ROR1 Antibodies
Background
The ROR1 gene encodes a type I transmembrane protein belonging to the receptor tyrosine kinase family, which is mainly expressed during embryonic development and plays a key role in cell differentiation and migration. This protein regulates intercellular communication by participating in mechanisms such as the Wnt signaling pathway, and is particularly indispensable in neurogenesis and cardiac formation processes. It is worth noting that ROR1 is significantly down-regulated in adult normal tissues, but abnormally activated in various malignant tumors, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia and breast cancer. The oncogenic signaling pathways it mediates make it an important research object for tumor-targeted therapy. This gene was first discovered by a research team in 1992 when identifying tyrosine kinase receptors. Its unique cancer-specific expression pattern has continuously driven the development of targeted drugs and provided a key entry point for understanding the molecular association between embryonic development and tumorigenesis.
Structure of ROR1
ROR1 is a type I transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 120 kDa. There are certain differences in this weight among different species, mainly due to sequence variations in the extracellular domain immunoglobulin and cysteine-rich regions.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 120 | 117 | 118 | 119 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains an intact extracellular IgG/Frizzled domain and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain | Extracellular domain structure homology is higher, intracellular signal transduction function of conservative | Sequence is highly conserved across the membrane area | The amino acid sequence similarity to human ROR1 exceeds 95% |
This protein is composed of 937 amino acid residues and has a typical spatial conformation of receptor tyrosine kinase. Its extracellular region contains immunoglobulin-like domains, cysteine-rich Frizzled domains and Kringle domains, which jointly mediate ligand recognition. The intracellular region retains a characteristic tyrosine kinase domain, which initiates downstream signaling pathways such as Wnt5a through auto-phosphorylation. The stability of its tertiary structure mainly depends on multiple disulfide bonds, which form and maintain the correct folded conformation in the extracellular domain.
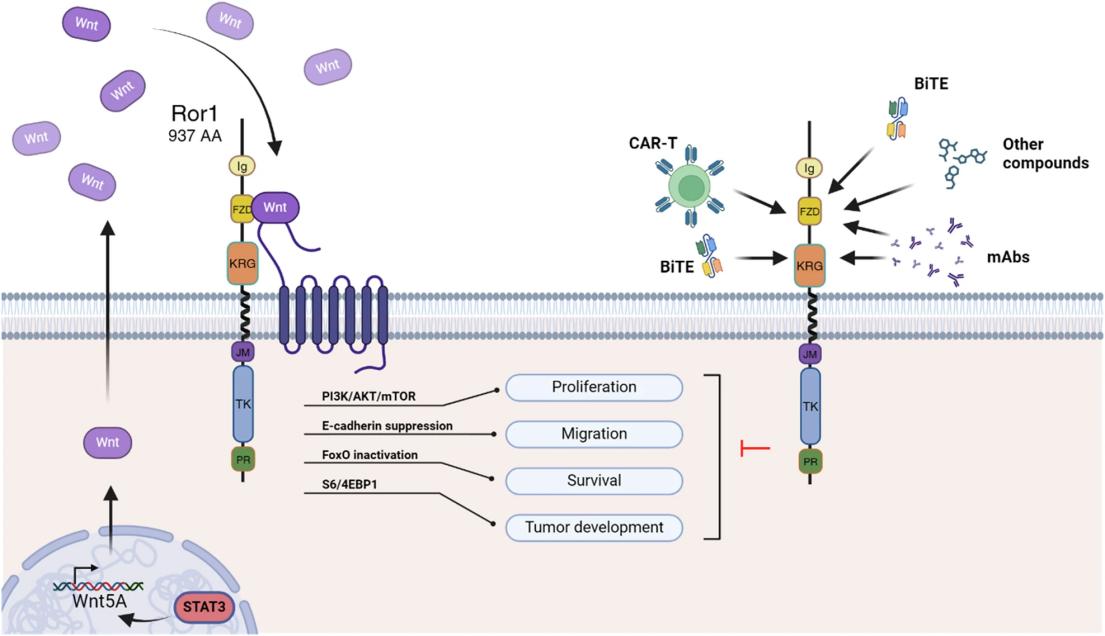 Fig. 1 ROR1 signaling and targeted therapies for tumor cell inhibition.1
Fig. 1 ROR1 signaling and targeted therapies for tumor cell inhibition.1
Key structural properties of ROR1:
- Extracellular section contains immunoglobulin domain sample structure
- Single cell transmembrane helical connection inside and outside the area
- Intracellular section has a typical structure of tyrosine kinase domain and C at the end of the tail
Functions of ROR1
The core function of the protein encoded by the ROR1 gene is to regulate embryonic development and cell migration. However, it also plays a role in various pathological processes, especially closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of embryonic development | In embryonic period high expression, dominate the neural tube formation, heart development and key processes such as physical growth. |
| Establishment of cell polarity | Cytoskeletal recombination and directed migration are regulated through non-classical Wnt signaling pathways (such as Wnt5a). |
| Promotion of tumor proliferation | Aberrant activation in a variety of cancers enhances the survival and proliferation of tumor cells through PI3K/AKT and other pathways. |
| Metabolic reprogramming | Affect the glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation balance, provide metabolic support for the rapid growth of cancer cells. |
| Development of therapeutic targets | Because of its specific high expression in cancer tissues, it has become an important target in CAR-T therapy and antibody drugs. |
Unlike typical broad-spectrum tyrosine kinase receptors, ROR1 mainly relies on its high-affinity binding to specific ligands (such as Wnt5a) to initiate signal transduction. This specificity gives it both efficacy and safety advantages in targeted therapy.
Applications of ROR1 and ROR1 Antibody in Literature
1. Osorio-Rodríguez, Daniel Andrés, Bernardo Armando Camacho, and César Ramírez-Segura. "Anti-ROR1 CAR-T cells: Architecture and performance." Frontiers in Medicine 10 (2023): 1121020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2023.1121020
The article indicates that ROR1 is highly expressed during the embryonic period and abnormally activated in various malignant tumors, making it an ideal target for tumor treatment. CAR-T therapy targeting ROR1 provides a new option for patients with relapsed/refractory tumors. However, its efficacy is affected by tumor heterogeneity and the microenvironment. Combined multi-target or inhibitor therapy is expected to improve the efficacy.
2. Lin, Weiwei, et al. "IGFBP5 is an ROR1 ligand promoting glioblastoma invasion via ROR1/HER2-CREB signaling axis." Nature communications 14.1 (2023): 1578. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37306-1
Research reveals that IGFBP5 is a ligand of ROR1. When combined, they activate the ROR1/HER2-CREB signaling axis, driving the invasion and tumorigenesis of glioma stem cells (GSCS). Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 targeted editing IGFBP5 through nanocapsules can effectively inhibit GSC invasion and prolong the survival of tumor-bearing mice, confirming that this pathway is a potential therapeutic target for glioblastoma.
3. Wang, Lei, et al. "A novel ROR1-targeting antibody-PROTAC conjugate promotes BRD4 degradation for solid tumor treatment." Theranostics 15.4 (2025): 1238. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.102531
This study developed a novel ROR1-degrading antibody-drug conjugate (DAC), which combines the BRD4 degrader PROTAC with an antibody targeting ROR1. This conjugate can precisely deliver degraders to ROR1-positive tumor cells, demonstrating excellent protein degradation ability and anti-tumor effects both in vivo and in vitro. When combined with PD-1 inhibitors, it can enhance the immune response and improve the tumor microenvironment.
4. Zhao, Yuming, et al. "Tyrosine kinase ROR1 as a target for anti-cancer therapies." Frontiers in Oncology 11 (2021): 680834. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.680834
The article indicates that the receptor tyrosine kinase ROR1 is crucial in embryonic development and is overexpressed in various malignant tumors, promoting tumorigenesis by activating non-classical signaling pathways such as WNT. Positive progress has been made in antibody immunotherapy against ROR1 at present, but the development of small molecule inhibitors is relatively lagging behind due to insufficient understanding of its tyrosine kinase activity. This review analyzed the structure and function of ROR1 and explored its targeted therapeutic strategies.
5. Tigu, Adrian-Bogdan, et al. "Therapeutic advances in the targeting of ROR1 in hematological cancers." Cell Death Discovery 10.1 (2024): 471. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-024-02239-1
The article indicates that ROR1 is an important target for the treatment of hematological malignancies. At present, various therapies for ROR1 are developing rapidly, including monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, small molecule inhibitors, bispecific T-cell linkers, and CAR-T cell therapy, etc. These innovative strategies have demonstrated significant therapeutic effects in both preclinical studies and clinical trials, presenting broad application prospects.
Creative Biolabs: ROR1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ROR1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ROR1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ROR1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Tigu, Adrian-Bogdan, et al. "Therapeutic advances in the targeting of ROR1 in hematological cancers." Cell Death Discovery 10.1 (2024): 471. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-024-02239-1
Anti-ROR1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (2Q1282) (CBMAB-C1624-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








