SSPN Antibodies
Background
SSPN gene encoding a transmembrane protein called sarcospan, mainly distributed in the muscle membranes of skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle cells. This protein, as a core component of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC), participates in the mechanical protection of muscle contraction by stabilizing the cell membrane structure. Research has found that mutations in the SSPN gene are closely related to neuromuscular diseases such as limb-band muscular dystrophy (LGMD), and the loss of its function can lead to the destruction of the integrity of the muscle fiber membrane. In 2000, this gene was first cloned by a research team from the University of California. Its quadruple transmembrane structure feature provides an important model for studying the stability of cell membranes. In recent years, scientists have targeted and modified SSPN through technologies such as CRISPR, opening up a new path for the development of novel gene therapies for muscular dystrophy.
Structure of SSPN
SSPN is a transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 25 kDa. There are slight differences in its molecular weight among different species, mainly depending on the degree of glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Rabbit |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 25 | 24.8 | 24.9 | 25.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains four transmembrane domain structure, C cytoplasm area highly conservative | Similar across the membrane area, n-terminal glycosylation sites is slightly different | With the human SSPN homology of more than 90% | High degree of glycosylation modification |
The SSPN protein is composed of 290 amino acids and has four highly conserved transmembrane domains (TM1-TM4), forming a stable membrane-anchored structure. Both its N-terminal and C-terminal are located in the cytoplasm, and the C-terminal domain interacts with skeletal proteins such as dystrophin. The secondary structure of SSPN is mainly composed of α -helices, which form a scaffold structure on the cell membrane and help stabilize the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) on the muscle fiber membrane. The palmitoylation modification site (Cys168) of this protein is crucial for membrane localization and functional maintenance.
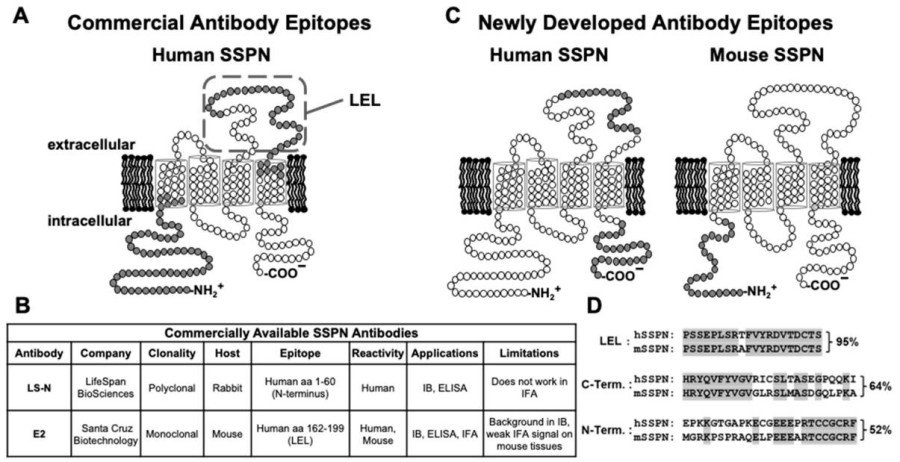 Fig. 1 SSPN epitopes are used for antibody development. 1
Fig. 1 SSPN epitopes are used for antibody development. 1
Key structural properties of SSPN:
- Quadruple transmembrane domain
- Palmitoylation modification site
- DGC complex binding domain
- Glycosylation modification
- Cysteine cluster
- Conservatively carry positively charged residues
- Hydrophobic amino acid enrichment region
Functions of SSPN
The main function of the SSPN gene-encoded protein is to maintain the stability of muscle cell membranes and participate in mechanical signal transduction, while also playing a key role in neuromuscular diseases.
| Function | Description |
| Cell membrane stability | As a core component of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC), it strengthens the membrane structure of muscle fibers and resists mechanical stress damage. |
| Signal transduction regulation | Mechanical signals are transmitted through the integrin-linked kinase (ILK) pathway, influencing the growth and repair of muscle cells. |
| Disease association | Mutations lead to limb-band muscular dystrophy (LGMD2C), causing progressive muscle weakness and membrane integrity damage. |
| Receptor anchoring | Provide membrane anchoring sites for extracellular matrix proteins, such as laminin, to maintain muscl-tendon junctions. |
| Therapeutic target | Gene upregulation can partially compensate for the deficiency of the DGC complex and become a potential therapeutic direction for muscular dystrophy. |
The binding of SSPN protein to dystrophin shows a linear dose-effect (unlike the S-type synergistic effect of hemoglobin), indicating its homeostasis maintenance characteristics as a structural scaffold. The expression level of SSPN in the muscles of diving mammals was significantly increased (3-5 times higher than that of terrestrial species), suggesting a special adaptation mechanism for membrane stability in high-pressure environments.
Applications of SSPN and SSPN Antibody in Literature
1. Hwang, Hyun Seok, et al. "Sarcospan deficiency increases oxidative stress and arrhythmias in hearts after acute ischemia-reperfusion injury." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.14 (2023): 11868.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411868
The article indicates that the absence of SSPN exacerbates cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: in SSPN−/− mice, the myocardial infarction area increases, and the susceptibility to arrhythmia increases, which is associated with abnormal calcium processing (reduced SR calcium reserve, upregulation of RyR2) and intensified oxidative stress (activation of NADPH oxidase 4/CAMKII).
2. Rahimi Kahmini, Aida, et al. "Aging reveals a sex-dependent susceptibility of sarcospan-deficient mice to cardiometabolic disease." American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology 327.4 (2024): H1067-H1085. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00702.2023
The article indicates that the absence of SSPN resies obesity induced by a high-fat diet, but there are gender and age differences: SSPN−/− mice (especially female ones) experience a slower weight gain under a high-fat diet, but aged mice show abnormal glucose tolerance. Left ventricular hypertrophy (normal diet) and diastolic dysfunction (high-fat diet) occurred in aged male SSPN−/− mice, and changes in adipose tissue inflammatory factors suggest gender-dependent metabolic regulatory mechanisms.
3. Mokhonova, Ekaterina I., et al. "The Development of Robust Antibodies to Sarcospan, a Dystrophin-and Integrin-Associated Protein, for Basic and Translational Research." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.11 (2024): 6121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116121
The article indicates the therapeutic potential of SSPN as a DGC scaffold protein and breakthroughs in antibody development: This four-transmembrane protein plays a key role in muscle diseases, and its overexpression can improve Dupont muscular dystrophy. The research team successfully developed highly specific rabbit polyclonal/monoclonal antibodies and mouse monoclonal antibodies targeting the intracellular/extracellular domains of SSPN. Their performance in applications such as Western blotting and immunofluorescence was significantly superior to that of commercial antibodies, providing new tools for mechanism research and clinical translation.
4. Shu, Cynthia, et al. "Development of a high-throughput screen to identify small molecule enhancers of sarcospan for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy." Skeletal Muscle 9.1 (2019): 32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13395-019-0218-x
The article indicates that the SSPN promoter reporting system facilitates DMD drug screening: A C2C12 muscle cell line stably expressing the human SSPN promoter -EGFP reporter gene was constructed in the study. Through high-throughput screening, it was found that L-type calcium channel antagonists (such as felodioping) can specifically up-regulate SSPN transcription and protein expression, providing a new target for DMD treatment strategies to improve muscle cell membrane adhesion.
5. Peter, Angela K., et al. "Nanospan, an alternatively spliced isoform of sarcospan, localizes to the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle and is absent in limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2F." Skeletal Muscle 7.1 (2017): 11.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13395-017-0127-9
The study identified the type II transmembrane splicing variant nanospan of SSPN, which is specifically enriched in the sarcoplasmic reticulum region near the Z-line and triad, and is not related to DGC but disappears in δ -SG-deficient muscles. Biopsies of DMD patients showed that nanospan was dominant and significantly reduced in type I fibers, suggesting that it might be involved in the calcium regulation mechanism.
Creative Biolabs: SSPN Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SSPN antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SSPN Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SSPN antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Mokhonova, Ekaterina I., et al. "The Development of Robust Antibodies to Sarcospan, a Dystrophin-and Integrin-Associated Protein, for Basic and Translational Research." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.11 (2024): 6121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116121
Anti-SSPN antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12567) (CBMAB-1057-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








