OCA2 Antibodies
Background
The OCA2 gene encodes a transmembrane protein located on the melanosome membrane, which mainly participates in the synthesis and transport of melanin. This protein regulates the pH value and tyrosinase activity within melanosomes, controlling the ratio of eumelanin to browomelanin, and thereby influencing the pigmentation of the skin, hair and eyes. The genetic variation of the OCA2 gene is the main cause of type 2 oculocutaneous albinism, which is characterized by abnormal vision, transparent iris and skin susceptibility to ultraviolet damage. This gene was first identified in 1994 through chromosomal localization cloning technology. Its research not only revealed the molecular mechanism of human pigment formation but also provided genetic evidence for tracing the history of human migration - for instance, the single nucleotide polymorphism (rs12913832) in the HERC2 region of the OCA2 gene was confirmed to be a key variation determining the blue-eye trait. The in-depth exploration of OCA2 continuously drives the development of fields such as genetic disease diagnosis and treatment, skin color evolution adaptation, and molecular anthropology.
Structure of OCA2
The OCA2 gene encodes a transmembrane protein located on the melanosome membrane, with a molecular weight of approximately 110 kDa. The amino acid sequence of this protein shows certain differences among different species, which affects the specific mechanism by which it regulates the pH value of melanosomes and substrate transport.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Pig |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 110 | 108 | 105 | 109 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Loss of function of P protein causes albinism | Color lightening model | Affect the pigment pattern of the embryo | Research model of skin pigmentation |
This protein is composed of 838 amino acids, and its transmembrane domain forms an ion channel-like structure, which is responsible for regulating the pH environment within melanosomes. The core functional domain of the OCA2 protein contains a key substrate binding site, which affects the activity of tyrosinase through allosteric effects. Its N-glycosylation modification is crucial for the correct folding and membrane localization of proteins, while the leucine zipper motif at the C-terminal mediates the homologous dimerization process of proteins, which is indispensable for maintaining its transport function.
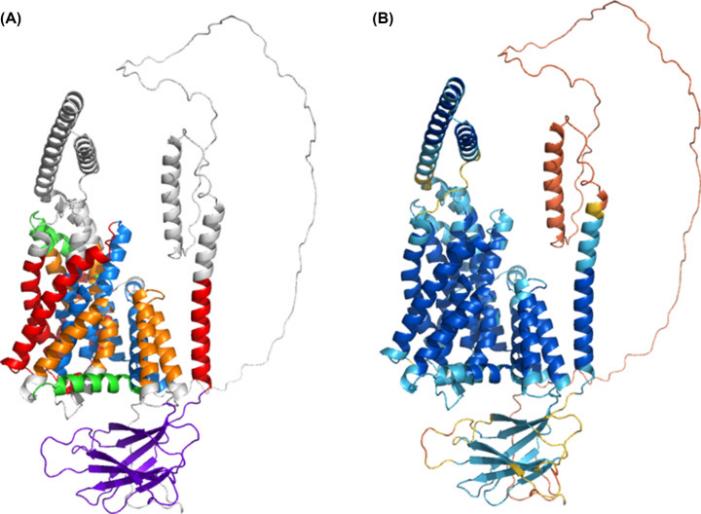 Fig. 1 AlphaFold2 Oca2 model.1
Fig. 1 AlphaFold2 Oca2 model.1
Key structural properties of OCA2:
- Multiple transmembrane topological structures
- Form ion channels on the melanosome membrane
- With pH sensing and regulation function domain
- Leucine zipper motif mediates dimerization
Functions of OCA2
The core function of the OCA2 protein is to regulate the acid-base balance and substrate transport within melanosomes. However, it is also widely involved in various physiological processes such as pigment synthesis, embryonic development, and the formation of visual pathways.
| Function | Description |
| Melanosome pH regulation | Transporting ions through transmembrane structures to maintain the weakly acidic environment inside melanosomes is a necessary condition for the activity of tyrosinase. |
| Regulation of melanin types | Its pH regulation function directly affects the synthesis ratio of eumelanin and pheomelanin, ultimately determining the color of hair, skin and eyes. |
| Embryonic development participation | Expressed during the migration of neural crest cells and the development of retinal pigment epithelium, it is crucial for the normal formation of the visual system. |
| The pathological basis of albinism | The loss of gene function leads to an imbalance in the pH of melanosomes and a severe insufficiency in melanin synthesis, triggering the typical symptoms of type 2 ocular skin albinism. |
| Association of skin color differences among people | The genetic variation of non-pathogenic polymorphism (such as HERC2 area) is in Europe people light skin and blue eyes character appears one of the main factors. |
The functional realization of this protein depends on its precise ion channel activity, which contrasts with the co-oxygen-binding characteristics of hemoglobin, demonstrating its dedicated role in maintaining the homeostasis of the organelle microenvironment.
Applications of OCA2 and OCA2 Antibody in Literature
1. Cho, Eunbyul, et al. "Modulating OCA2 Expression as a Promising Approach to Enhance Skin Brightness and Reduce Dark Spots." Biomolecules 14.10 (2024): 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14101284
This study confirmed that the OCA2 gene is an effective target for improving skin pigmentation. By screening active ingredients that can reduce OCA2 expression and developing corresponding formulas, clinical trials have shown that its effect in improving skin tone and fading pigmentation is superior to that of vitamin C, providing a new strategy for pigment management.
2. Clark, Bethan, et al. "Oca2 targeting using CRISPR/Cas9 in the Malawi cichlid Astatotilapia calliptera." Royal Society Open Science 9.4 (2022): 220077. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.220077
The research successfully applied CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology for the first time in Lake Malawi mackerel to target and knockout the oca2 gene. The results show that the deletion of this gene leads to a complete lack of melanin in the fish, which not only verifies the key role of oca2 in the formation of fish pigments, but also provides an important tool for studying the diversity and evolution of this species group.
3. Mesdaghi, Shahram, et al. "Structural insights into pink-eyed dilution protein (Oca2)." Bioscience Reports 43.7 (2023): BSR20230060. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20230060
This study utilized advanced technologies such as AlphaFold2 to precisely resolve the three-dimensional structure of the human OCA2 protein for the first time. The model reveals that it has the typical topological structure of a transporter protein, a GOLD domain responsible for intracellular transport, and suggests that it may perform substrate transport functions through an "elevator" mechanism, overturning previous understanding of its structure.
4. Green, David J., et al. "The co-occurrence of genetic variants in the TYR and OCA2 genes confers susceptibility to albinism." Nature Communications 15.1 (2024): 8436. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-52763-y
Research has found that individuals carrying A specific combination of TYR and OCA2 gene variations (OCA2:c.1327G>A) simultaneously with heterozygous have a significantly increased risk of developing albinism. This reveals the significant impact of inter-gene interactions on the manifestations of rare diseases such as albinism, providing a new perspective for understanding the complexity of diseases.
5. Caduff, Madleina, et al. "OCA2 splice site variant in German Spitz dogs with oculocutaneous albinism." PLoS One 12.10 (2017): e0185944. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185944
In a family of German sharp-billed dogs, researchers discovered an abnormal coat color that causes the puppies to have light brown fur and blue eyes. Through genetic analysis, they confirmed that this trait was caused by a pathogenic mutation at the 5' end splicing site of the OCA2 gene and corrected the incorrect annotation of this gene in the canine reference genome.
Creative Biolabs: OCA2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality OCA2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom OCA2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our OCA2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Mesdaghi, Shahram, et al. "Structural insights into pink-eyed dilution protein (Oca2)." Bioscience Reports 43.7 (2023): BSR20230060. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20230060
Anti-OCA2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (61-3E7) (CBMAB-1183-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1200) (CBMAB-C1467-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-CD300A Recombinant Antibody (172224) (CBMAB-C0423-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CDKL5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1629) (CBMAB-C1689-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








