SCUBE3 Antibodies
Background
SCUBE3 is a secretory glycoprotein, mainly expressed in the embryonic development tissues and adult connective tissues of vertebrates. This protein participates in key biological processes such as cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation, and tissue morphogenesis by regulating the activity of signaling pathways such as BMP (bone morphogenetic protein) and TGF-β. Research has found that SCUBE3 plays a significant role in angiogenesis, bone development, and the regulation of the tumor microenvironment, and its mutations are associated with a variety of genetic diseases. This gene was first identified in 2004. Its multi-dimensional domain characteristics provide a model for studying the interaction mechanisms of extracellular proteins and are of great value for understanding developmental biology and the pathological mechanisms of diseases.
Structure of SCUBE3
Myoglobin is a relatively small protein with a molecular weight of approximately 16.7 kDa. This weight may slightly vary between species due to minor differences in amino acid sequence.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 115 | 114.8 | 116.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Sample contains nine EGF repetitive sequence and one CUB domain structure | Homologous structure is highly conserved, CUB structure domain sequence consistency of 92% | With collateral scube3a and scube3b homologous gene, encoding protein slightly differentiation |
This protein is composed of a signal peptide, multiple EGF-like repeat sequences and one CUB domain. Its tertiary structure shows that the CUB domain forms a typical β -sandwich fold, maintaining stability through the formation of intramolecular disulfide bonds by conserved cysteine residues. SCUBE3 plays a key role in embryonic development, bone formation and angiogenesis by specifically binding to BMP ligands to regulate signaling pathways.
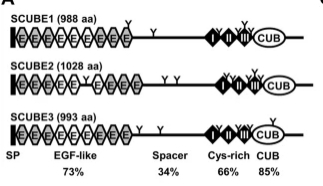 Fig. 1 Graphic illustration of the domain structure of human SCUBE1, 2 and 3.1
Fig. 1 Graphic illustration of the domain structure of human SCUBE1, 2 and 3.1
Key structural properties of SCUBE3:
- Modular multi-domain composition, including signal peptides, multiple EGF-like repeat sequences and CUB domains
- The CUB domain forms a typical β -sandwich folding conformation
- Conservative cysteine residues network stable intra-molecular disulfide bond
- Egf-like domains mediate specific interactions between proteins and cell surface receptors as well as extracellular matrix
Functions of SCUBE3
The main function of the SCUBE3 gene-encoded protein is to participate in cell signal transduction and tissue development regulation, and it plays an important role in various pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of the BMP signaling pathway | As a co-receptor, it enhances the binding of BMP ligands to receptors, precisely regulating osteogenic and angiogenic differentiation during embryonic development and tissue regeneration. |
| Cell adhesion and migration | Through the EGF structure domain mediated cell - interactions between cells and cell - matrix, affect the neural crest cell migration and the wound healing process. |
| Angiogenesis regulation | Expressed in vascular endothelial cells, promote angiogenesis and branching morphogenesis, has important physiological significance of ischemia and tissue repair. |
| Regulation of tumor progression | In a variety of abnormally high expression in cancer, by activating BMP/Smad signaling pathways influence tumor invasion, metastasis and microenvironment remodeling. |
| Cartilage and bone development | Widely expressed in endochondral ossification process, adjust the cartilage cell differentiation and mineralization, maintain the normal development of bones and the steady state. |
SCUBE3 collaboratively regulates the activity of signaling pathways such as BMP and TGF-β through its multi-domain characteristics. Its function is highly environmentally dependent, being highly expressed and widely involved in morphogenesis during the embryonic period, but its expression is limited in adults, mainly related to the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and injury repair.
Applications of SCUBE3 and SCUBE3 Antibody in Literature
1. Wang, Zijie, et al. "Epithelium-derived SCUBE3 promotes polarized odontoblastic differentiation of dental mesenchymal stem cells and pulp regeneration." Stem Cell Research & Therapy 14.1 (2023): 130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-023-03353-0
The article indicates that SCUBE3 is a crucial epithelial secreted protein in tooth development, which can transfer to the mesenchymal tissue and promote the proliferation, migration and odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells through the TGF-β and BMP2 pathways, demonstrating significant potential for dental pulp regeneration applications.
2. Xu, Pan, et al. "SCUBE3 downregulation modulates hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting CCNE1 via TGFβ/PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway." Cancer Cell International 22.1 (2022): 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-02402-z
The article indicates that SCUBE3 is highly expressed in liver cancer. By binding to the TGFβRII receptor and activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway, it upregulates the expression of CCNE1, promoting tumor proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis. SCUBE3 can serve as a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for liver cancer.
3. Huo, Qin, et al. "SCUBE3 serves as an independent poor prognostic factor in breast cancer." Cancer Cell International 21.1 (2021): 268. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-01947-3
The article indicates that the expression of SCUBE3 is significantly upregulated in breast cancer tissues. Its high expression is closely related to the status of ER, PR, HER2 and poor prognosis, and can be used as an independent poor prognostic factor and potential diagnostic marker.
4. Qi, Yuan-yuan, et al. "SCUBE3 is likely a susceptibility gene for systemic lupus erythematosus for Chinese populations." Journal of Immunology Research 2020.1 (2020): 8897936. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8897936
The article indicates that the SCUBE3 gene polymorphism (such as rs1888822) is significantly associated with the susceptibility of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in the Chinese population. The expression of SCUBE3 mRNA in patients is significantly decreased, and this gene may be involved in the pathogenesis of SLE through the TGF-β signaling pathway.
5. Tu, Cheng-Fen, et al. "SCUBE3 (signal peptide-CUB-EGF domain-containing protein 3) modulates fibroblast growth factor signaling during fast muscle development." Journal of Biological Chemistry 289.27 (2014): 18928-18942. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.551929
The article indicates that SCUBE3 promotes rapid muscle fiber formation in zebrafish embryos by enhancing the FGF8 signaling pathway. Its absence inhibits the expression of FGF receptors and myogenic differentiation, playing a key upstream regulatory role in muscle development.
Creative Biolabs: SCUBE3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SCUBE3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SCUBE3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SCUBE3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Lin, Yuh-Charn, et al. "The biology of SCUBE." Journal of biomedical science 30.1 (2023): 33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-023-00925-3
Anti-SCUBE3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-COL12A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C3117) (CBMAB-C4560-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0733) (CBMAB-F0435-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








