PRDM1 Antibodies
Background
The PRDM1 gene encodes a transcription factor called B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1 (Blimp-1), which mainly regulates the transcriptional activity of target genes by binding to specific DNA sequences within the cell nucleus. Its core function is to drive the process of B lymphocytes differentiating into plasma cells and maintain the terminal differentiation state of cells by inhibiting the expression of multiple immune-related genes, such as BCL6 and CIITA. In the development of the immune system, PRDM1 plays a crucial role in establishing the functional integrity of antibody-secreting cells, and its abnormal expression is closely related to autoimmune diseases, lymphoma and immunodeficiency syndrome. This gene was first identified in 1994. The study of its three-dimensional structure revealed how the zinc finger domain specifically recognizes the gene promoter region. This mechanism provides a molecular basis for understanding immune cell differentiation and tumorigenesis, and has now become an important target in the research of immune regulation and tumor treatment.
Structure of PRDM1
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the PRDM1 gene is approximately 92 kDa, and its precise value varies among different species. For specific data, please refer to the table below:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 92.5 | 91.8 | 89.2 | 90.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 1076 amino acids, the typical structure of PR/SET domain | Sequence variation exists in the N-terminal regulatory region | The small number structure of zinc finger domains | Proline enrichment region sequence is relatively simple |
This protein is composed of multiple functional domains: although the PR/SET domain at the N-terminal lacks histone methyltransferase activity, it participates in protein-protein interactions; The central proline-rich region mediates transcriptional inhibitory function; The C-terminal contains five C2H2-type zinc finger structures, which are responsible for the recognition and binding of specific DNA sequences. Its secondary structure is mainly α -helix, which, together with β -folding, forms a stable spatial conformation. The zinc finger module coordinates with zinc ions through conserved cysteine and histidine residues to form fingered protrusions, which precisely embed into the DNA grooves for target gene regulation. This multi-domain structure enables it to recruit histone modification complexes, which play a core regulatory role in the terminal differentiation of B cells.
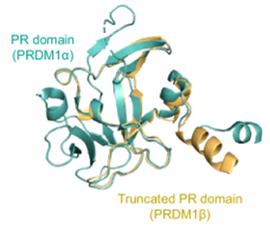 Fig. 1 Protein structures of PRDM1α and PRDM1β.1
Fig. 1 Protein structures of PRDM1α and PRDM1β.1
Key structural properties of PRDM1:
- Transcription factor modules composed of multiple domains
- N-terminal PR/SET domain mediated protein interaction but had no catalytic activity
- The C-terminal zinc finger array achieves DNA-specific recognition through ββα folding
- Proline enrichment region formed intramolecular interaction interface regulation of transcription
Functions of PRDM1
The core function of the PRDM1 gene is to act as the "master regulatory switch" for cell differentiation, but its mechanism of action covers a multi-level immune regulatory network:
| Function | Description |
| Cell fate determination | By inhibiting the expression of B-cell-related genes (such as BCL6 and PAX5), B lymphocytes are driven to differentiate into plasma cells at the terminal stage. |
| Maintenance of immune homeostasis | Negative regulating T cell activation threshold, prevent excessive immune response, the lack of easy cause autoimmune disease. |
| Epigenetic reconfiguration | Recruit histone modification complexes (such as HDACs, G9a) to the promoter region of the target gene to establish a transcriptional inhibitory chromatin state. |
| Tumor suppressive regulation | As a tumor suppressor factor in lymphoma, it functions by blocking the cell cycle process and promoting apoptotic signaling pathways. |
| Metabolic reprogramming | Coordinate the metabolic network transitions required for mitochondrial biosynthesis and antibody secretion in plasma cells. |
This gene achieves functional specificity through a "synergistic inhibition circuit" : its zinc finger domain recognizes a specific palindromic sequence (5'-GAAAGGCAA-3') in the promoter of the target gene, while the N-terminal inhibition domain recruits chromatin remodeling complexes, forming a positive feedback regulatory circuit. This dual-lock mechanism ensures precise control over the fate transformation of immune cells under conditions such as cell stress, differentiation signals, or oncogenic mutations. Its functional disorders are closely related to diseases such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Applications of PRDM1 and PRDM1 Antibody in Literature
1. Li, Qing, et al. "PRDM1/BLIMP1 induces cancer immune evasion by modulating the USP22-SPI1-PD-L1 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells." Nature communications 13.1 (2022): 7677. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35469-x
The article indicates that PRDM1 in liver cancer can promote the expression of PD-L1, induce T cell exhaustion, and weaken its own anti-cancer effect. Studies have shown that the combination of PD-1 blockade can enhance the therapeutic effect, providing a new combined treatment approach for such patients.
2. Hu, Xing, et al. "PHLDA1-PRDM1 mediates the effect of lentiviral vectors on fate-determination of human retinal progenitor cells." Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 81.1 (2024): 305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-024-05279-z
Research has found that lentiviral vectors activate PRDM1 by up-regulating PHLDA1, leading to abnormal differentiation of retinal progenitor cells into photoreceptors. Inhibiting the PHLDA1-PRDM1 axis can avoid this risk, providing a safe new strategy for gene therapy of congenital eye diseases.
3. Guo, Huidong, et al. "PRDM1 drives human primary T cell hyporesponsiveness by altering the T cell transcriptome and epigenome." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 879501. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.879501
Studies have revealed that low expression of PRDM1 is associated with acute graft-versus-host disease. PRDM1 can serve as a key factor, inducing low T cell response through epigenetic regulation and promoting Treg amplification, providing a new target for the prevention and treatment of aGVHD.
4. Jin, Han, et al. "Identification of a PRDM1-regulated T cell network to regulate atherosclerotic plaque inflammation." Genome Medicine 17.1 (2025): 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-025-01541-6
Research has found that the down-regulation of PRDM1 expression in T cells within plaques can exacerbate atherosclerosis. This factor constitutes a key protective network, and its absence leads to plaque instability, making it a potential therapeutic target.
5. Zhou, Bo, et al. "A potential prognostic marker PRDM1 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma." Journal of Oncology 2022.1 (2022): 1934381. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1934381
Research has found that PRDM1 is highly expressed in pancreatic cancer. Its methylation modification, the tumor-related pathways it regulates, and its association with immune cell infiltration jointly promote cancer and lead to a poor prognosis, making it a potential biomarker and therapeutic target.
Creative Biolabs: PRDM1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PRDM1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PRDM1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PRDM1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zhou, Jianfeng, et al. "Chromatin landscape dynamics during reprogramming towards human naïve and primed pluripotency reveals the divergent function of PRDM1 isoforms." Cell Death Discovery 10.1 (2024): 474. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-024-02230-w
Anti-PRDM1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (P67.6) (CBMAB-C10189-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0733) (CBMAB-F0435-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






