PIKFYVE Antibodies
Background
PIKFYVE is a phosphoinositol kinase mainly present in eukaryotic cells and is located in the intracellular endosome-lysosomal membrane system. The protein encoded by this gene is anchored to the membrane structure through its unique FYVE domain, and it possesses both kinase activity and phosphatase activity. It can catalyze the conversion of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate to phosphatidylinositol 3, 5-diphosphate. This process is crucial for maintaining endosome maturation, lysosomal functional homeostasis and autophagic flux regulation. In 2001, when Shisheva's team systematically characterized its function at the molecular level, they discovered that abnormal activity of PIKFYVE would directly cause abnormal lysosomal morphology and intracellular vesicle transport disorders, which are closely related to pathological processes such as neurodegenerative diseases and cancer immune responses. Its unique bifunctional enzyme characteristics provide an important theoretical basis for the development of novel therapies targeting the lysosomal pathway.
Structure of PIKFYVE
PIKFYVE is a high-molecular-weight protein, with a molecular weight of approximately 240-250 kDa across different species. This protein contains multiple conserved domains, and its composition varies slightly among different species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 244 | 242 | 245 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains FYVE and DEP domains | FYVE domains structure highly conservative | Kinase domain structure sequence similarity is extremely high |
PIKFYVE is composed of 2098 amino acids, forming a complex multi-domain architecture. The core is a characteristic FYVE domain that anchors the protein to the endosomal membrane by binding to phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. The catalytic domain at the C-terminal has unique bifunctional activity, which can not only act as phosphoinositol 5-kinase to synthesize PI(3,5)P2, but also function as a phosphatase. The activity of this protein is crucial for maintaining the membrane dynamic balance of the endosome-lysosomal system. Its dysfunction will directly lead to abnormal lysosomal morphology and obstruction of the autophagy process.
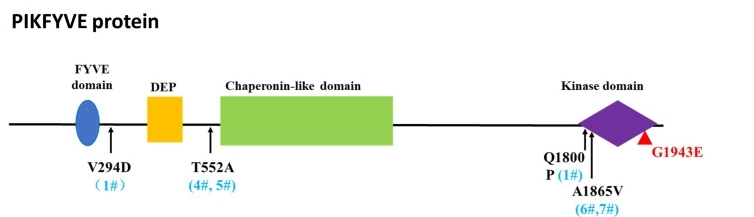 Fig. 1 The amino acid changes of identified variants and their positions in PIKFYVE protein.1
Fig. 1 The amino acid changes of identified variants and their positions in PIKFYVE protein.1
Key structural properties of PIKFYVE:
- Multi-domain composite architecture
- Characteristic FYVE zinc finger anchor structure used in film
- Unique bifunctional catalytic domain (kinase/phosphatase)
Functions of PIKFYVE
The core function of PIKFYVE is to regulate intracellular vesicle transport and membrane dynamic balance. In addition, it is also involved in various cellular processes, including autophagy regulation and the maintenance of ion homeostasis.
| Function | Description |
| Membrane transport regulation | By generating PI(3,5)P2 signaling molecules, it guides the maturation of endosomes and the vesicle transport process between lysosomes and Golgi apparatus. |
| Autophagic flow management | Maintain the functional integrity of lysosomes and ensure the effective fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes as well as the degradation of their contents. |
| Ion steady-state | Affect the lysosome ion channel activity, participate in bivalent cation of intracellular calcium ion balance adjustment. |
| Inflammatory regulation | By influencing the assembly of the endosomal signal platform, it participates in the positive and negative regulation of the TLR/ILR signal pathway. |
| Cell survival | The inactivation of its function can cause vacuolation of lysosomes, eventually leading to cell death. |
The uniqueness of PIKFYVE lies in the fact that the kinase activity for synthesizing PI(3,5)P2 and the phosphatase activity for degrading this signal coexist in the same protein molecule. This biffunctional design enables rapid local circulation of lipid second messengers and can maintain membrane microdomain signal homestability more precisely compared to single-function enzyme systems.
Applications of PIKFYVE and PIKFYVE Antibody in Literature
1. Cheng, Caleb, et al. "Targeting PIKfyve-driven lipid metabolism in pancreatic cancer." Nature (2025): 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08917-z
This study reveals that PIKfyve is a key vulnerable target for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Inhibiting PIKfyve can disrupt tumor metabolism, forcing PDAC to rely on lipid synthesis pathways. The combined use of PIKfyve inhibitors and KRAS-MAPK targeted therapy has demonstrated a synergistic anti-tumor effect in preclinical models.
2. Choi, Jae Eun, et al. "PIKfyve, expressed by CD11c-positive cells, controls tumor immunity." Nature communications 15.1 (2024): 5487. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48931-9
Studies have shown that PIKfyve is a negative regulatory factor for dendritic cell (DC) function. Inhibiting PIKfyve can enhance DC function through the non-classical NF-κB pathway, activate T-cell immunity, and thereby inhibit tumor growth. The combination of PIKfyve inhibitors with immune checkpoint blockers or vaccine adjuvants has demonstrated a significant synergistic anti-tumor effect.
3. Hasegawa, Junya, Ken Inoki, and Lois S. Weisman. "PIKFYVE-dependent regulation of MTORC1 and TFEB." Autophagy Reports 1.1 (2022): 247-251. https://doi.org/10.1080/27694127.2022.2082201
Research has found that PIKfyve maintains the activity of MTORC1 on lysosomes by regulating RRAG GTPases, thereby inhibiting the transcription factor TFEB. Inhibiting PIKfyve disrupts the interaction between MTORC1 and TFEB, causing TFEB to remain activated by PPP2 phosphatase and incorporated into the nucleus even when nutritionally abundant, thereby initiating the transcription of related genes.
4. Liggins, Marc C., et al. "PIKfyve regulates melanosome biogenesis." PLoS genetics 14.3 (2018): e1007290. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1007290
This study reveals a new role of PIKfyve in melanosome formation. Inhibiting PIKfyve can block melanosome maturation, affect the transport of PMEL and TYRP1 proteins, and lead to the accumulation of multi-vesicular endosom-like structures. This function is independent of its known role in lysosomal regeneration, indicating that PIKfyve precisely regulates the delivery of proteins from endosomes to melanosomes.
5. Bao, Yi, et al. "Targeting the lipid kinase PIKfyve upregulates surface expression of MHC class I to augment cancer immunotherapy." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 120.49 (2023): e2314416120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2314416120
This study found that targeted inhibition of PIKfyve can effectively upregulate the expression of MHC-I on the surface of cancer cells. This mechanism can reverse the immune escape of tumors, enhance the response to immunotherapy, and provide a new combined treatment strategy for a variety of refractory cancers, including pancreatic cancer.
Creative Biolabs: PIKFYVE Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PIKFYVE antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PIKFYVE Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PIKFYVE antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Mei, Shaoyi, et al. "Disruption of PIKFYVE causes congenital cataract in human and zebrafish." Elife 11 (2022): e71256. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.71256
Anti-PIKFYVE antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DLG1 Monolconal Antibody (4F3) (CBMAB-0225-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BBS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0253) (CBMAB-0254-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BZLF1 Recombinant Antibody (BZ.1) (CBMAB-AP705LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (A2) (CBMAB-A2316-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








