RAD51C Antibodies
Background
RAD51C is an important DNA repair protein in the human body and is a member of the RAD51 homologous recombinase family. The protein encoded by this gene plays a key role in the homologous recombination repair process of DNA double-strand breaks, and participates in DNA strand exchange and damage repair by forming complexes with other recombinases (such as RAD51B, RAD51D, etc.). Research has found that mutations in the RAD51C gene are associated with hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOC) and may increase sensitivity to PARP inhibitors. Its functional research not only deepens people's understanding of the mechanism of DNA damage repair, but also provides new molecular targets for tumor-targeted therapy.
Structure of RAD51C
Myoglobin is a relatively small protein with a molecular weight of approximately 16.7 kDa. This weight may slightly vary between species due to minor differences in amino acid sequence.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 37.0 | 36.8 | 37.2 | 36.9 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Composed of 376 amino acids, it belongs to the RAD51 protein family | The homology with human is up to 85% | The typical structure of rec a domain | Contains conserved ATP binding sites |
The RAD51C protein forms oligomers through its core RecA domain, which mediates DNA binding and strand exchange activities. Its tertiary structure contains a typical nucleotide-binding pocket, and the binding and hydrolysis of ATP regulate its interaction with DNA and repair function. This protein forms a stable BCDX2 complex with partners such as RAD51B and RAD51D, playing a key role in DNA homologous recombination repair.
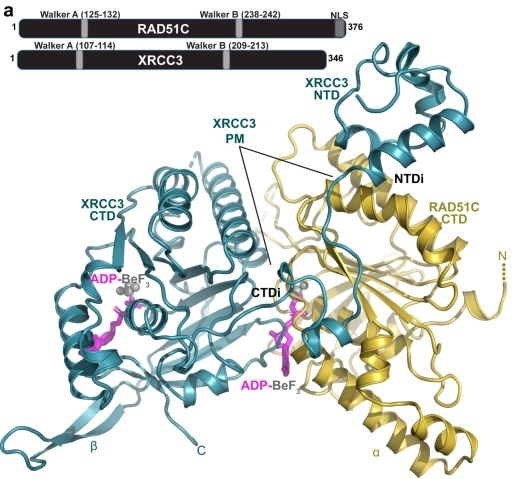 Fig. 1 Structure of the RAD51C-XRCC3 (CX3) complex with key domains and bound ATP analog.1
Fig. 1 Structure of the RAD51C-XRCC3 (CX3) complex with key domains and bound ATP analog.1
Key structural properties of RAD51C:
- Stable heteropolymer complex
- Conservative RecA-like domains
- Nucleotide-binding pocket
- The key DNA binding interface
Functions of RAD51C
The core function of the RAD51C gene is homologous recombination repair (HRR) to maintain genomic stability. In addition, it is also involved in key cellular processes such as DNA damage response, regulation of cell cycle checkpoints, and telomere maintenance.
| Function | Description |
| DNA double-strand break repair | As a RAD51 collateral homologous protein, it catalyzes DNA strand invasion and exchange in DNA homologous recombination repair, ensuring accurate repair. |
| BCDX2 complex assembly | Forms complexes with RAD51B, RAD51D, and XRCC2 that mediate core steps during repair and maintain genomic integrity. |
| Cell cycle regulation | Participate in the activation of DNA damage checkpoints in the S/G2 phase, prevent damaged DNA from entering mitosis, and avoid mutation accumulation. |
| Tumor suppressive function | As a tumor suppressor gene, its germline mutations are significantly associated with the susceptibility to hereditary breast cancer, ovarian cancer and other cancers. |
| Copy fork protection and restart | Under replication stress conditions, stably stagnate replication forks to prevent fork collapse and facilitate the smooth restart of replication. |
RAD51C has high substrate specificity in the HRR pathway. The loss of its function will lead to repair defects and increase sensitivity to PARP inhibitors. This characteristic has been applied to targeted treatment strategies for tumors.
Applications of RAD51C and RAD51C Antibody in Literature
1. Yang, et al. "Ovarian and breast cancer risks associated with pathogenic variants in RAD51C and RAD51D." JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute 112.12 (2020): 1242-1250. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djaa030
This study confirmed that pathogenic variations in the RAD51C and RAD51D genes significantly increase the risk of ovarian cancer (TOC) and breast cancer (BC) in the fallopian tubes. At the age of 80, the cumulative risks of TOC for carriers were 11% and 13% respectively, and the risks of BC were 21% and 20% respectively. The risk increases with the aggravation of family history, reaching up to 32-36% (TOC) and 44-46% (BC). The results support the inclusion of these two genes in cancer risk assessment and genetic counseling.
2. Greenhough, Luke A., et al. "Structure and function of the RAD51B–RAD51C–RAD51D–XRCC2 tumour suppressor." Nature 619.7970 (2023): 650-657. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06179-1
The research has revealed the core role of RAD51C in the BCDX2 complex. This complex, by simulating the structure of RAD51 nucleoprotein filaments, synergistically stimulates the nucleation and extension of RAD51 on DNA, which is crucial for replication cross protection and double-strand break repair. Its functional defects will lead to cancer susceptibility.
3. Hanson, Helen, et al. "UK consensus recommendations for clinical management of cancer risk for women with germline pathogenic variants in cancer predisposition genes: RAD51C, RAD51D, BRIP1 and PALB2." Journal of medical genetics 60.5 (2023): 417-429. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg-2022-108898
Studies have revealed that germline pathogenic variations of genes such as RAD51C moderately increase the risk of ovarian and breast cancer, but there is a lack of clinical management guidelines. The British expert meeting reached a consensus on this, aiming to provide clear clinical practice recommendations for the risk management of carriers (such as RAD51C).
4. Longo, Michael A., et al. "RAD51C-XRCC3 structure and cancer patient mutations define DNA replication roles." Nature communications 14.1 (2023): 4445. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40096-1
This study analyzed the structure of the RAD51C-XRCC3 complex and revealed the new function of RAD51C in replicating the pressure response. It regulates the protection, reactivation and reversal of DNA replication forks through specific domains respectively, and these functions are related to tumorigenesis. The research provides a key molecular basis for the functional testing and classification of RAD51C mutations in cancer patients.
5. Yamamoto, Hideki, and Akira Hirasawa. "Homologous recombination deficiencies and hereditary tumors." International journal of molecular sciences 23.1 (2021): 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010348
This study demonstrates that homologous recombination (HR) is a key mechanism for maintaining genomic stability. In addition to BRCA1/2, germline variations of genes such as RAD51C are also associated with the risk of hereditary tumors. Multi-gene panel testing can detect these HR-related gene variations, providing a basis for the precise prevention, diagnosis and treatment of tumors.
Creative Biolabs: RAD51C Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality RAD51C antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom RAD51C Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our RAD51C antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Longo, Michael A., et al. "RAD51C-XRCC3 structure and cancer patient mutations define DNA replication roles." Nature communications 14.1 (2023): 4445. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40096-1
Anti-RAD51C antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTN4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-6075) (CBMAB-0020CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








