a highly conserved intracellular tail, which can bind to various intracellular signal-adapting proteins (such as ANKYRIN) to conduct extracellular adhesion signals into the cell, thereby regulating cell migration, axon growth and neuronal survival.
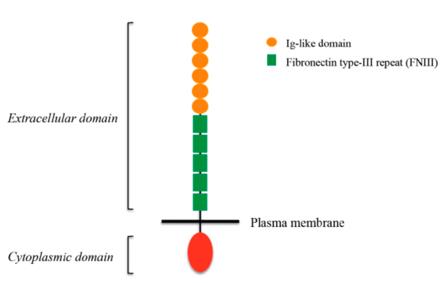 Fig. 1 L1CAM structure.1
Fig. 1 L1CAM structure.1
Key structural properties of L1CAM:
- Multidomain extracellular structures (including Ig-like and FNiII-like repetitive domains)
- Single transmembrane helical connection of intracellular and extracellular functional domains
- Conservative intracellular tail ANKYRIN combining motif
- Calcium dependent homologous/heterologous affinity interaction interface
- High glycosylation modification affects its mobility and recognition specificity
Functions of L1CAM
L1CAM is a transmembrane glycoprotein whose main function is to mediate intercellular adhesion and signal transduction, especially playing a core role in the development of the nervous system. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of pathophysiological processes, including cancer metastasis and neurodegenerative diseases. Its core functions can be summarized as follows:
| Function | Description |
| Neural development and orientation | Through homologous and heterologous (with other ligands) interactions, it guides axon growth, neuronal migration and targeted recognition, which is crucial for the formation of neural circuits. |
| Cell adhesion and aggregation | Mediate the strong adhesion between neurons and between neurons and glial cells, promoting cell aggregation and tissue structure stability. |
| Intracellular signal transduction | Intracellular domains bind to downstream signaling molecules (such as ANKYRIN and ERM proteins), activating pathways like Src kinase and MAPK, and regulating cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. |
| Promotion of cancer metastasis | Abnormally high expression in a variety of cancers, by enhancing tumor cell invasion, angiogenesis and resistance loss of nest apoptosis, drive tumor progression and metastasis. |
| Damage repair and regeneration | Expression after central nervous system damage, participate in the glial scar formation, as well as the axon regeneration has two-way adjustment function (promote or inhibit depends on micro environment). |
The interaction network between L1CAM and other cell adhesion molecules is extremely complex, and its function is highly dependent on cell type, post-translational modifications (such as glycosylation), and microenvironmental signals. Unlike single-function oxygen storage proteins, L1CAM is more like a multifunctional "signal hub", and its scope and intensity of action depend on the molecular and cellular background in which it is located.
Applications of L1CAM and L1CAM Antibody in Literature
1. Angiolini, Francesca, and Ugo Cavallaro. "The pleiotropic role of L1CAM in tumor vasculature." International journal of molecular sciences 18.2 (2017): 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020254
The article indicates that L1CAM is abnormally expressed in tumor blood vessels, has a pro-angiogenic effect, and hinders vascular normalization. Targeting L1CAM may become a novel therapeutic strategy for anti-angiogenesis and promoting vascular normalization, and is expected to improve the therapeutic effect of tumors.
2. Romani, Chiara, et al. "L1CAM expression as a predictor of platinum response in high‐risk endometrial carcinoma." International Journal of Cancer 151.4 (2022): 637-648. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.34035
Studies have shown that high expression of L1CAM is associated with poor response to platinum-based chemotherapy and a poor prognosis in patients with high-risk endometrial cancer, and it is expected to serve as a predictive biomarker for optimizing the efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy.
3. Loers, Gabriele, Ute Bork, and Melitta Schachner. "Functional Relationships between L1CAM, LC3, ATG12, and Aβ." International journal of molecular sciences 25.19 (2024): 10829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910829
Research has revealed that the cell adhesion molecule L1 mediates autophagy by interacting with proteins such as LC3 and ATG12, promoting the clearance of β -amyloid protein, and is expected to provide a new therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's disease by enhancing L1 function.
4. Dräger, Oliver, et al. "Role of L1CAM in retinoblastoma tumorigenesis: identification of novel therapeutic targets." Molecular oncology 16.4 (2022): 957-981. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.13054
Studies have revealed that L1CAM is highly expressed in retinoblastoma and can promote tumor growth, drug resistance and metastasis. Targeting L1CAM or its splicing enzyme can inhibit tumor progression, providing a new strategy for the treatment of this intraocular malignant tumor in children.
5. Giordano, Marco, et al. "L1CAM promotes ovarian cancer stemness and tumor initiation via FGFR1/SRC/STAT3 signaling." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 40.1 (2021): 319. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-02117-z
Research has revealed that L1CAM is highly expressed in ovarian cancer stem cells and drives tumorigenesis and chemotherapy resistance by activating the FGFR1/SRC/STAT3 pathway. Its monoclonal antibody can inhibit the characteristics of stem cells, providing a new direction for targeted therapy.
Creative Biolabs: L1CAM Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality L1CAM antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom L1CAM Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our L1CAM antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Angiolini, Francesca, and Ugo Cavallaro. "The pleiotropic role of L1CAM in tumor vasculature." International journal of molecular sciences 18.2 (2017): 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020254
Anti-L1CAM antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179983) (CBMAB-A1369-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12567) (CBMAB-1057-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








