RARG Antibodies
Background
RARG (retinoic acid receptor γ) is a nuclear receptor protein, mainly found in the skin, bones and nerve tissues of vertebrates. This protein participates in key physiological processes such as cell differentiation, development and immune regulation by binding to retinoic acid and regulating the transcriptional activity of target genes. Research has found that RARG plays a significant role in embryonic development, especially indispensable in limb formation and heart development. This receptor was first identified in the 1990s, and the analysis of its three-dimensional structure has provided important clues for understanding the functional mechanism of the nuclear receptor family. The specific ligand binding characteristics of RARG make it a potential drug target for the treatment of skin diseases and cancers, and related research continues to drive the progress in the field of nuclear receptor signaling pathways.
Structure of RARG
Myoglobin is a relatively small protein with a molecular weight of approximately 16.7 kDa. This weight may slightly vary between species due to minor differences in amino acid sequence.
| Species | Human | Mice | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 51.2 | 50.8 | 52.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Highly conserved DNA binding domain (C-terminal) | Minor variations exist in the ligand-binding domain | Evolutionary adaptation leads to functional differentiation |
RARG is composed of approximately 450 amino acids and has a typical nuclear receptor structure, including an N-terminal regulatory domain, a central DNA-binding domain (DBD), and a C-terminal ligand-binding domain (LBD). Its three-dimensional structure presents a ligand-dependent conformational change, in which LBD contains 12 α -helices (H1-H12), forming hydrophobic pockets to bind retinoic acid. The H12 helix shifts after ligand binding and becomes a key structure for the recruitment of coactivators. Conserved zinc cysteine finger molds (DBD) ensure target gene recognition, while phosphorylation sites (such as Ser77) can regulate transcriptional activity. The function of this receptor depends on the formation of a heterodimer with RXR (retinoid X receptor), thereby regulating the expression of genes related to development and metabolism.
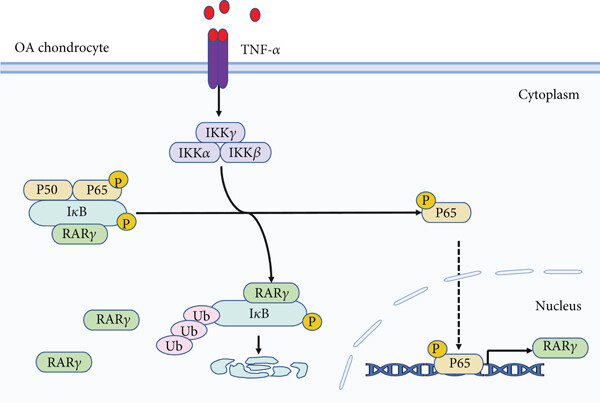 Fig. 1 Key mechanism of RARγ-NF-κB/IκBα positive feedback loop driving cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis.1
Fig. 1 Key mechanism of RARγ-NF-κB/IκBα positive feedback loop driving cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis.1
Key structural properties of RARG:
- Modular domain composition
- Hydrophobic ligand-binding pocket
- Zinc finger mold
- H12 screw switch mechanism
Functions of RARG
The core function of RARG is to regulate gene expression as a ligand-activated transcription factor, while also playing a key role in various physiological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Gene transcriptional regulation | After binding with retinoic acid, co-activators are recruited to initiate the transcription of target genes, regulating embryonic development and cell differentiation. |
| Regulation of limb development | Activating the expression of HOX genes in limb bud formation guides the formation of bone and soft tissue patterns. |
| Cardiac morphogenesis | By regulating key genes for cardiac development such as Tbx5, it affects ventricular septa and ventricular cyclization. |
| Maintenance of epidermal homeostasis | In the cutin and regulate cutin protein expression in cells, participate in skin barrier function is established in this paper. |
| Immune regulation | By inhibiting the NF-κB pathway, it can reduce the production of proinflammatory factors and play an anti-inflammatory role. |
After RARG forms a heterodimer with RXR, its DNA binding affinity increases by approximately 100 times compared to the monomer state. This synergistic effect enables it to precisely recognize the promoter region containing the DR5 sequence. Unlike the widely expressed RARA, RARG exhibits obvious spatiotemporal expression specificity and has irreplaceable functions in the development of limbs, the heart and the skin.
Applications of RARG and RARG Antibody in Literature
1. Xiu, Lin, et al. "High expression of RARG accelerates ovarian cancer progression by regulating cell proliferation." Frontiers in Oncology 12 (2022): 1063031. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.1063031
Research has found that RARG is highly expressed in ovarian cancer, promoting cell proliferation and is significantly associated with a poor prognosis for patients. Knocking down RARG can inhibit tumor growth, suggesting its value as a potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer.
2. Yu, Yue-Wei, et al. "Retinoic Acid Receptor Gamma (RARγ) Promotes Cartilage Destruction through Positive Feedback Activation of NF-κB Pathway in Human Osteoarthritis." Mediators of Inflammation 2022.1 (2022): 1875736. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1875736
This article indicates that RARG is highly expressed in chondrocytes of osteoarthritis and is positively correlated with the degree of cartilage destruction. TNF-α promotes the expression of RARG by activating the NF-κB pathway, forming a positive feedback loop that intensifies cartilage degradation. RARG agonists accelerate the progression of arthritis, while inhibitors play a protective role, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target.
3. Koterazawa, Y., Koyanagi-Aoi, M., Uehara, K. et al. "Retinoic acid receptor γ activation promotes differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into esophageal epithelium. " J Gastroenterol 55, 763–774 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-020-01695-7
This article reveals that the activation of RARG significantly promotes the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (hIPSCs) derived from the anterior intestine into esophageal epithelial cells. RARG agonists enhance this differentiation process while inhibitors inhibit it, indicating the key regulatory role of RARG in esophageal development.
4. Han, Young-Hoon, et al. "A unique cytoplasmic localization of retinoic acid receptor-γ and its regulations." Journal of Biological Chemistry 284.27 (2009): 18503-18514. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.007708
This article reveals that RARG activation significantly promotes the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (hIPSCs) derived from the foregut into esophageal epithelial cells. RARG agonists enhance this differentiation process while inhibitors inhibit it, indicating the key regulatory role of RARG in esophageal development.
5. Zeng, Wenjun, et al. "Targeting to the non-genomic activity of retinoic acid receptor-gamma by acacetin in hepatocellular carcinoma." Scientific Reports 7.1 (2017): 348. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00233-5
This article found that RARG promotes the development of liver cancer by regulating the AKT-p53 signaling network. The flavonoid acacetin specifically binds to RARG to block its non-genomic effects and restore the p53 signaling pathway, providing a new target for the treatment of liver cancer.
Creative Biolabs: RARG Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality RARG antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Western Blot , Flow Cytometry, and Immunohistochemistry and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom RARG Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our RARG antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, please contact us.
Reference
- Yu, Yue-Wei, et al. "Retinoic Acid Receptor Gamma (RARγ) Promotes Cartilage Destruction through Positive Feedback Activation of NF-κB Pathway in Human Osteoarthritis." Mediators of Inflammation 2022.1 (2022): 1875736. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1875736
Anti-RARG antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (8G8) (CBMAB-E1329-FY)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261270) (CBMAB-C0813-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CRYAB Recombinant Antibody (A4345) (CBMAB-A4345-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






