Phosphotyrosine Antibodies
Background
Phosphotyrosine is not an independent gene but a functional state after phosphorylation modification of tyrosine residues in proteins, and it is widely present in the signal transduction systems of vertebrate cells. This modification is accomplished through tyrosine kinase catalysis, which can regulate protein conformation and activity, and thereby mediate key life processes such as cell growth, differentiation and metabolism. Its discovery can be traced back to the research on the carcinogenic mechanism of tumor viruses in the 1970s. This breakthrough directly revealed the principle of protein phosphorylation regulation in cell signal transduction, laying a molecular foundation for the subsequent drug development of various kinase inhibitors. As a core regulatory element of the cellular signaling network, the research on the dynamic modification of phosphorylated tyrosine has greatly advanced people's understanding of the pathological mechanisms of cancer, immune diseases, etc., and promoted the development of targeted treatment strategies.
Structure of Phosphotyrosine
Phosphotyrosine is not an independent gene product but a functional unit formed by phosphorylation modification of tyrosine residues in proteins. Its molecular mass depends on the host protein being modified. There are significant differences in the structural microenvironment of this modification site among different proteins:
| Species | Src kinase | Insulin receptor | STAT transcription factor | SH2 adaptor protein |
| Modification site structure | Auto-phosphorylated tyrosine residues | Activate the cyclic tyrosine cluster | Binding site of SH2 domain | Signal recruitment module |
| Functional features | Regulate kinase activity and substrate recognition | Mediate metabolic signal transduction | Participate in nuclear signal transmission | Promote the assembly of signal complexes |
This modification is dynamically regulated by tyrosine kinase/phosphatase, and its molecular mechanism includes: conserved phosphorylation site sequence, SH2 domain-specific recognition module, and phosphorylation-induced conformational rearrangement. This reversible modification precisely regulates the opening and closing of cellular signaling pathways by altering the charge distribution and spatial conformation of proteins.
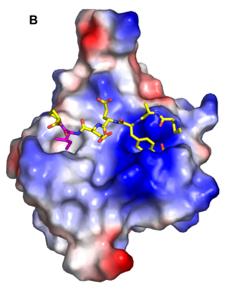 Fig. 1 Phosphotyrosine Binding in the SH2 Domain Electropositive Pocket.1
Fig. 1 Phosphotyrosine Binding in the SH2 Domain Electropositive Pocket.1
Key structural properties of Phosphotyrosine:
- Covalent structure of aromatic cyclic phosphates
- Phosphate groups with double negative charges
- Tyrosine hydroxyl phosphorylation modification
Functions of Phosphotyrosine
The core function of tyrosine phosphate is to act as a molecular switch for cellular signal transduction. However, it is also involved in the regulation of various pathophysiological processes, including cell growth, differentiation and immune response.
| Function | Description |
| Signal switch | By reversible phosphorylation to activate or inactivate protein functions, it directly regulates the opening and closing of intracellular signaling pathways. |
| Regulation of cell proliferation | Mitogenic signals are transmitted in the growth factor receptor pathway to drive cell cycle progression and division. |
| Immune regulation | Involved in T cell and B cell receptor signal transduction, regulation of immune cell activation, differentiation and response intensity. |
| Metabolic regulation | Mediates downstream signals of insulin receptors and affects core metabolic processes such as glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis. |
| Pathological occurrence | Abnormal phosphorylation is the core molecular mechanism in many diseases such as cancer and autoimmune diseases, which drives the pathological process. |
Consistent with the transient and reversible phosphorylation modification characteristics, the phosphotyrosine signal has the features of rapid initiation and precise termination, which makes it the basis for efficient and dynamic signal transduction, especially suitable for cellular life activities that require rapid response.
Applications of Phosphotyrosine and Phosphotyrosine Antibody in Literature
1. Kaneko, Tomonori, et al. "Phosphotyrosine recognition domains: the typical, the atypical and the versatile." Cell Communication and Signaling 10.1 (2012): 32.https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-811X-10-32
The article indicates that the SH2 domain is a key module for tyrosine phosphorylation (pTyr) recognition. In recent years, the domains such as PTB and C2 discovered together constitute the pTyr recognition superfamily. Their regulatory mechanisms are complex and diverse, and they have significant value in cell signal transduction and disease treatment.
2. Ushiro, Hiroshi, and S. Cohen. "Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes." Journal of Biological Chemistry 255.18 (1980): 8363-8365.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)43497-7
The article indicates that EGF can activate protein kinases in the cell membrane of A-431. This kinase (i.e., the EGF receptor complex) mainly phosphorylates tyrosine in the substrate protein rather than serine or threonine.
3. Martensen, T. M. "Phosphotyrosine in proteins. Stability and quantification." Journal of Biological Chemistry 257.16 (1982): 9648-9652. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)34121-8
This study established a method for quantitative analysis of phosphorylated tyrosine in proteins. Through rapid alkaline hydrolysis treatment, the recovery rate of phosphorylated tyrosine can reach up to 80% and is stable. Quantitative or radiochemical detection can be carried out using an amino acid analyzer.
4. Zhang, Zhong-Yin. "Are Protein-tyrosine Phosphatases Specific for Phosphotyrosine?." Journal of Biological Chemistry 270.27 (1995): 16052-16055. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(17)48826-0
This article develops a highly sensitive fluorescence-based biosensor using quantum dots conjugated with plastic antibodies to detect myoglobin at femtomolar concentrations, providing a cost-effective, selective, and stable alternative for early myocardial infarction diagnosis in human serum.
5. Kalab, Petr, et al. "p95, the major phosphotyrosine-containing protein in mouse spermatozoa, is a hexokinase with unique properties." Journal of Biological Chemistry 269.5 (1994): 3810-3817. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)41932-6
Research has found that the p95/116 protein in mouse sperm, which can bind to the ZP3 glycoprotein of the egg, is actually hexokinase phosphorylated from tyrosine. This phosphorylated form is unique to sperm and testicles and is distinct from other tissues.
Creative Biolabs: Phosphotyrosine Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality Phosphotyrosine antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom Phosphotyrosine Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our Phosphotyrosine antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Nachman, Joseph, et al. "Conformational determinants of phosphotyrosine peptides complexed with the Src SH2 domain." PLoS One 5.6 (2010): e11215. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011215
Anti-Phosphotyrosine antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








