SPP1 Antibodies
Background
SPP1 gene encoding a secreted phosphorylated glycoprotein, mainly exists in bone, immune cells and epithelial tissue. This protein plays a key role in bone remodeling, inflammatory response and tissue repair by binding to integrins and CD44 receptors on the cell surface, regulating cell adhesion, migration and signal transduction. Research has found that SPP1 promotes cancer cell metastasis in the tumor microenvironment and is closely related to the stability of atherosclerotic plaques. This gene was first identified by researchers in bone matrix in 1979. Its multifunctional characteristics and complex molecular regulatory mechanisms have become an important direction in the research of cancer, osteoporosis and autoimmune diseases, providing a molecular basis for the development of targeted treatment strategies.
Structure of SPP1
SPP1 (secretory phosphoprotein 1, also known as osteopontin) is a secretory glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 44-75 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly due to species differences and post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation and glycosylation. This protein is composed of approximately 300 amino acids and has a typical RGD cell adhesion sequence as well as multiple functional domains. Its tertiary structure presents an extended flexible conformation and can mediate cell signal transduction through the binding of integrins and CD44 receptors. SPP1 of different species vary in amino acid sequence and modification degree, thereby affecting their interaction with ligands and biological functions.
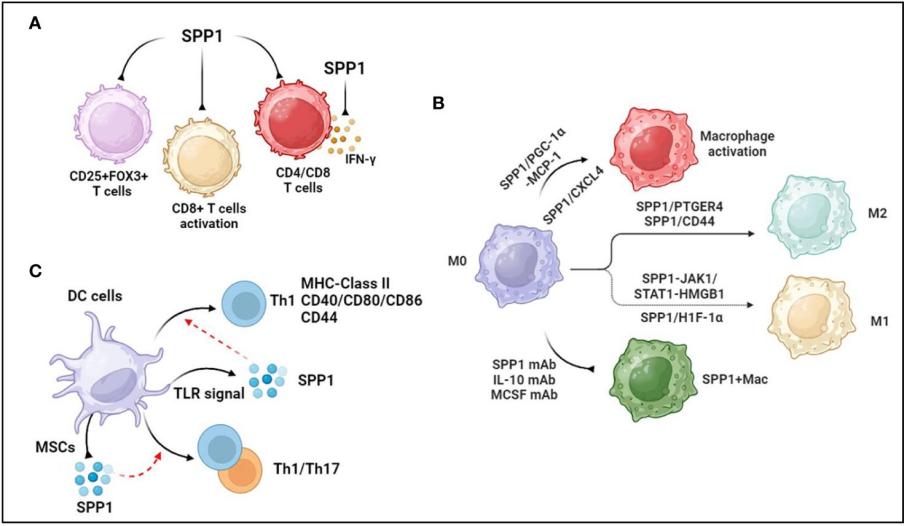 Fig. 1 Association between SPP1 and immune cells.1
Fig. 1 Association between SPP1 and immune cells.1
Key structural properties of SPP1:
- With stretch type flexible structure domain, including RGD sequence cell adhesion
- Multiple phosphorylation sites and calcium ion binding regions
- Signal transduction is mediated by the binding of integrins (such as αvβ3) to CD44 receptors
Functions of SPP1
The main function of SPP1 (osteopontin) is to mediate the interaction between cells and the matrix and regulate the immune response. In addition, it is widely involved in multiple pathophysiological processes such as tissue repair, tumorigenesis and biomineralization.
| Function | Description |
| Cell adhesion and migration | By binding the RGD sequence with integrins, it promotes the adhesion, spreading and directional migration of cells on the matrix. |
| Immune regulation | Regulate macrophage polarization and cytokine secretion, and participate in inflammatory responses and tissue remodeling processes. |
| Tumor progression | In a wide variety of cancer high expression, and promote the tumor cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and resistance to chemotherapy. |
| Regulation of bone mineralization | As an important component of bone matrix, it regulates the crystallization and deposition of hydroxyapatite and affects bone development and repair. |
| Vascular remodeling and calcification | Turn osteogenesis cells involved in vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation, promote atherosclerotic plaque calcification. |
SPP1 activates downstream signaling pathways (such as Akt and MAPK pathways) through multiple receptors (such as integrin αvβ3 and CD44), thereby exerting pleiotonic regulatory functions in different microenvironments. Its expression level is closely related to tissue fibrosis, autoimmune diseases and cancer prognosis.
Applications of SPP1 and SPP1 Antibody in Literature
1. De Schepper, Sebastiaan, et al. "Perivascular cells induce microglial phagocytic states and synaptic engulfment via SPP1 in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease." Nature neuroscience 26.3 (2023): 406-415. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-023-01257-z
Research has found that SPP1 is mainly secreted by perivascular cells, which can activate the phagocytic function of microglia and mediate their synaptic clearance, leading to synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease models. Inhibiting SPP1 can effectively prevent synaptic damage.
2. Liu, angxiang, et al. "ANGPTL2+ cancer-associated fibroblasts and SPP1+ macrophages are metastasis accelerators of colorectal cancer." Frontiers in immunology 14 (2023): 1185208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1185208
Studies have found that SPP1 is highly expressed in liver metastases of colorectal cancer and is mainly enriched in tumor-associated macrophages. SPP1+ macrophages significantly promote the metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by regulating pathways such as epithelial-mesenchymal transition and are potential therapeutic targets.
3. Zhao, Yanli, et al. "Osteopontin/SPP1: a potential mediator between immune cells and vascular calcification." Frontiers in immunology 15 (2024): 1395596. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395596
Research has found that SPP1 is highly expressed in immune cells such as macrophages and is a key factor driving vascular calcification. It promotes the calcification of atherosclerotic plaques by mediating inflammatory responses, leading to heart failure, and can serve as a potential therapeutic target.
4. Hoeft, Konrad, et al. "Platelet-instructed SPP1+ macrophages drive myofibroblast activation in fibrosis in a CXCL4-dependent manner." Cell reports 42.2 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112131
The article indicates that SPP1 is highly expressed in immune cells such as macrophages and is a key factor driving vascular calcification. It promotes the calcification of atherosclerotic plaques by mediating inflammatory responses, leading to heart failure, and can serve as a potential therapeutic target.
5. Matsubara, Eri, et al. "The significance of SPP1 in lung cancers and its impact as a marker for protumor tumor-associated macrophages." Cancers 15.8 (2023): 2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082250
Research has found that SPP1 (osteopontin) is a novel marker of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), and its expression in lung adenocarcinoma is significantly associated with poor prognosis and chemotherapy resistance. The SPP1/CD44 axis may become a key mechanism for the interaction between cancer cells and Tams.
Creative Biolabs: SPP1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SPP1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SPP1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SPP1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zhao, Yanli, et al. "Osteopontin/SPP1: a potential mediator between immune cells and vascular calcification." Frontiers in immunology 15 (2024): 1395596. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395596
Anti-SPP1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DHFR Recombinant Antibody (D0821) (CBMAB-D0821-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC25 Recombinant Antibody (CBLC132-LY) (CBMAB-C9786-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






