PLAA Antibodies
Background
PLAA gene encodes an enzyme involved in phospholipid metabolism, which is mainly found in the peroxisome of eukaryotic cells. This protein maintains the stability of cell membranes and participates in the myelin formation of neural tissues by catalyzing the key steps of the phospholipid synthesis pathway. Studies have found that mutations in the PLAA gene are closely related to rare neurodegenerative diseases (such as rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata type), and patients will experience abnormal bone development and neurological dysfunction. Although this gene was first identified in the 1990s, it was not until 2015 that the precise structure of its protein complex was successfully resolved through cryo-electron microscopy technology. As an important research object in the field of lipid metabolism, the PLAA gene provides a key molecular basis for understanding peroxisome function and abnormal diseases of sphingolipid metabolism.
Structure of PLAA
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the PLAA gene is approximately 85 kDa, and there are minor differences among different species, mainly due to conserved variations in functional domains:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 85.3 | 84.9 | 85.1 | 84.6 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains UBX domain and CDC48 interaction region | Highly conserved, with only individual amino acid substitutions | The functional domains are exactly the same | Short alternative spliceosome is present |
The PLAA protein is composed of 796 amino acids and has a typical AAA-ATPase domain and UBX regulatory motif, forming a synergistic bilayer tertiary structure. Its N-terminal is responsible for binding to ubiquitine-modified proteins, while the CDC48 binding region at the C-terminal drives substrate unfolding through ATP hydrolysis.
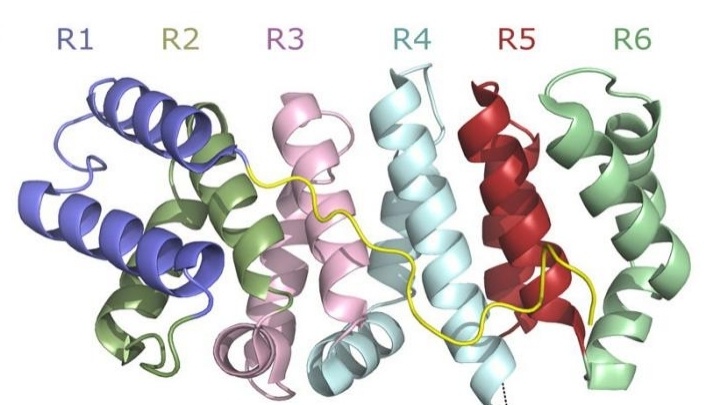 Fig. 1 Structural Domains of PLAA: WD40 β-Propeller, Central PFU, and C-terminal PUL Domains with ARM-Colored Secondary Elements.1
Fig. 1 Structural Domains of PLAA: WD40 β-Propeller, Central PFU, and C-terminal PUL Domains with ARM-Colored Secondary Elements.1
Key structural properties of PLAA:
- D2 ring (amino acids at positions 302-308)
- Hydrophobic channel (composed of α -helical bundles)
- The UBX domain (amino acids at positions 650-720)
Functions of PLAA
The core function of the PLAA gene-encoded protein (phospholipase A2 activating protein) is to regulate intracellular phospholipid metabolism, and it is also involved in a variety of key physiological and pathological processes:
| Function | Description |
| Phospholipase A2 activation | By binding and activating the PLA2 enzyme, it catalyzes the hydrolysis of membrane phospholipids to generate precursors of inflammatory mediators such as arachidonic acid. |
| Endoplasmic reticulum-related degradation (ERAD) | As a CDC48/p97 complex linker protein, it recognizes ubiquitinated misfolded proteins and guides them into the proteasome degradation pathway. |
| Peroxisome function is maintained | Mediating the biosynthesis of phospholipids, it plays a decisive role in the formation of nerve myelin and sperm motility. |
| Cellular stress response | Regulate lipid raft dynamics during oxidative stress and affect apoptotic signaling pathways (such as TNF-α receptor recruitment). |
| Regulation of autophagy initiation | Through the interaction of the ULK1 complex, it promotes the formation of autophagy precursor membranes (especially under nutrient-deficient conditions). |
The action mode of PLAA protein shows ATP concentration dependence, similar to the oxygen dissociation curve of myoglobin. The enzymatic reaction kinetics curve of PLAA exhibits allosteric characteristics, and a synergistic activation effect occurs when the concentration of phospholipid reaches the threshold (about 50μM).
Applications of PLAA and PLAA Antibody in Literature
1. Shen, Zhangjin, et al. "PLAA suppresses ovarian cancer metastasis via METTL3-mediated m6A modification of TRPC3 mRNA." Oncogene 41.35 (2022): 4145-4158. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02411-w
The article indicates that PLAA is significantly down-regulated in ovarian cancer, and its low expression is associated with a poor prognosis. PLAA degrades METTL3 through ubiquitination, reduces the m6A modification of TRPC3, and inhibits Ca²⁺influx, thereby preventing the migration and metastasis of cancer cells. This mechanism provides a new target for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
2. Iacomino, Michele, et al. "Allelic heterogeneity and abnormal vesicle recycling in PLAA-related neurodevelopmental disorders." Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 17 (2024): 1268013. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2024.1268013
The article indicates that the nascent missense variations in the PUL domain of the PLAA gene are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) in children, including intellectual disability and autism. The variation leads to the weakening of the PLAA-p97/VCP interaction, affecting the synaptic vesicle cycle and expanding the understanding of the phenotype and mechanism of PLAA-related neurological diseases.
3. Ribardo, Deborah A., et al. "Prostaglandin levels in stimulated macrophages are controlled by phospholipase A2-activating protein and by activation of phospholipase C and D." Journal of Biological Chemistry 276.8 (2001): 5467-5475. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m006690200
The article indicates that PLAA (phospholipase A2 activating protein) participates in the inflammatory response by regulating the expression of PLA2 and COX-2, promoting the synthesis of PGE2 in macrophages. Its 503-538 sites are homologous to melittin, and after activation, it can enhance the generation of PGE2. The expression of PLAA is elevated in the inflammatory intestinal mucosa, suggesting its potential as a new target for inflammation treatment.
4. Fu, Qing-Shan, et al. "Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition by a novel domain from human phospholipase A2-activating protein." Journal of Biological Chemistry 284.28 (2009): 19043-19052. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.009126
The article indicates that the PFU domain (386-465 residues) of the human PLAA protein binds ubiquitin (Ub) through a novel folding structure, with its α2 helix being the key binding site. This domain exists in the form of cis/trans isomers, both of which have Ub binding capabilities, revealing the molecular mechanism of PLAA in ubiquitination and endoplasmic reticulum-related degradation (ERAD).
5. Seguin, S. J., et al. "Inhibition of autophagy, lysosome and VCP function impairs stress granule assembly." Cell Death & Differentiation 21.12 (2014): 1838-1851. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2014.103
Research has found that PLAA, as a VCP cofactor, participates in the assembly regulation of stress granules (SG). When the autophagy-lysosomal pathway or VCP function is impaired, PLAA silencing leads to the abnormal retention of defective ribosomal products (DRIPs) and 60S ribosomes in the SG, altering the morphology and composition of the SG and suggesting its potential mechanism of action in neurodegenerative diseases.
Creative Biolabs: PLAA Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PLAA antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PLAA Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PLAA antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Qiu, Liyan, et al. "Structure and function of the PLAA/Ufd3-p97/Cdc48 complex." Journal of Biological Chemistry 285.1 (2010): 365-372.https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m109.044685
Anti-PLAA antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FOSB Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3593) (CBMAB-F2522-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-APOE Recombinant Antibody (A1) (CBMAB-0078CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALK (Phosphorylated Y1278) Recombinant Antibody (D59G10) (PTM-CBMAB-0035YC)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






